The Geography of Collaboration: A Detailed Look at Vichy France
Related Articles: The Geography of Collaboration: A Detailed Look at Vichy France
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geography of Collaboration: A Detailed Look at Vichy France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geography of Collaboration: A Detailed Look at Vichy France

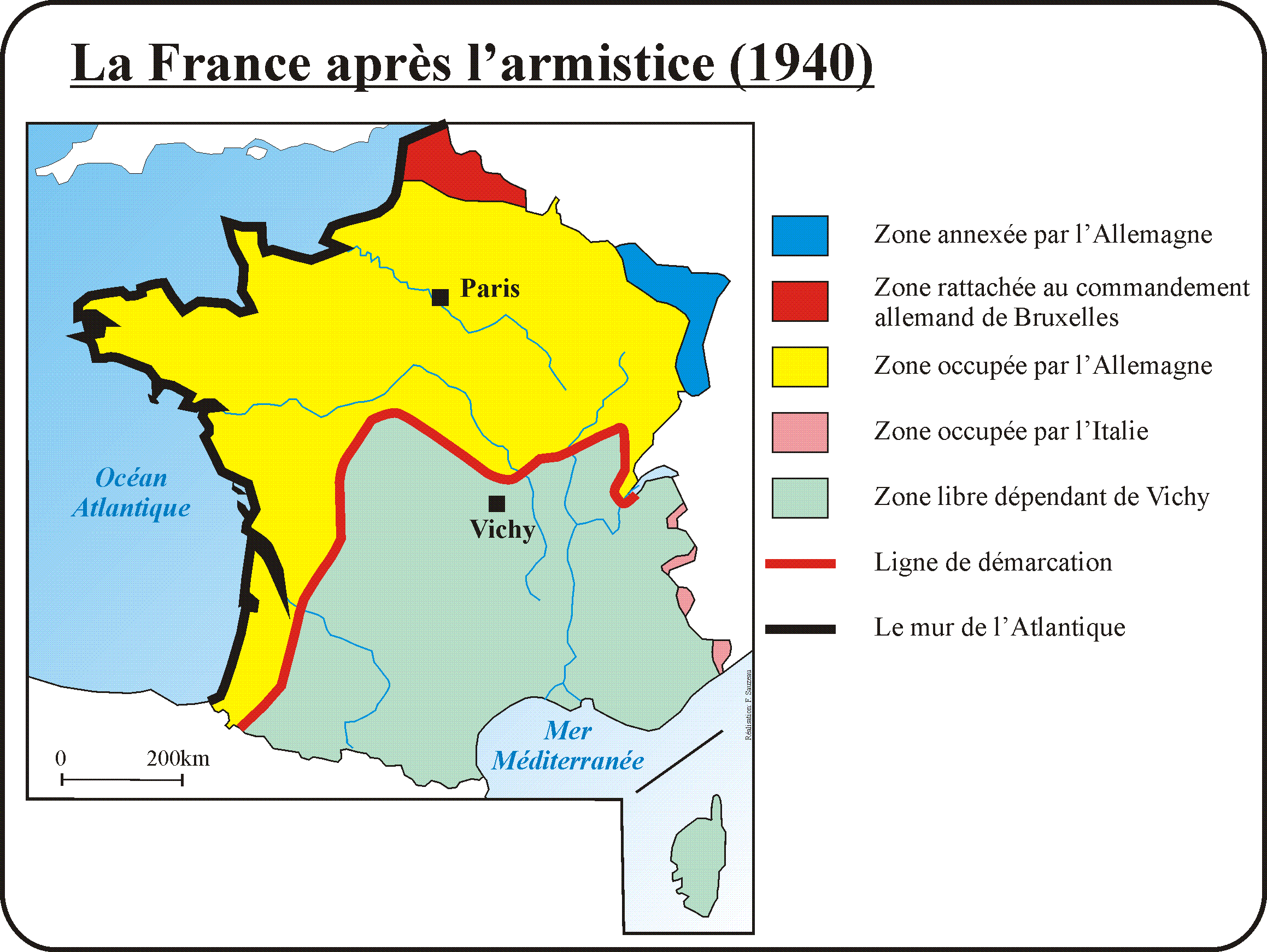
The map of Vichy France, a state established in southern France during World War II, tells a story of collaboration, resistance, and the complex geopolitical landscape of occupied Europe. This region, officially known as the "French State," existed from 1940 to 1944, governed by a regime headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain, who sought to collaborate with the Nazi regime. Understanding the geographical boundaries and political realities of Vichy France is crucial for comprehending the historical complexities of the war and its aftermath.
The Boundaries of Collaboration:
Vichy France, geographically distinct from the northern and western regions of France occupied directly by Nazi Germany, comprised a swathe of territory encompassing the south-central and southeastern parts of the country. Its boundaries were defined by the armistice agreement signed between France and Germany in June 1940.
Key Geographic Features:
- Southern France: The core of Vichy France encompassed the Rhône-Alpes region, including cities like Lyon, Grenoble, and Marseille. The region was known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from the Alps to the Mediterranean coast.
- Mediterranean Coast: The coastline of Vichy France stretched along the Mediterranean Sea, offering access to shipping routes and strategic ports like Toulon and Nice.
- Central France: The region extended northwards to include cities like Clermont-Ferrand, Limoges, and Toulouse, encompassing significant industrial areas and agricultural heartlands.
- Alsace-Lorraine: While technically part of Nazi Germany’s occupied territory, the region of Alsace-Lorraine was administered by Vichy France, highlighting the complex political realities of the time.
Beyond the Lines:
Vichy France was not a homogenous entity. It encompassed diverse regions with distinct cultural and economic identities. The mountainous terrain of the Alps provided a haven for resistance groups, while the urban centers of Lyon and Marseille became hubs of both collaboration and resistance. The Mediterranean coast, with its strategic ports, was subject to intense German scrutiny and control.
The Political Landscape:
The Vichy regime, headed by Marshal Pétain, sought to portray itself as a legitimate government, distinct from the Nazi regime. However, the regime’s policies were deeply intertwined with Nazi ideology, particularly in terms of anti-Semitism, racial discrimination, and the persecution of Jews. The Vichy government actively collaborated with the Germans in deporting Jews to concentration camps.
The Legacy of Collaboration:
The map of Vichy France serves as a stark reminder of the complexities of collaboration during wartime. The regime’s policies, fueled by a mix of anti-Semitism, fear, and a desire for order, led to the suffering of countless individuals. The legacy of Vichy France continues to be debated and analyzed, prompting reflections on the nature of political power, the limits of human morality, and the dangers of collaboration with oppressive regimes.
FAQs on Vichy France:
Q1: What was the relationship between Vichy France and Nazi Germany?
A: Vichy France was a collaborationist regime that actively sought to cooperate with Nazi Germany. The regime implemented policies aligned with Nazi ideology, including anti-Semitism and racial discrimination.
Q2: How did the Vichy regime differ from the Nazi regime?
A: While the Vichy regime collaborated with the Nazis, it presented itself as a distinct entity with its own political agenda. However, its policies were deeply influenced by Nazi ideology and it played a significant role in the persecution of Jews.
Q3: What role did Vichy France play in the Holocaust?
A: Vichy France actively participated in the deportation of Jews to concentration camps. The regime implemented anti-Semitic laws and policies, contributing to the systematic persecution of Jewish communities within its territory.
Q4: What was the role of the French Resistance in Vichy France?
A: Resistance groups operated throughout Vichy France, engaging in acts of sabotage, espionage, and providing aid to Allied forces. The resistance played a crucial role in undermining the Vichy regime and contributing to the eventual liberation of France.
Q5: How did the map of Vichy France change over time?
A: The map of Vichy France remained relatively stable throughout its existence, although there were minor adjustments to its boundaries and administrative divisions. The region of Alsace-Lorraine, initially part of Nazi Germany’s occupied territory, was later placed under the administration of Vichy France.
Tips for Understanding Vichy France:
- Study the historical context: To comprehend the complexities of Vichy France, it is essential to understand the political and social landscape of pre-war France, the events leading to the German occupation, and the rise of fascism in Europe.
- Explore primary sources: Consulting firsthand accounts, diaries, letters, and official documents from the period can provide valuable insights into the lived experiences of people under the Vichy regime.
- Analyze the regime’s policies: Examining the laws, decrees, and propaganda produced by the Vichy government offers crucial insights into its ideology and its collaboration with the Nazi regime.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Consider the viewpoints of historians, survivors, and resistance fighters to gain a multifaceted understanding of the era.
- Reflect on the legacy: The map of Vichy France serves as a reminder of the dangers of collaboration, the importance of resistance, and the enduring need to combat prejudice and discrimination.
Conclusion:
The map of Vichy France offers a powerful lens through which to examine the complexities of World War II and the consequences of collaboration. The regime’s policies, deeply intertwined with Nazi ideology, led to the persecution of Jews and the suffering of countless individuals. The legacy of Vichy France continues to shape contemporary debates about the nature of political power, the role of history in shaping identity, and the enduring need to combat intolerance and prejudice. Understanding the geography of collaboration, as reflected in the map of Vichy France, is essential for comprehending the historical complexities of the war and its enduring impact on the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geography of Collaboration: A Detailed Look at Vichy France. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
