The Interconnected Web of Earth’s Systems: A Visual Exploration of the Four Spheres
Related Articles: The Interconnected Web of Earth’s Systems: A Visual Exploration of the Four Spheres
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Interconnected Web of Earth’s Systems: A Visual Exploration of the Four Spheres. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Interconnected Web of Earth’s Systems: A Visual Exploration of the Four Spheres
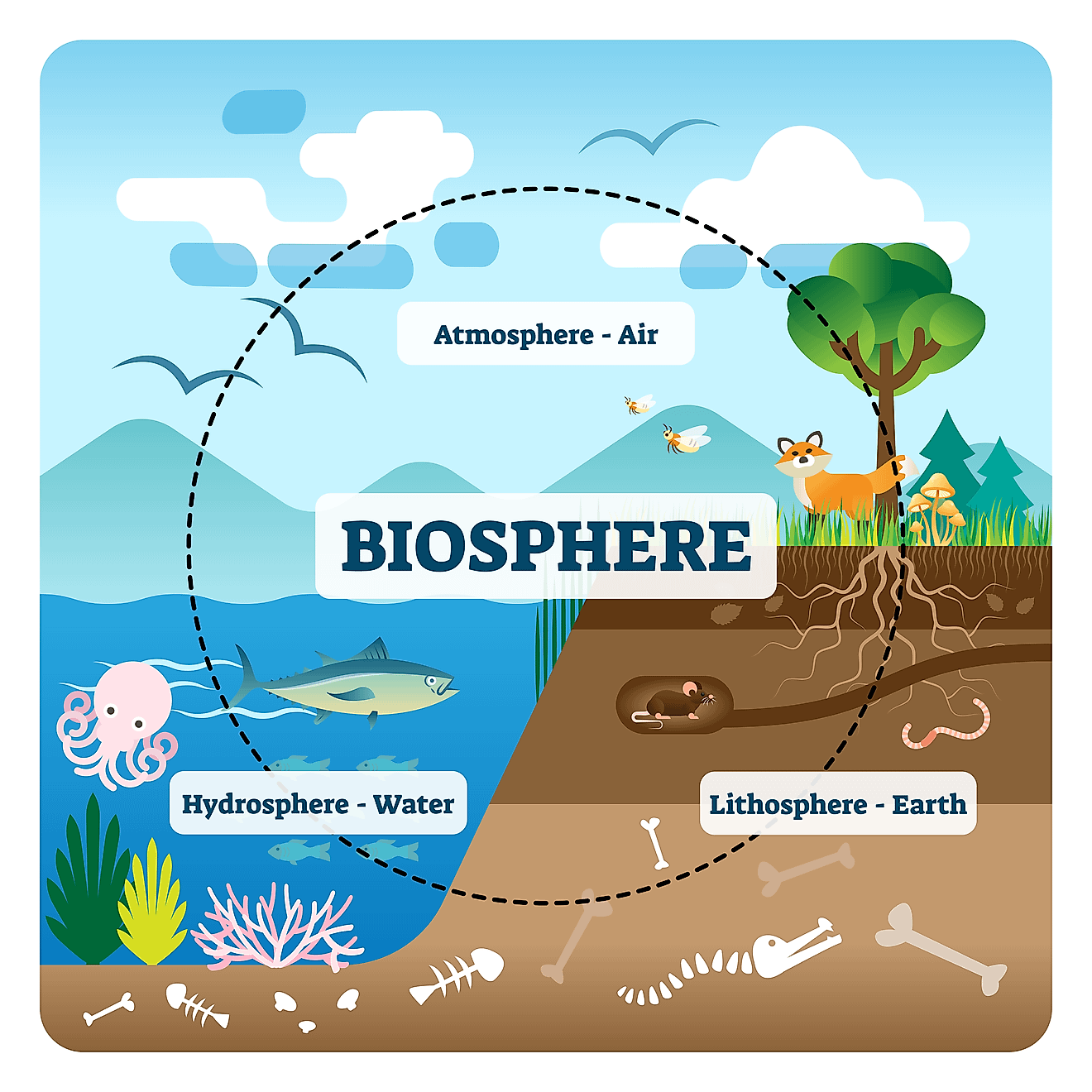
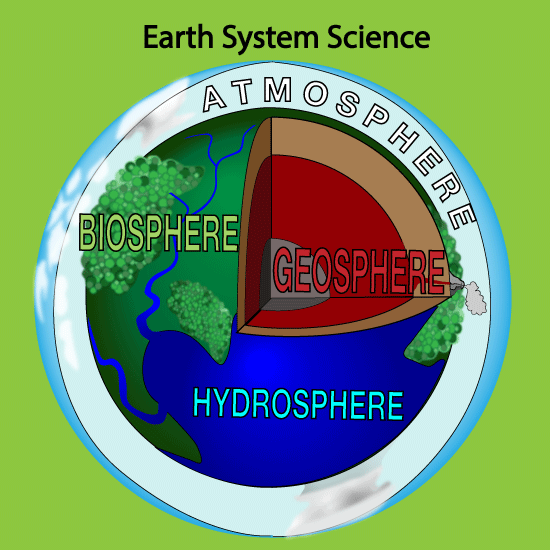
Earth, our vibrant and dynamic planet, is not a monolithic entity. It is a complex tapestry woven from four interconnected spheres: the geosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere. Understanding these spheres and their intricate relationships is fundamental to comprehending the planet’s past, present, and future.
A concept map, a visual representation of interconnected ideas, provides a powerful tool for exploring these relationships. It allows for a comprehensive and accessible understanding of how the four spheres interact and influence each other, shaping the Earth’s environment and sustaining life.
A Visual Journey Through Earth’s Spheres
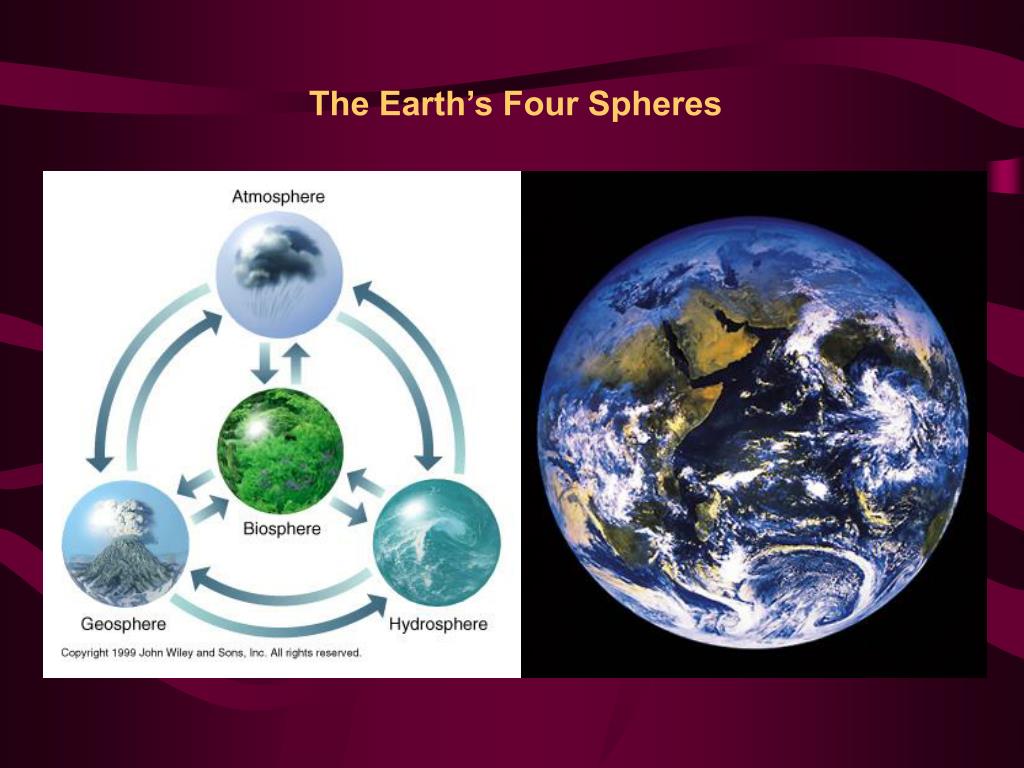
Imagine a concept map, with the Earth at its center, radiating outwards with four branches, each representing a sphere.
-
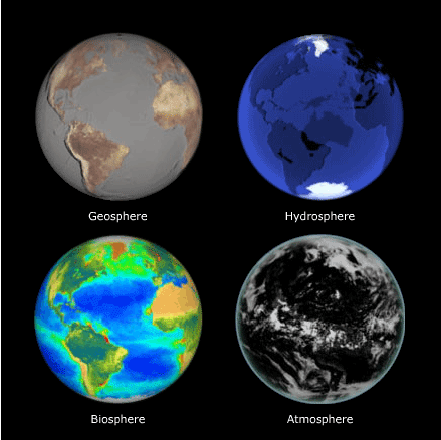
Geosphere: The solid, rocky part of the Earth, encompassing the crust, mantle, and core. It is the foundation upon which the other spheres rest. This branch would include elements like mountains, volcanoes, rocks, minerals, and tectonic plates.
-
Hydrosphere: The sphere of water, encompassing oceans, lakes, rivers, groundwater, and even the water vapor in the atmosphere. It is the lifeblood of the planet, vital for all living organisms. This branch would depict the water cycle, evaporation, precipitation, and the diverse forms of water bodies.
-
Atmosphere: The gaseous envelope surrounding the Earth, composed of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases. It shields us from harmful solar radiation and regulates the Earth’s temperature. This branch would depict the layers of the atmosphere, weather patterns, climate change, and the role of gases in regulating the planet’s temperature.
-
Biosphere: The sphere of life, encompassing all living organisms, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and complex ecosystems. It thrives within the other spheres, utilizing their resources and influencing their dynamics. This branch would depict the diversity of life, food webs, ecosystems, and the interconnectedness of living organisms with their environment.
Connecting the Dots: The Interplay of Spheres
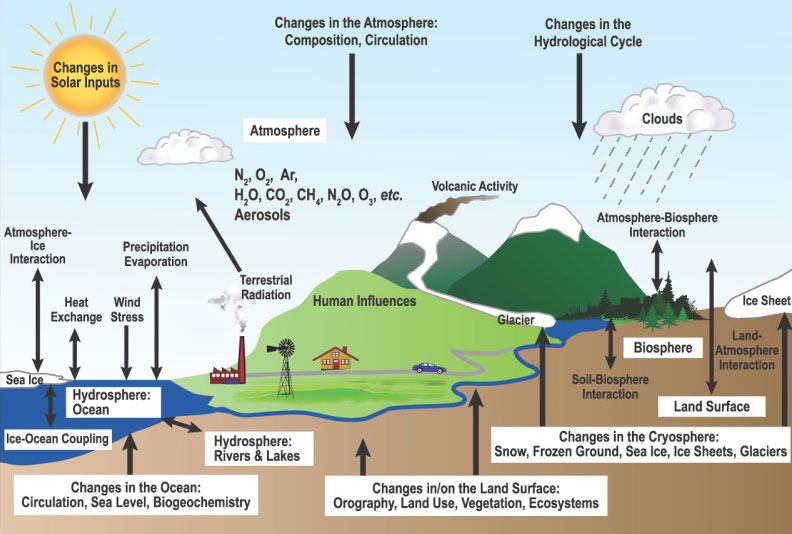
The beauty of a concept map lies in its ability to showcase the intricate connections between these spheres. Arrows and lines would link the branches, demonstrating how they interact and influence one another. For instance:
- Geosphere and Hydrosphere: Volcanic eruptions can alter the course of rivers, while tectonic plate movement can create new landmasses and reshape coastlines.
- Hydrosphere and Atmosphere: Evaporation from oceans drives the water cycle, while precipitation replenishes water bodies and influences weather patterns.
- Atmosphere and Biosphere: The atmosphere provides oxygen for respiration and protects life from harmful radiation, while plants and animals contribute to the composition of the atmosphere through photosynthesis and respiration.
- Biosphere and Geosphere: Living organisms play a crucial role in weathering rocks, creating soil, and influencing the Earth’s surface.
The Importance of Understanding the Interconnectedness
This interconnectedness highlights the importance of understanding the four spheres in a holistic manner. A change in one sphere can have cascading effects on others, leading to complex and often unpredictable outcomes.
For example, climate change, a phenomenon primarily driven by human activity, is impacting all four spheres. The increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are leading to rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels, affecting the hydrosphere and geosphere. These changes, in turn, disrupt ecosystems and biodiversity, impacting the biosphere.
FAQs: Demystifying the Earth’s Systems
-
What is the difference between the geosphere and the lithosphere? The lithosphere is a rigid layer that encompasses the upper part of the mantle and the crust. It is a part of the geosphere, which includes the entire solid Earth.
-
What is the role of the atmosphere in regulating Earth’s temperature? The atmosphere acts like a blanket, trapping heat from the sun and preventing it from escaping into space. This natural process is known as the greenhouse effect.
-
How does the biosphere influence the geosphere? Living organisms, through processes like weathering and erosion, contribute to the formation of soil, shaping the Earth’s surface and impacting the geosphere.
-
What is the significance of the water cycle in the hydrosphere? The water cycle is a continuous process that involves evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. It ensures the circulation of water, replenishing water bodies and supporting life.
Tips for Creating a Concept Map of Earth’s Spheres
- Start with a central idea: Place the Earth at the center of the map.
- Branch out the spheres: Draw four branches emanating from the center, representing the geosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere.
- Use keywords and phrases: Label each branch with clear and concise terms that represent the key aspects of each sphere.
- Connect the branches: Use arrows or lines to show the interactions and relationships between the spheres.
- Add examples and details: Include specific examples and details to illustrate the connections and processes within each sphere.
- Use colors and symbols: Employ different colors and symbols to visually distinguish the different spheres and their relationships.
Conclusion: A Unified Understanding for a Sustainable Future
A concept map of the four spheres is not merely a visual representation; it is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate and interconnected nature of our planet. It emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to environmental issues, recognizing that actions in one sphere can have far-reaching consequences for others.
By visualizing the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems, we gain a deeper appreciation for the fragility and resilience of our planet. This understanding serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, promoting responsible stewardship and sustainable practices for a healthier and more balanced future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Interconnected Web of Earth’s Systems: A Visual Exploration of the Four Spheres. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!