The Map Flagstaff Fire: A Case Study in Wildfire Dynamics and Management
Related Articles: The Map Flagstaff Fire: A Case Study in Wildfire Dynamics and Management
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Map Flagstaff Fire: A Case Study in Wildfire Dynamics and Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Map Flagstaff Fire: A Case Study in Wildfire Dynamics and Management
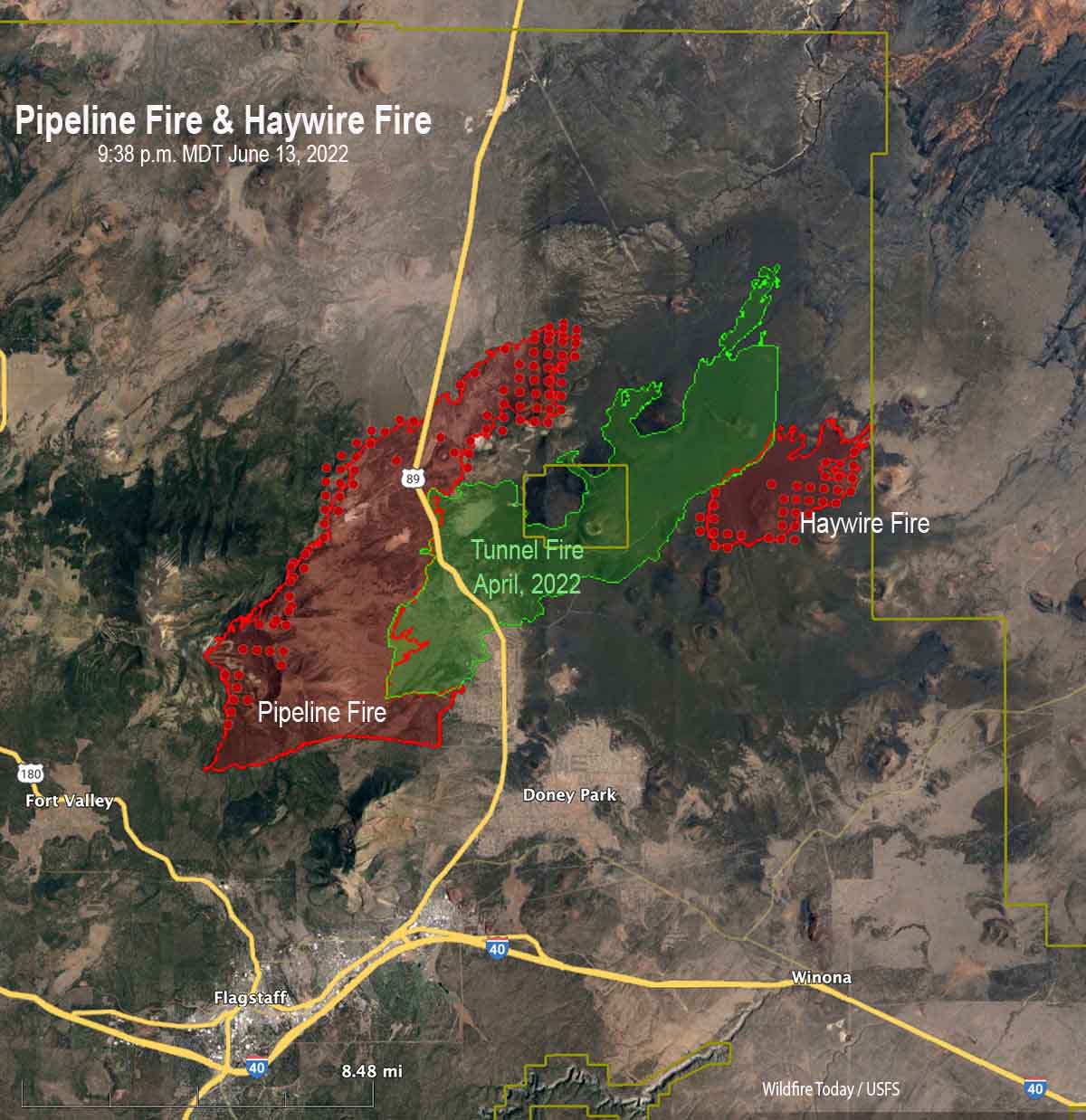
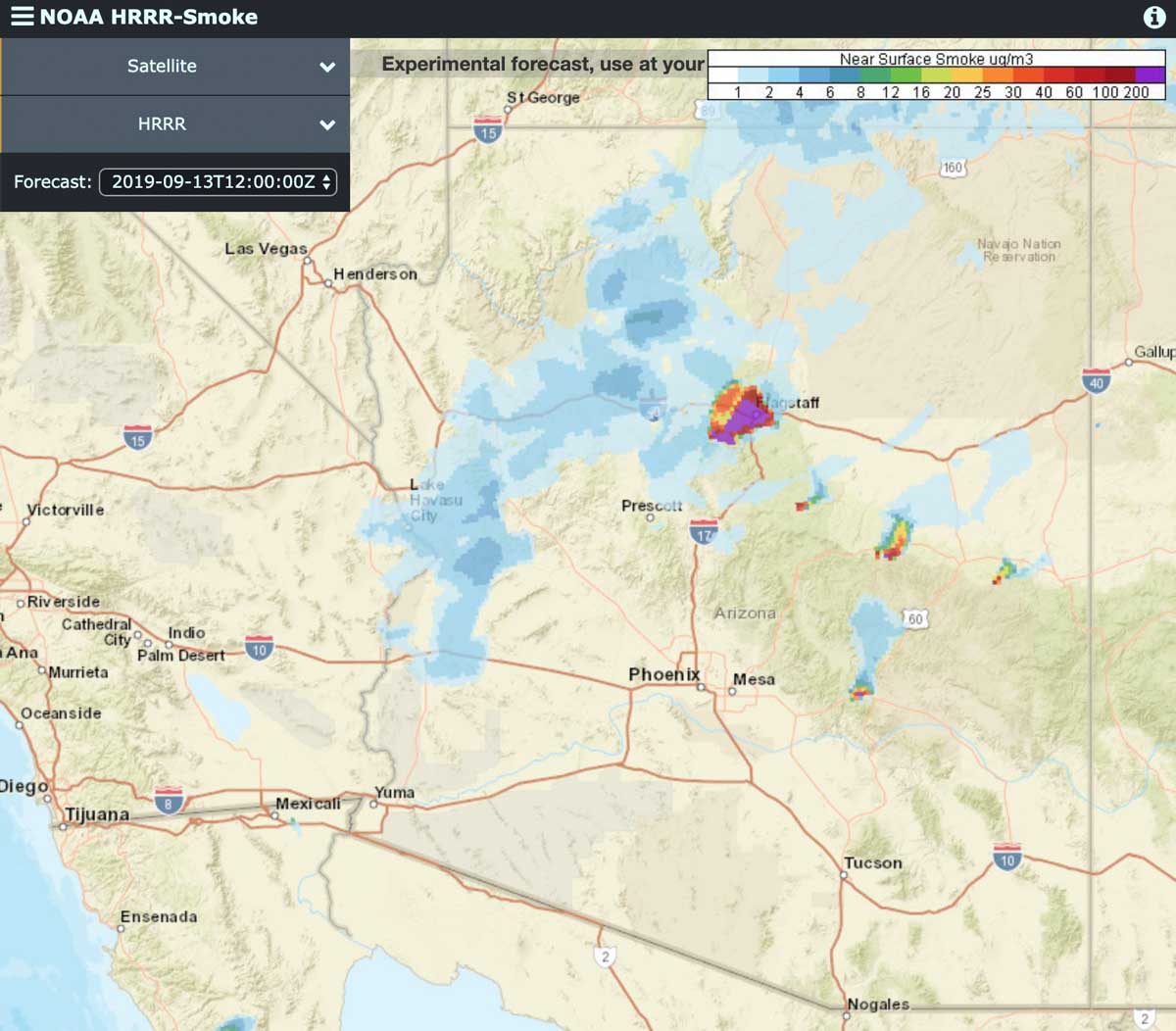
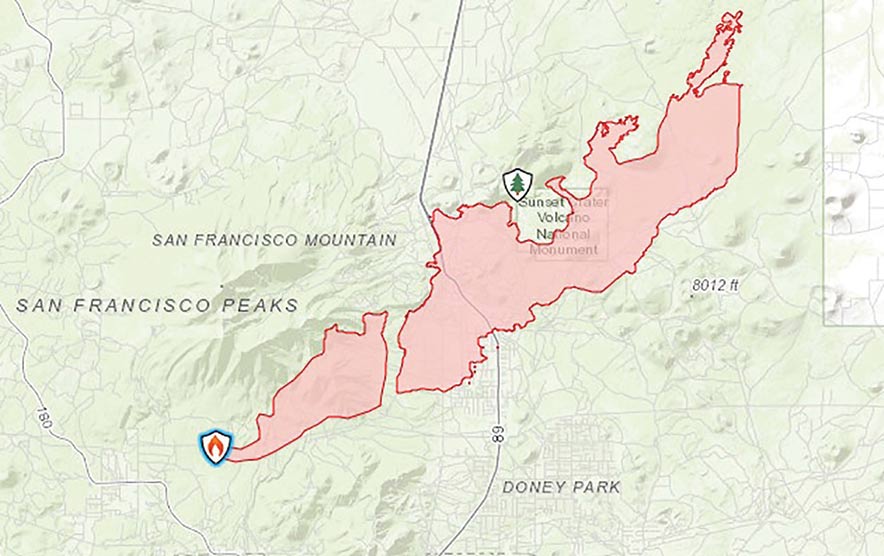
The Map Flagstaff Fire, a devastating wildfire that ravaged the Coconino National Forest in Arizona in 2000, serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of wildfires and the complexities of managing them in a rapidly changing environment. This fire, which consumed over 190,000 acres, significantly impacted the local ecosystem, communities, and economy, highlighting the critical need for effective fire management strategies.
Understanding the Context: A Complex Web of Factors
The Map Flagstaff Fire ignited on June 18, 2000, in the heart of the Coconino National Forest, an area known for its diverse ecosystems and abundant ponderosa pine forests. The fire’s rapid spread was fueled by several interconnected factors:
- Drought and Dry Conditions: Arizona was experiencing a severe drought in 2000, leading to exceptionally dry vegetation and a heightened risk of fire ignition.
- Fuel Accumulation: Decades of fire suppression policies had allowed for an accumulation of dead and decaying vegetation, creating a dense understory that acted as a fuel source for the fire.
- Wind and Topography: Strong winds, coupled with the mountainous terrain of the Coconino National Forest, contributed to the rapid spread of the fire.
- Human Activity: The fire’s ignition was attributed to human activity, emphasizing the importance of fire prevention and responsible land management.
The Fire’s Impact: A Devastating Legacy
The Map Flagstaff Fire had profound impacts on the natural environment, local communities, and the economy:
- Ecological Impacts: The fire consumed vast areas of ponderosa pine forests, impacting wildlife habitats and biodiversity. The loss of trees and vegetation also led to increased erosion and sedimentation in nearby streams and rivers.
- Community Impacts: The fire forced the evacuation of thousands of residents and businesses, disrupting lives and livelihoods. The smoke and ash generated by the fire also posed health risks to local communities.
- Economic Impacts: The fire caused significant damage to infrastructure, including roads, power lines, and communication systems, impacting tourism and local businesses. The cost of fire suppression and post-fire restoration efforts also placed a heavy burden on local and federal budgets.
Lessons Learned: A Turning Point in Fire Management
The Map Flagstaff Fire was a pivotal event in the history of wildfire management. It highlighted the need for a shift from a purely suppression-based approach to a more holistic and adaptive strategy:
- Prescribed Fire: Recognizing the ecological benefits of fire, the U.S. Forest Service began implementing prescribed fire programs to reduce fuel loads and restore fire-adapted ecosystems.
- Fuel Management: Active management practices, such as thinning and clearing vegetation, were implemented to reduce fuel accumulations and create fire breaks.
- Community Engagement: Increased efforts were made to educate and involve local communities in fire prevention and preparedness, fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The fire emphasized the need to adapt to the changing climate, including increased drought and wildfire risk, by developing strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on fire regimes.
The Legacy of the Map Flagstaff Fire: A Path Forward
The Map Flagstaff Fire serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of wildfires and the complexities of managing them in a rapidly changing world. The lessons learned from this fire have shaped contemporary fire management strategies, emphasizing the need for a collaborative and adaptive approach that prioritizes ecological integrity, community safety, and economic resilience.
FAQs
- What caused the Map Flagstaff Fire? The fire was ignited by human activity, but the specific cause remains unknown.
- How long did the Map Flagstaff Fire burn? The fire burned for over two months, from June 18 to August 26, 2000.
- How many acres did the Map Flagstaff Fire burn? The fire consumed over 190,000 acres of the Coconino National Forest.
- What were the impacts of the Map Flagstaff Fire? The fire caused significant ecological, community, and economic impacts, including damage to forests, wildlife habitats, infrastructure, and local economies.
- What lessons were learned from the Map Flagstaff Fire? The fire highlighted the need for a more holistic and adaptive approach to fire management, including prescribed fire, fuel management, community engagement, and climate change adaptation.
Tips for Preventing Wildfires
- Be cautious with fire: Always use fire safely and responsibly. Never leave a fire unattended and ensure it is completely extinguished before leaving the area.
- Clear vegetation around structures: Create defensible space around homes and other structures by removing flammable vegetation.
- Maintain equipment: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment, such as lawnmowers and chainsaws, to prevent sparks and malfunctions.
- Be aware of fire restrictions: Stay informed about fire restrictions and follow all regulations.
Conclusion
The Map Flagstaff Fire stands as a stark reminder of the destructive power of wildfires and the critical importance of effective fire management. By learning from past events and embracing a collaborative and adaptive approach, we can mitigate the risks associated with wildfires and ensure the long-term health and resilience of our forests and communities.

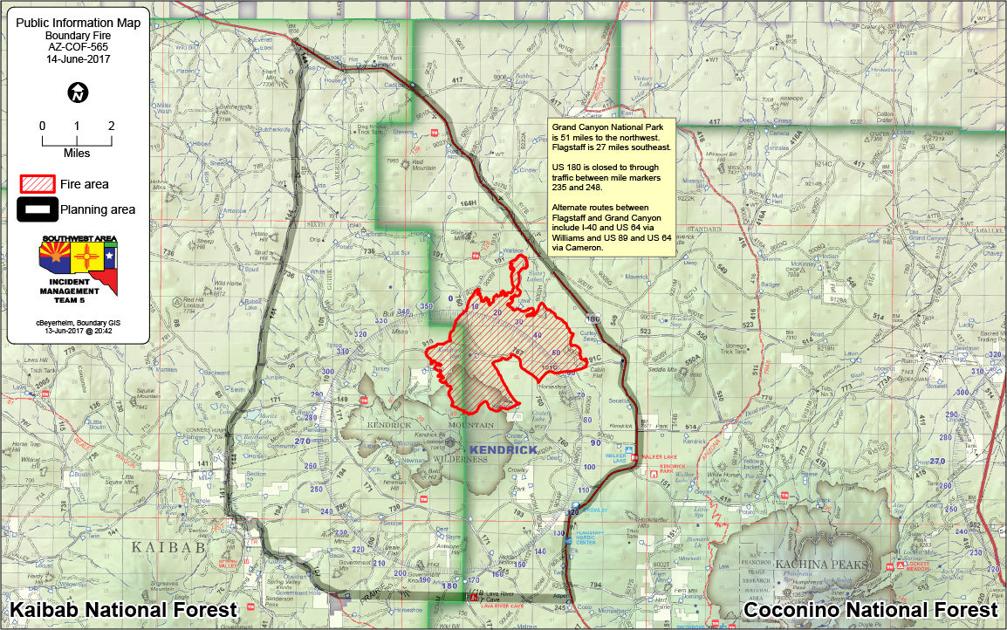
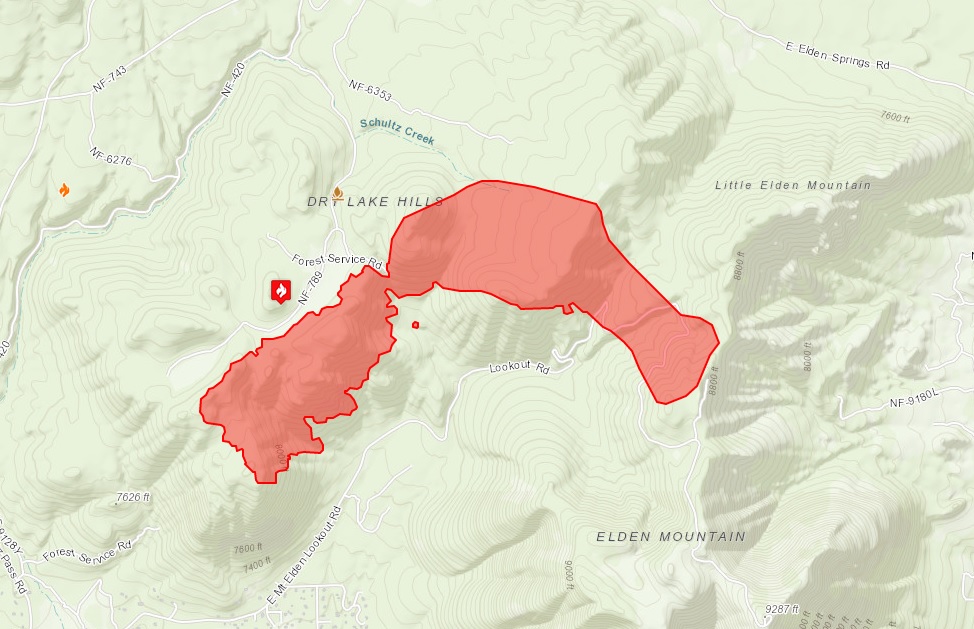
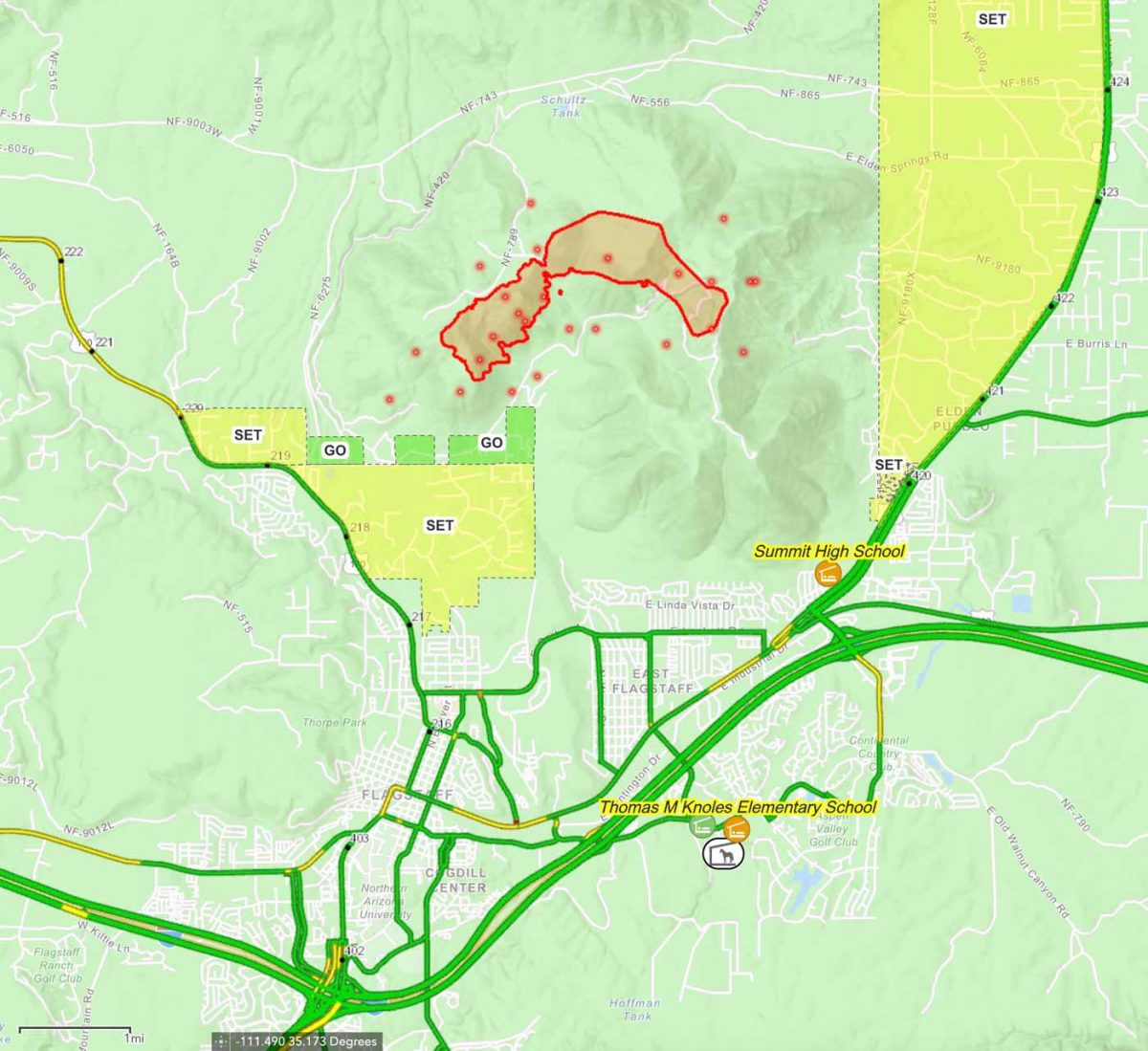


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Map Flagstaff Fire: A Case Study in Wildfire Dynamics and Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!