The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Legacy of Earthquakes and a Blueprint for Preparedness
Related Articles: The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Legacy of Earthquakes and a Blueprint for Preparedness
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Legacy of Earthquakes and a Blueprint for Preparedness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Legacy of Earthquakes and a Blueprint for Preparedness

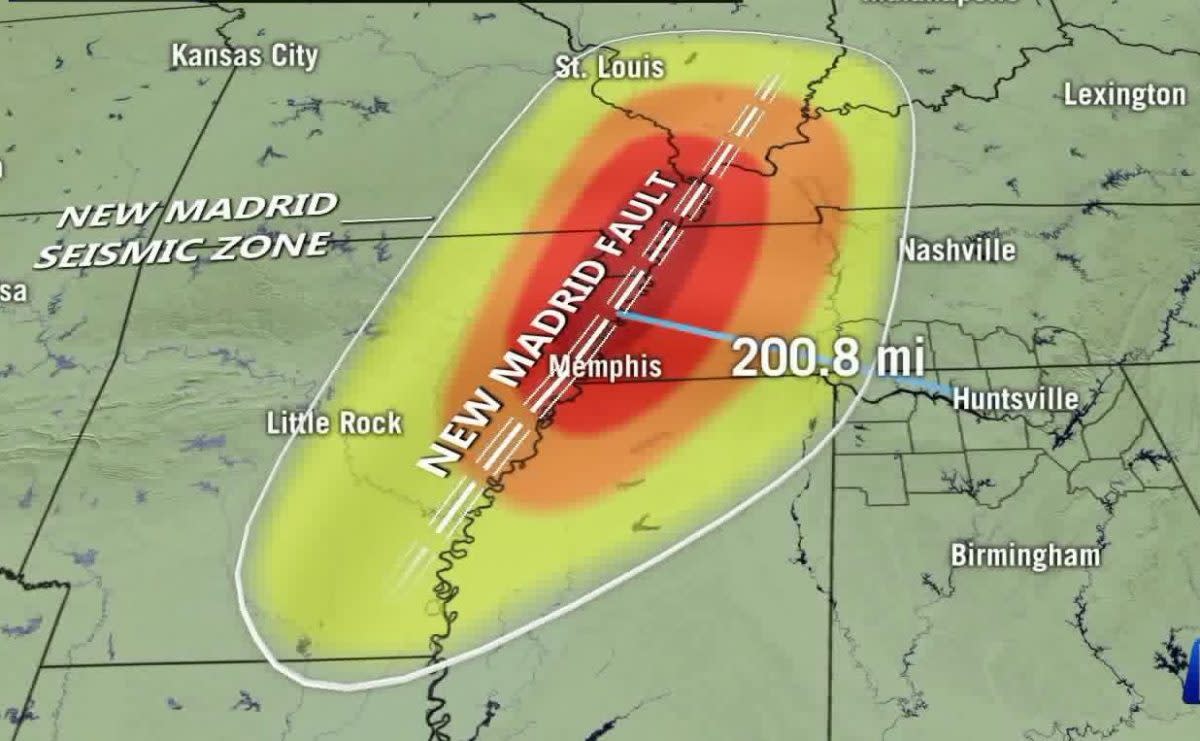
The New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ), a vast region encompassing parts of Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Kentucky, is a geological scar etched into the North American landscape. It is not a single fault line, but a complex web of interconnected faults, a legacy of a cataclysmic period of tectonic activity that shook the continent centuries ago. While the NMSZ is known for its potential to generate devastating earthquakes, it is also a crucial site for understanding the dynamics of the Earth’s crust and for informing earthquake preparedness strategies.
A History of Seismic Fury:
The NMSZ is renowned for the series of powerful earthquakes that occurred in the winter of 1811-1812. These earthquakes, estimated to have ranged from magnitude 7.0 to 8.0 on the Richter scale, were among the most powerful ever recorded in North America. The tremors not only shook the ground but also reshaped the landscape, creating massive sinkholes, altering river courses, and triggering widespread landslides. The effects were felt as far away as Washington, D.C., and even reverberated across the Atlantic Ocean, triggering tsunamis in the Caribbean Sea.
The Geological Origins of the NMSZ:
The NMSZ’s existence is a testament to the dynamism of the Earth’s crust. Approximately 500 million years ago, the region was part of the ancient supercontinent, Rodinia, which began to break apart. This rifting process resulted in the formation of the Reelfoot Rift, a zone of weakened crust that stretched for hundreds of miles. The Reelfoot Rift, now largely buried beneath layers of sediment, is a key feature of the NMSZ, as it serves as a conduit for the stresses that build up within the Earth’s crust.
The Modern Threat:
While the NMSZ is known for its historical seismic activity, the threat it poses today remains a significant concern. The region experiences a steady stream of smaller earthquakes, reminding scientists and residents alike of the potential for a major event. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that there is a 25-40% chance of a magnitude 7.0 or greater earthquake occurring within the next 50 years in the NMSZ.
Understanding the Fault Lines:
The NMSZ is not a single fault line, but rather a complex network of interconnected faults. These faults represent zones of weakness within the Earth’s crust, where rocks can slip past each other, releasing energy in the form of earthquakes.
Mapping the Fault Lines:
Mapping the fault lines within the NMSZ is crucial for understanding the potential for future earthquakes. Scientists use a variety of techniques, including seismic surveys, geological mapping, and remote sensing, to identify and map the fault lines. These maps provide valuable information about the location, size, and orientation of the faults, which helps to assess the seismic hazard in the region.
The Importance of Fault Line Maps:
Fault line maps serve as a critical tool for earthquake preparedness. They allow scientists to:
- Identify areas at high risk of earthquake damage: By understanding the location and orientation of fault lines, scientists can pinpoint areas that are most vulnerable to shaking during an earthquake.
- Develop earthquake-resistant building codes: Building codes can be tailored to the specific seismic hazards of a region, ensuring that structures are designed to withstand the forces of an earthquake.
- Plan emergency response strategies: Fault line maps help emergency responders to understand the potential impact of an earthquake and to develop effective response plans.
- Educate the public about earthquake risks: By providing clear and accurate information about fault lines and earthquake hazards, scientists can help to raise public awareness and encourage individuals to take steps to prepare for earthquakes.
FAQs about the NMSZ and Fault Line Maps:
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in the NMSZ?
A: The NMSZ experiences a steady stream of smaller earthquakes, typically ranging from magnitude 2 to 4. These smaller earthquakes are relatively common and often go unnoticed by the public. However, the potential for a major earthquake remains a significant concern.
Q: What are the potential impacts of a major earthquake in the NMSZ?
A: A major earthquake in the NMSZ could have catastrophic consequences, including:
- Ground shaking: Widespread ground shaking could cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Liquefaction: The shaking could cause loose, saturated soil to behave like a liquid, leading to ground collapse and building failures.
- Tsunamis: While less likely than in coastal regions, a major earthquake in the NMSZ could trigger tsunamis in the Mississippi River and its tributaries.
- Landslides: The shaking could trigger landslides in hilly and mountainous areas.
Q: What can be done to prepare for an earthquake in the NMSZ?
A: There are several steps that individuals and communities can take to prepare for an earthquake:
- Secure heavy objects: Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Develop an emergency plan: Create a plan for what to do in the event of an earthquake, including where to meet and how to contact family members.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit that includes food, water, first-aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Learn about earthquake safety: Educate yourself about earthquake safety procedures, such as "drop, cover, and hold on."
- Support earthquake preparedness initiatives: Advocate for policies that promote earthquake preparedness, such as building codes and emergency response plans.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness:
- Secure heavy objects: Ensure that heavy objects such as bookcases, mirrors, and televisions are securely anchored to walls or floors.
- Develop a family emergency plan: Discuss and practice emergency procedures with family members, including evacuation routes and meeting points.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit that includes essential items such as food, water, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, a battery-powered radio, and copies of important documents.
- Learn about earthquake safety procedures: Familiarize yourself with the "drop, cover, and hold on" safety procedure, which involves dropping to the ground, covering your head and neck with your arms, and holding onto a sturdy object.
- Participate in earthquake drills: Participate in regular earthquake drills to practice emergency procedures and enhance preparedness.
- Stay informed about earthquake risks and preparedness: Stay updated on earthquake risks in your area and access resources from organizations such as the USGS and FEMA.
Conclusion:
The New Madrid Seismic Zone is a testament to the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust and serves as a constant reminder of the potential for devastating earthquakes. Understanding the fault lines within the NMSZ is crucial for developing effective earthquake preparedness strategies. By learning about the geological history of the region, mapping the fault lines, and implementing preparedness measures, individuals and communities can mitigate the risks associated with earthquakes and build resilience in the face of future seismic events.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The New Madrid Seismic Zone: A Legacy of Earthquakes and a Blueprint for Preparedness. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!