The Political Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Political Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Political Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Political Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Overview
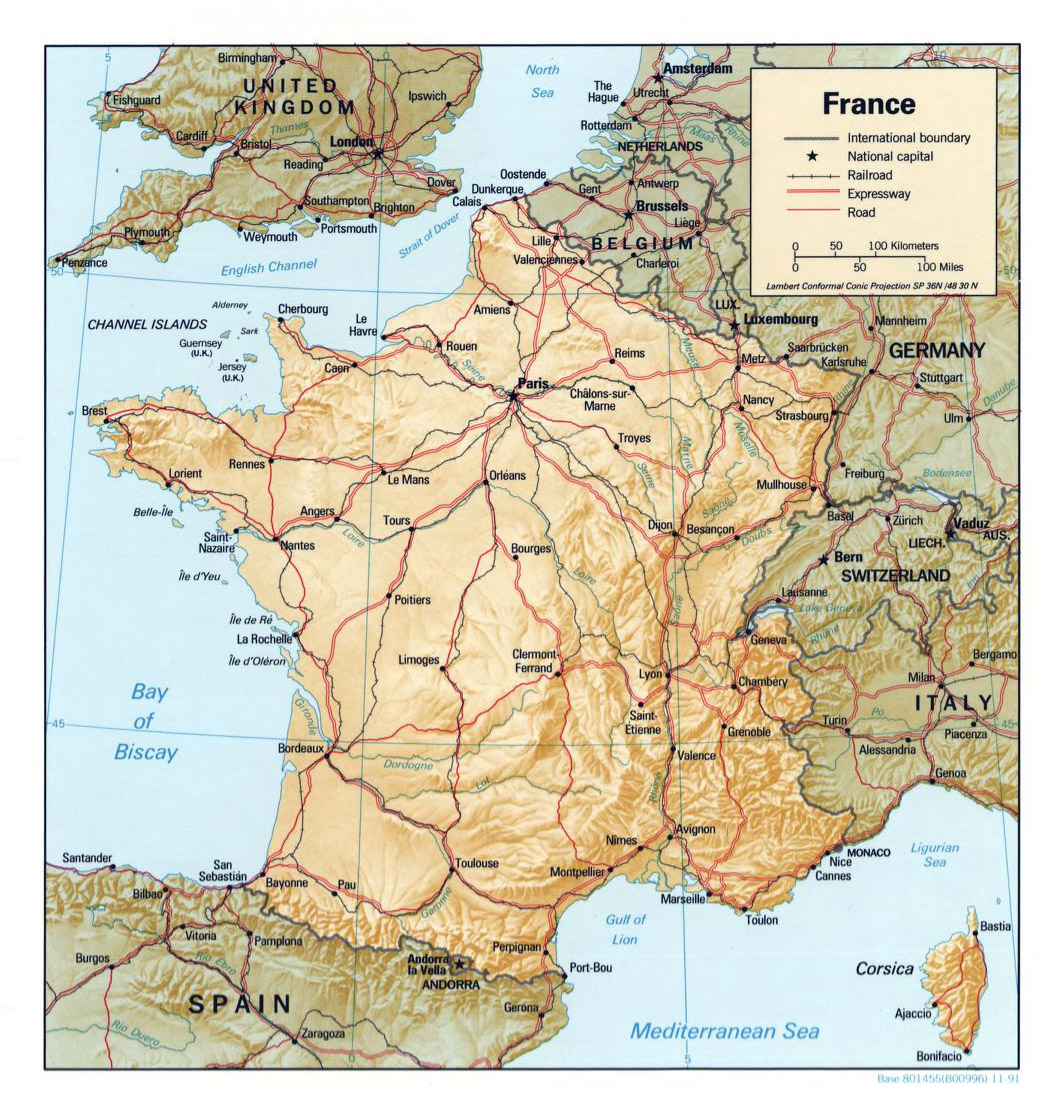
France, a nation steeped in history and renowned for its cultural vibrancy, boasts a complex and evolving political landscape. Understanding the intricate web of administrative divisions, political parties, and electoral processes is crucial to grasping the nuances of French governance and its impact on the nation’s trajectory. This article delves into the political map of France, exploring its key components and their significance.
Administrative Divisions: A Framework for Governance
France’s administrative structure is a hierarchical system, with each level playing a distinct role in governance. At the highest level is the central government, headquartered in Paris. This entity exercises overall authority over the nation, encompassing policy-making, law enforcement, and the management of key national institutions.
Below the central government lies a network of regions, currently numbering 18. These regions are responsible for managing regional affairs, including economic development, education, and cultural initiatives. Each region has its own elected council and a president, who acts as the region’s chief executive.
Further down the hierarchy are the departments, which are subdivisions of regions. There are 101 departments in mainland France, each with its own elected council and president. Departments are responsible for administering local services, including healthcare, social welfare, and infrastructure.
The smallest administrative units are the communes, which are the basic building blocks of French local government. There are over 36,000 communes, each with its own elected council and mayor. Communes are responsible for managing local services such as waste collection, public transportation, and urban planning.
Political Parties: Shaping the French Political Spectrum
The French political landscape is characterized by a multi-party system, where a multitude of political parties compete for power. While the number of parties fluctuates, certain major players have consistently shaped the political landscape.
The Republican Party (LR), a center-right party, traditionally advocates for economic liberalism, free markets, and a strong national defense. The Socialist Party (PS), on the left of the spectrum, prioritizes social justice, economic equality, and a strong welfare state.
The National Rally (RN), formerly known as the National Front, is a far-right party that has gained prominence in recent years. This party is known for its anti-immigration stance, skepticism towards European integration, and populist rhetoric.
The Green Party (EELV) champions environmental protection, sustainable development, and social justice. This party has gained traction in recent years, particularly among younger voters concerned about climate change.
The rise of centrist parties like La République En Marche (LREM), founded by Emmanuel Macron, has further diversified the political spectrum. These parties often focus on pragmatic solutions, bridging ideological divides and seeking consensus.
Electoral Processes: Shaping the Political Map
France’s electoral system is characterized by a combination of direct and indirect elections. Presidential elections are held every five years, with voters directly choosing the President of the Republic.
Legislative elections, also held every five years, determine the composition of the National Assembly. Voters elect their representatives in two rounds of voting, with a candidate needing a majority of votes to win in the second round.
The political map of France is significantly influenced by these electoral processes. The outcome of elections can determine the composition of government, the direction of policy, and the overall political climate.
The Significance of the Political Map
Understanding the political map of France is crucial for several reasons:
- Policy-Making: The structure of government and the influence of political parties directly impact the policies implemented at the national and local levels.
- Economic Development: Regional and local governments play a significant role in attracting investment, fostering innovation, and promoting economic growth.
- Social Welfare: The allocation of resources for social programs, healthcare, and education is influenced by the policies adopted by different levels of government.
- Cultural Identity: Regional and local governments play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage, promoting artistic expression, and fostering a sense of community.
- International Relations: The political landscape of France influences its role in international organizations, its foreign policy, and its relationships with other countries.
FAQs
Q: What are the main political parties in France?
A: The major political parties in France include the Republican Party (LR), the Socialist Party (PS), the National Rally (RN), the Green Party (EELV), and the centrist La République En Marche (LREM).
Q: How are elections conducted in France?
A: France employs a combination of direct and indirect elections. The President of the Republic is elected directly by the people, while the National Assembly is elected through a two-round system.
Q: What is the role of the regions in French governance?
A: Regions are responsible for managing regional affairs, including economic development, education, and cultural initiatives. They have elected councils and presidents.
Q: What is the significance of the communes in French politics?
A: Communes are the basic building blocks of local government in France. They manage local services and are responsible for urban planning.
Q: How does the political map of France influence the country’s international role?
A: France’s political landscape shapes its foreign policy, its participation in international organizations, and its relationships with other countries.
Tips
- Consult reliable sources: When researching the political map of France, rely on reputable sources such as academic journals, government websites, and established news organizations.
- Pay attention to regional variations: The political landscape of France varies significantly across different regions. Consider the specific characteristics of each region when analyzing its political dynamics.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about current political events in France to understand the evolving political landscape and the impact of elections and policy changes.
Conclusion
The political map of France is a dynamic and complex system, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse population, and evolving political landscape. Understanding its key components – administrative divisions, political parties, and electoral processes – is essential for comprehending the nuances of French governance and its impact on the nation’s future. By studying this map, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of French politics and its influence on various aspects of French society.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-163113170-5c4f1e6346e0fb00014c3781.jpg)




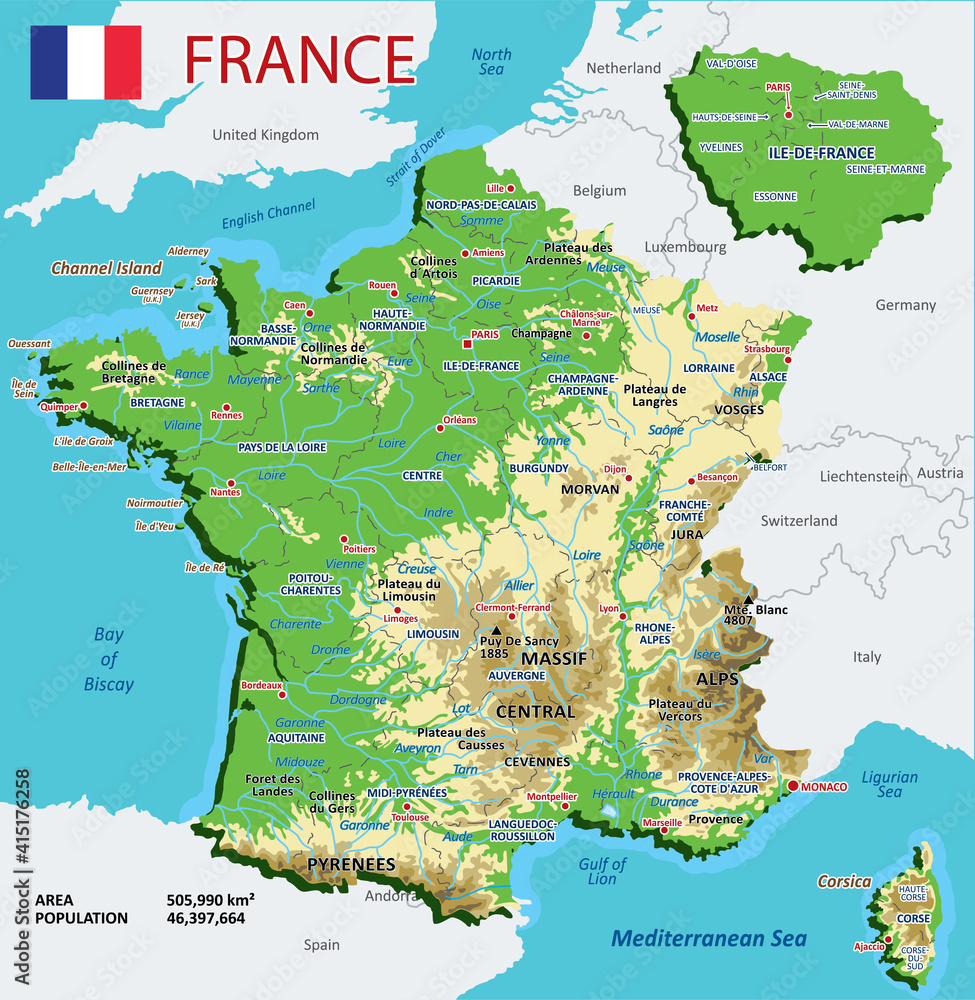
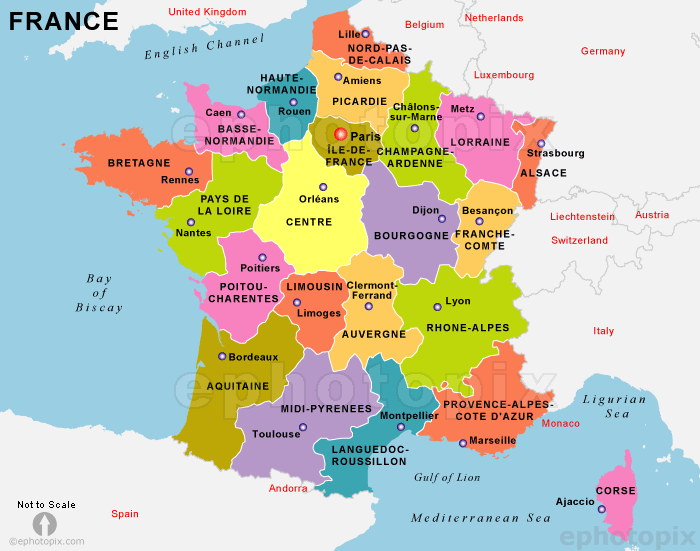
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Political Landscape of France: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!