The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Map Find
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Map Find
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Map Find. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Map Find
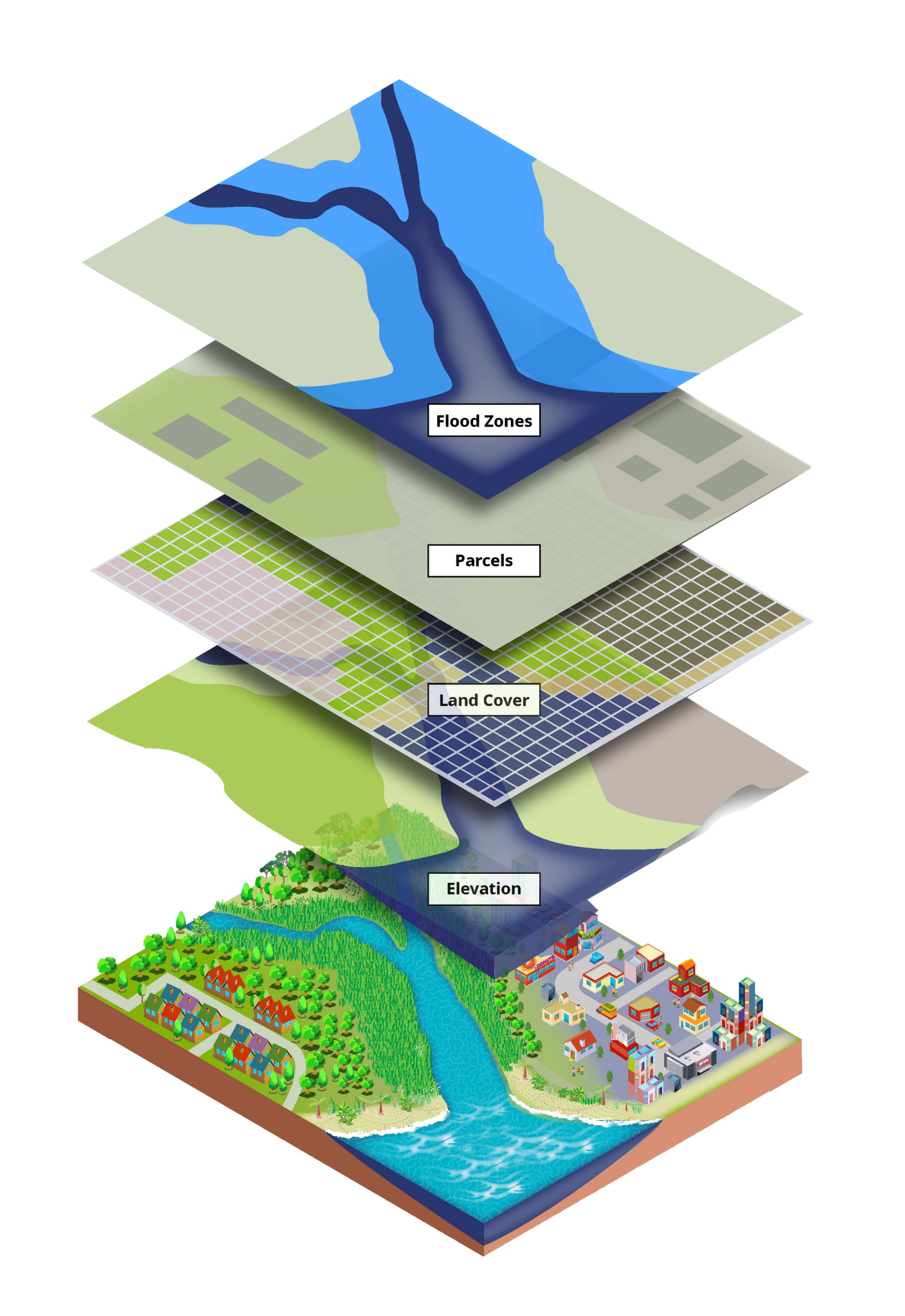
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to visualize and analyze spatial data has become crucial for a wide range of applications. This is where "map find," a powerful tool for locating and understanding information within geographic contexts, plays a vital role.
Defining the Concept:
"Map find" encompasses the processes and technologies used to locate and extract meaningful information from maps and spatial datasets. It involves a combination of geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and data analysis techniques to identify, analyze, and interpret spatial patterns and relationships. This field is not limited to static maps; it extends to dynamic representations of the Earth, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and real-time sensor data.
The Importance of Map Find:
The significance of map find lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights. It empowers decision-makers across various sectors, including:
- Urban Planning and Development: Map find facilitates the visualization of urban growth patterns, identifying areas for infrastructure development, optimizing transportation networks, and understanding population distribution.
- Environmental Management: By analyzing spatial data, map find enables the monitoring of deforestation, pollution levels, and natural resource depletion. It supports conservation efforts, disaster preparedness, and sustainable land use practices.
- Business and Marketing: Businesses utilize map find to optimize logistics, target specific customer demographics, and analyze market trends based on location. It helps understand consumer behavior, identify potential business opportunities, and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Healthcare and Public Health: Mapping disease outbreaks, analyzing health indicators, and optimizing resource allocation are crucial for public health initiatives. Map find assists in understanding disease patterns, identifying vulnerable populations, and improving healthcare delivery systems.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management: In emergency situations, map find provides vital information for search and rescue operations, evacuation planning, and resource allocation. It helps visualize disaster impact, assess damage, and coordinate relief efforts.
Key Components of Map Find:
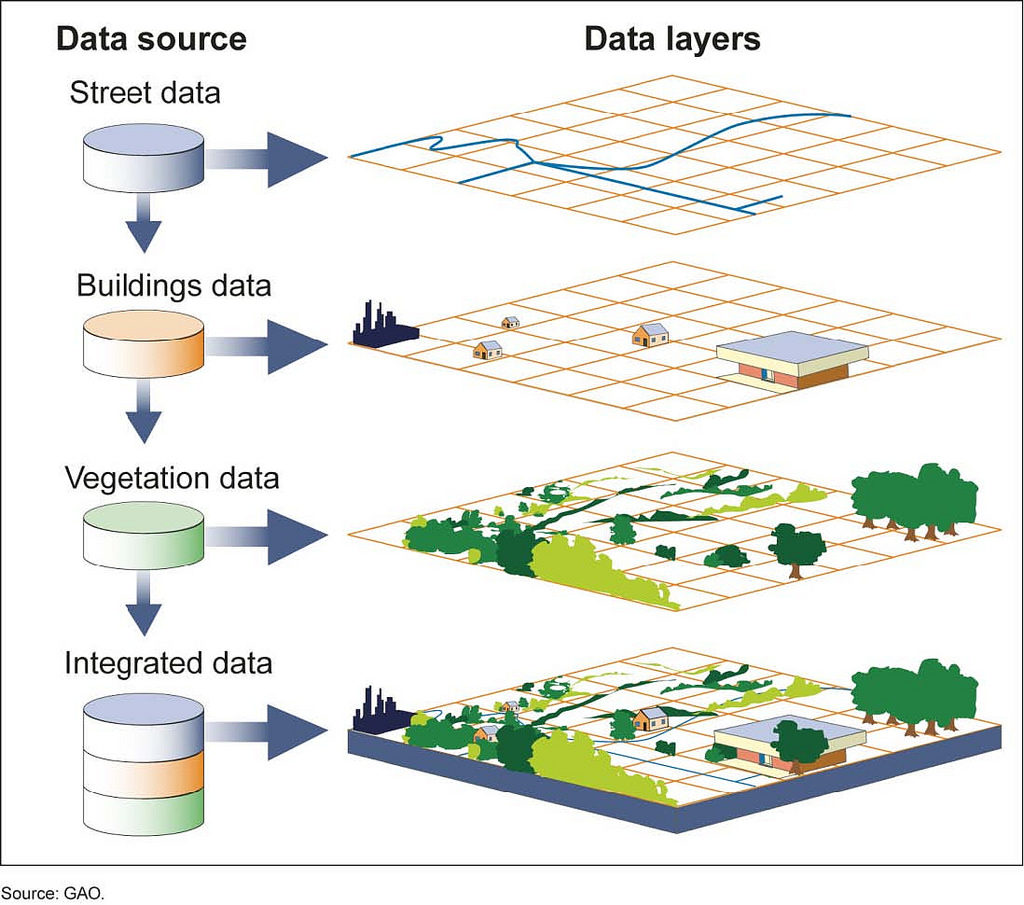
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides a framework for capturing, storing, analyzing, and displaying geographic data. It allows users to create maps, perform spatial analysis, and generate reports based on location-specific information.
- Remote Sensing: This technology utilizes sensors on satellites, aircraft, or drones to collect data about the Earth’s surface. Data can be analyzed to identify land cover changes, monitor environmental conditions, and assess natural resource availability.
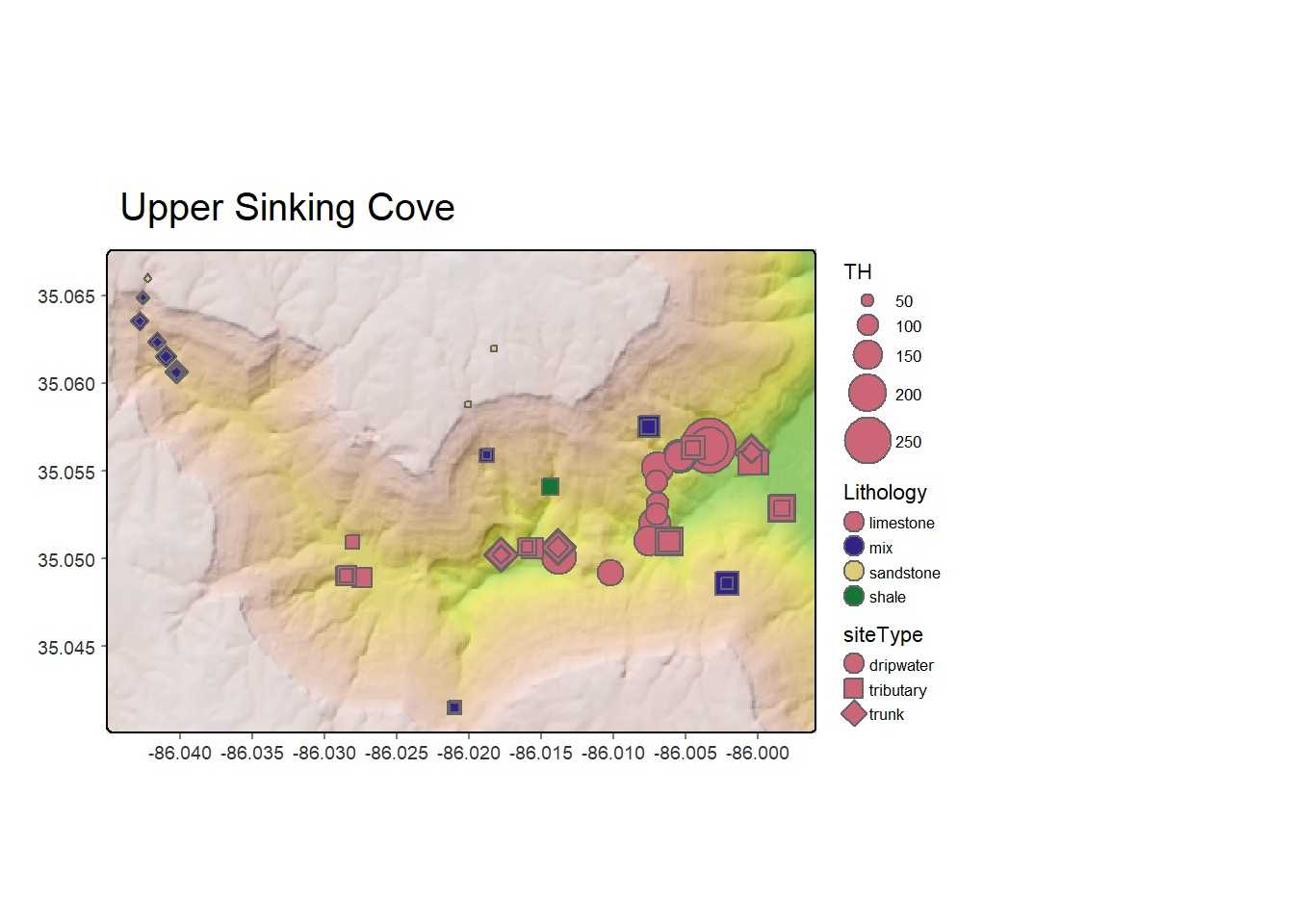
- Data Analysis Techniques: Statistical analysis, spatial modeling, and machine learning algorithms are used to extract meaningful insights from spatial data. These techniques help identify patterns, predict trends, and generate actionable information.
- Visualization Tools: Map find relies on powerful visualization tools to communicate spatial data effectively. Interactive maps, charts, and graphs allow users to explore data, identify trends, and share insights with others.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What are the key differences between map find and traditional mapping?
A: While traditional maps provide static representations of geographic features, map find goes beyond visualization by integrating data analysis, spatial modeling, and dynamic data sources. It allows users to interact with maps, explore data, and derive insights beyond simple visual representation.
Q: What are some examples of map find applications?
A: Map find applications are diverse and include:
- Crime mapping: Identifying crime hotspots and analyzing patterns to improve policing strategies.
- Traffic flow analysis: Optimizing traffic management, identifying congestion points, and planning infrastructure improvements.
- Real estate analysis: Identifying property values, market trends, and potential investment opportunities based on location.
- Environmental monitoring: Tracking deforestation, pollution levels, and climate change impacts.
Q: What are the challenges associated with map find?
A: Challenges include:
- Data accuracy and reliability: Ensuring the quality and consistency of spatial data is crucial for accurate analysis.
- Data accessibility and availability: Access to comprehensive and up-to-date spatial data is essential for effective map find applications.
- Technical expertise: Using map find tools effectively requires specialized skills and knowledge in GIS, remote sensing, and data analysis.
Tips for Utilizing Map Find:
- Define clear objectives: Establish specific goals and questions to guide the analysis and ensure meaningful insights.
- Select appropriate data sources: Choose data that is relevant to the objectives and meets the required quality standards.
- Utilize appropriate tools and techniques: Select the most suitable GIS software, analysis methods, and visualization tools for the specific application.
- Validate results and communicate findings: Ensure the accuracy of results and effectively communicate insights to relevant stakeholders.
Conclusion:
Map find is a powerful tool for harnessing the potential of spatial data to address complex challenges and inform decision-making. By integrating GIS, remote sensing, and data analysis techniques, it enables the visualization, analysis, and interpretation of geographic information to unlock valuable insights. As technology continues to advance, map find will continue to play a crucial role in various fields, empowering individuals and organizations to make informed decisions based on location-specific information.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Map Find. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!