The Quest for the Best Map of the Earth: A Journey Through Cartographic Excellence
Related Articles: The Quest for the Best Map of the Earth: A Journey Through Cartographic Excellence
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Quest for the Best Map of the Earth: A Journey Through Cartographic Excellence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Quest for the Best Map of the Earth: A Journey Through Cartographic Excellence
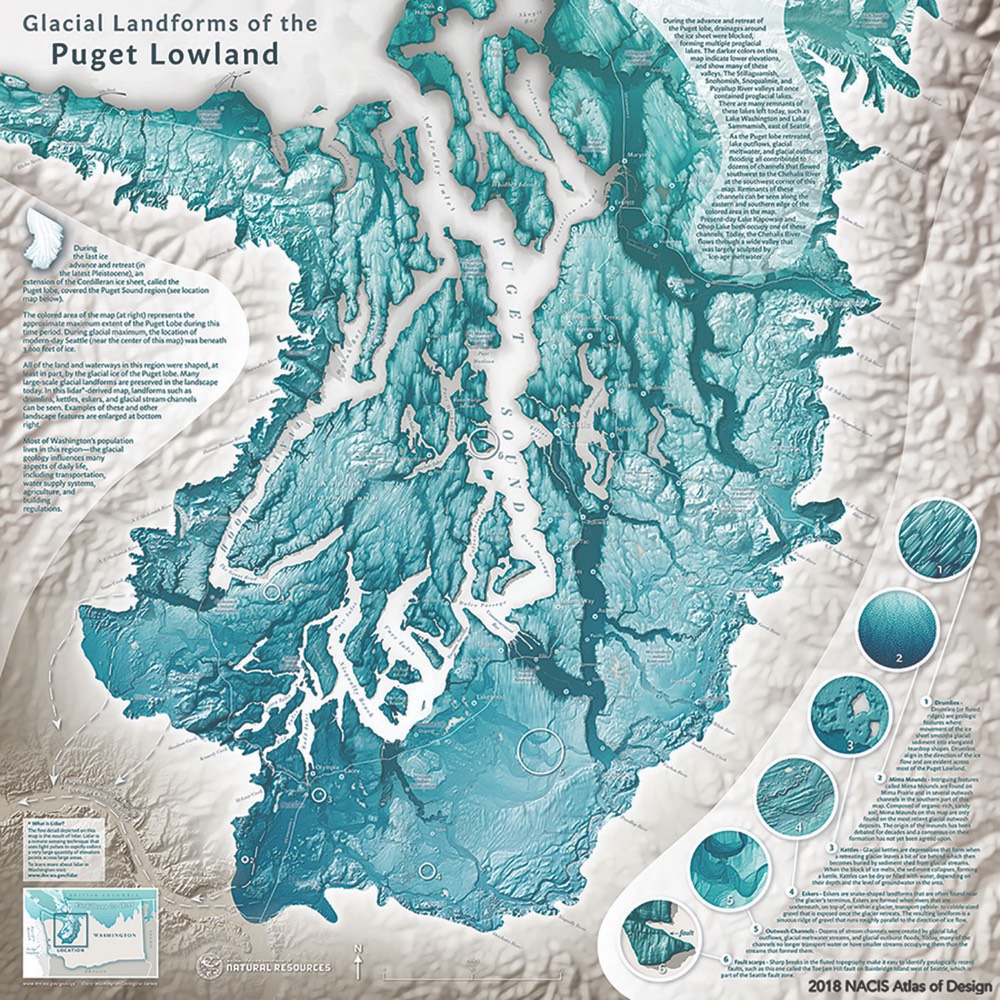
The world, in its vastness and complexity, has captivated humans for millennia. We have sought to understand its intricacies, to chart its features, and to navigate its terrains. This quest for understanding has led to the development of countless maps, each offering a unique perspective on our planet. But what constitutes the "best" map of the Earth? This question, far from being a simple one, delves into the very essence of cartography, its purpose, its limitations, and its evolving role in our understanding of the world.
To determine the "best" map, one must first define the criteria for evaluation. Is it accuracy, aesthetic appeal, functionality, or a combination of these factors? Each criterion carries its own weight and significance, depending on the intended use of the map. For a seasoned navigator, accuracy and detail are paramount. For a student of geography, a map emphasizing geographical features and cultural landscapes might be more suitable. And for a casual observer, a visually appealing map that captures the beauty and diversity of the Earth might be the most desirable.
Navigating the Cartographic Landscape: A Journey Through Map Types
The diverse needs of map users have led to the development of a wide array of map types, each tailored to specific purposes. Some prominent examples include:
- World Maps: These maps provide a global perspective, depicting the Earth’s continents and oceans. They are commonly used for educational purposes, general reference, and global analysis.
- Political Maps: These maps emphasize political boundaries, highlighting countries, states, and cities. They are essential for understanding global political dynamics, international relations, and administrative divisions.
- Physical Maps: These maps focus on the Earth’s physical features, showcasing mountains, rivers, lakes, and other natural formations. They are valuable for understanding geographical processes, environmental studies, and natural resource management.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific data or themes, such as population density, climate patterns, or economic activity. They are essential for visualizing and analyzing complex data, facilitating informed decision-making, and raising awareness about critical issues.
The Challenge of Representing a Sphere on a Flat Surface: The Evolution of Projections
The Earth, being a sphere, poses a significant challenge to cartographers seeking to represent it on a flat surface. This challenge has led to the development of various map projections, each employing different mathematical formulas to project the spherical Earth onto a two-dimensional plane. Each projection inevitably introduces distortions, impacting the accuracy of shapes, distances, areas, and directions.
Common Map Projections and Their Strengths and Limitations
- Mercator Projection: This projection, widely used for navigational purposes, preserves angles and shapes, making it ideal for sailing and air travel. However, it significantly distorts areas, particularly near the poles, exaggerating the size of landmasses in higher latitudes.
- Gall-Peters Projection: This projection aims to accurately represent areas, minimizing distortion in landmass sizes. However, it distorts shapes and angles, making it unsuitable for navigation.
- Robinson Projection: This projection seeks to balance distortions in area, shape, and direction, resulting in a visually appealing and relatively accurate representation of the Earth. However, it introduces some distortions in all aspects.
- Winkel Tripel Projection: This projection minimizes distortions in area, shape, and direction, offering a balanced and visually pleasing representation of the Earth. However, it can distort distances in some regions.
Beyond Traditional Maps: The Rise of Digital Cartography and Interactive Mapping
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized cartography, opening new possibilities for map creation and dissemination. Digital maps offer interactive features, dynamic data visualization, and seamless integration with other technologies.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap are prominent examples of online mapping platforms that provide comprehensive and interactive maps, offering real-time traffic updates, street views, and location-based services.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows users to create, analyze, and manage spatial data, enabling sophisticated mapping and analysis of complex datasets.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Mapping: VR and AR technologies offer immersive experiences, allowing users to explore virtual landscapes and superimpose digital information onto real-world environments, enhancing our understanding of the Earth’s geography.
The "Best" Map: A Relative Concept
Ultimately, the "best" map of the Earth is a relative concept, dependent on the specific needs and purposes of the user. A map designed for navigation will prioritize accuracy in distances and directions, while a map intended for educational purposes might emphasize geographical features and cultural landscapes.
FAQs: Demystifying the World of Maps
1. Why are maps important?
Maps are crucial for understanding the world around us. They provide a visual representation of geographical features, political boundaries, and other important information, facilitating navigation, planning, and decision-making.
2. What are the different types of maps?
Maps can be classified based on their purpose and content. Common types include world maps, political maps, physical maps, and thematic maps.
3. How are maps made?
Maps are created through a combination of surveying, data collection, and cartographic techniques. They involve projecting the spherical Earth onto a flat surface, selecting appropriate scales and projections, and designing visual elements to represent geographic features.
4. What are the challenges of making maps?
Challenges in mapmaking include representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface, minimizing distortions, selecting appropriate projections, and ensuring accuracy and clarity.
5. What are the latest developments in cartography?
Digital cartography, GIS software, and VR/AR mapping technologies are revolutionizing mapmaking, offering interactive features, dynamic data visualization, and immersive experiences.
Tips: Navigating the World of Maps
- Identify your purpose: Determine what information you need from the map before selecting one.
- Consider the scale: Choose a map with an appropriate scale for your needs.
- Understand the projection: Be aware of the distortions inherent in different map projections.
- Explore different map types: Consider the different types of maps available to meet your specific requirements.
- Embrace digital cartography: Utilize online mapping platforms and GIS software for interactive and dynamic map experiences.
Conclusion: A Journey of Exploration and Discovery
The quest for the "best" map of the Earth is a continuous journey, driven by our desire to understand and navigate our planet. As technology advances and our understanding of the world evolves, the art and science of cartography will continue to shape our perception of the Earth, offering new perspectives and facilitating exploration, discovery, and informed decision-making.



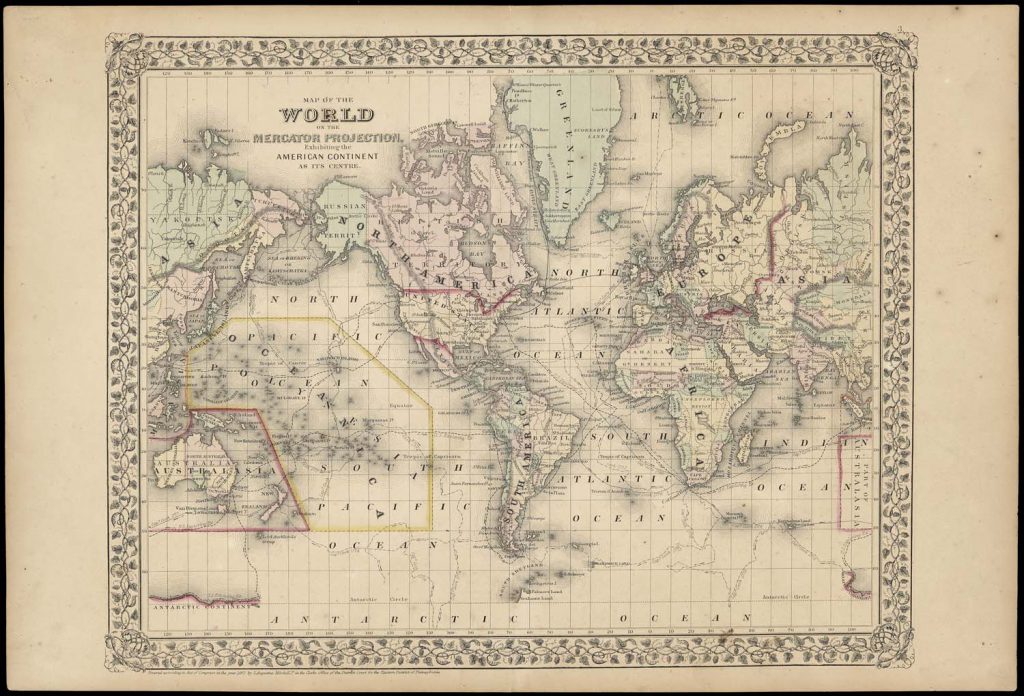
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Quest for the Best Map of the Earth: A Journey Through Cartographic Excellence. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!