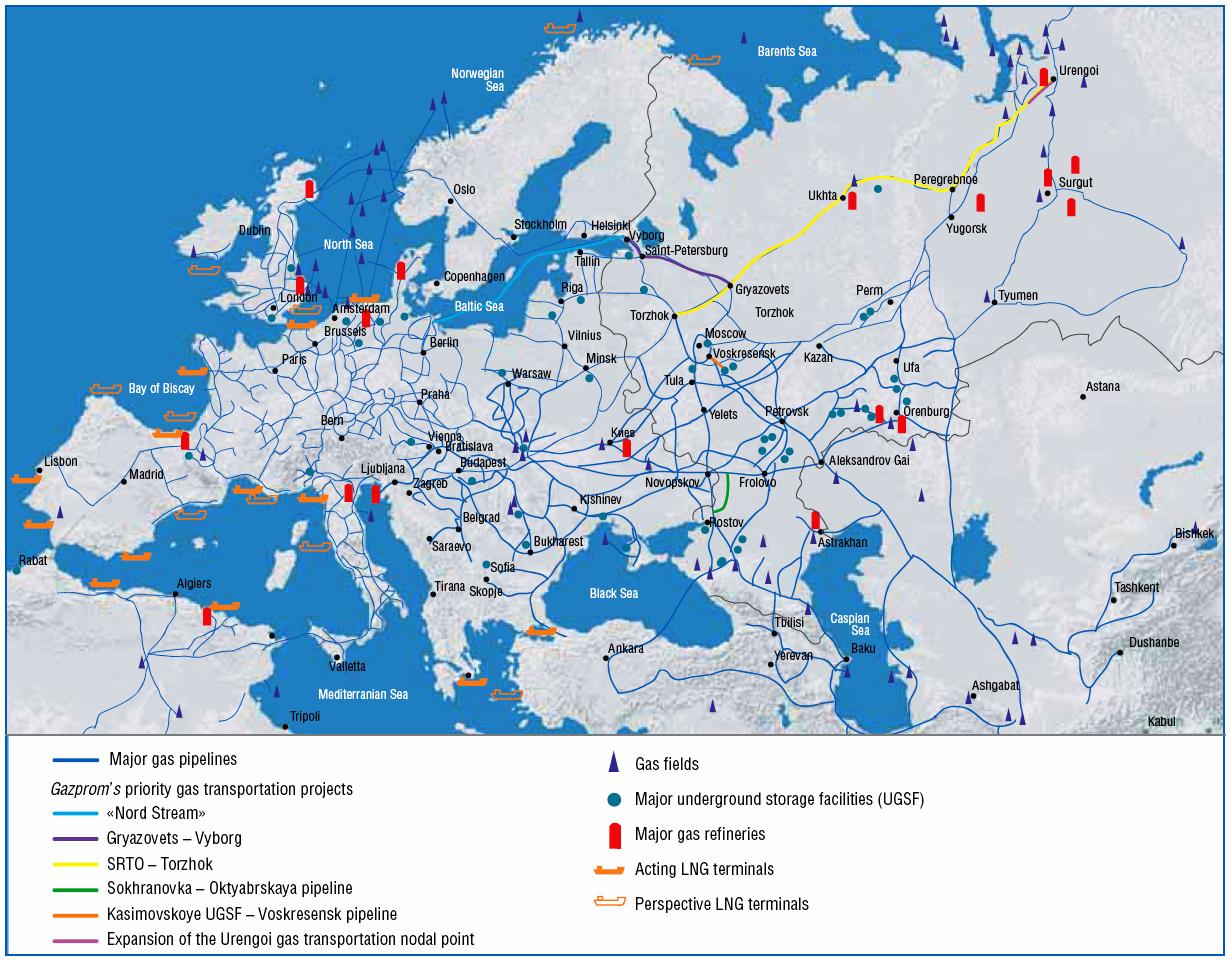
The Russian Gas Pipeline Network: A Lifeline to Europe
Related Articles: The Russian Gas Pipeline Network: A Lifeline to Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Russian Gas Pipeline Network: A Lifeline to Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Russian Gas Pipeline Network: A Lifeline to Europe

The Russian gas pipeline network, a sprawling web of interconnected infrastructure, has for decades served as a vital conduit for natural gas flowing from the vast Siberian fields to Europe. This network, spanning thousands of kilometers, has played a pivotal role in shaping energy dynamics, geopolitical relationships, and economic development across the Eurasian continent.
A Historical Perspective
The genesis of the Russian gas pipeline network can be traced back to the post-World War II era. The Soviet Union, with its vast natural gas reserves, sought to utilize this resource for both domestic consumption and export, particularly to Eastern European countries within its sphere of influence. The first major pipeline, the Friendship Pipeline, was constructed in the 1960s, transporting gas from the Soviet Union to Eastern Europe. This marked the beginning of a robust pipeline infrastructure that would expand and evolve significantly over the subsequent decades.
The Expansion of the Network
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the construction of several key pipelines, including the Soyuz Pipeline, which extended the reach of Russian gas to Western Europe. The emergence of the Yamal pipeline in the 1990s further expanded the network, linking Russia’s vast Siberian gas fields to European markets. The Nord Stream pipeline, inaugurated in 2011, represented a major shift, establishing a direct undersea route between Russia and Germany, bypassing transit countries and enhancing efficiency.
Strategic Significance
The Russian gas pipeline network holds immense strategic importance, both for Russia and for Europe. For Russia, it serves as a crucial revenue stream, generating substantial income from gas exports. The network also reinforces Russia’s geopolitical influence, allowing it to exert leverage over energy-dependent European countries.
From Europe’s perspective, the Russian gas pipeline network provides a reliable source of energy, meeting a significant portion of its natural gas demand. This reliance on Russian gas has, however, created a complex web of dependencies, raising concerns about energy security and geopolitical vulnerability.
The Network in the 21st Century
The 21st century has witnessed a period of both expansion and uncertainty for the Russian gas pipeline network. The completion of the Nord Stream 2 pipeline, a twin to the original Nord Stream, was met with considerable controversy, highlighting the growing geopolitical tensions surrounding energy supply.
Challenges and Future Prospects
The Russian gas pipeline network faces several challenges, including:
- Geopolitical Tensions: The network has become a focal point of geopolitical tensions, particularly in the context of the Ukraine crisis and the imposition of sanctions against Russia.
- Diversification of Supply: European countries are actively seeking to diversify their energy sources, reducing their dependence on Russian gas.
- Environmental Concerns: The network’s environmental impact, particularly regarding methane emissions, has raised concerns about its sustainability.
The future of the Russian gas pipeline network remains uncertain. While the network will likely continue to play a significant role in the global energy landscape, its future will depend on the evolving geopolitical dynamics, the pace of energy diversification, and the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions.
FAQs
Q: What are the main Russian gas pipelines to Europe?
A: Some of the most important Russian gas pipelines to Europe include:
- Nord Stream 1 and 2: Undersea pipelines connecting Russia directly to Germany, bypassing transit countries.
- Yamal Pipeline: Transports gas from the Yamal Peninsula in Siberia to Western Europe.
- Soyuz Pipeline: Connects Russia to Central and Eastern Europe.
- Friendship Pipeline: A major pipeline system transporting gas from Russia to Eastern Europe.
Q: Why is the Russian gas pipeline network so important?
A: The network is crucial for both Russia and Europe. For Russia, it generates significant income from gas exports and strengthens its geopolitical influence. For Europe, it provides a vital source of energy, meeting a significant portion of its natural gas demand.
Q: What are the risks associated with reliance on Russian gas?
A: Reliance on Russian gas poses risks for European countries, including:
- Geopolitical Vulnerability: Russia’s ability to manipulate gas supplies can exert political pressure on European countries.
- Energy Security Concerns: Disruptions to gas flows could lead to energy shortages and economic instability.
- Environmental Impact: The network’s environmental impact, particularly methane emissions, has raised concerns about its sustainability.
Q: What are the alternatives to Russian gas?
A: European countries are actively pursuing alternative energy sources, including:
- Renewable Energy: Wind, solar, and hydropower are increasingly important sources of energy.
- Natural Gas from Other Sources: Importing gas from countries like Norway, Qatar, and the United States.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Reducing energy consumption through improved technology and building standards.
Tips for Understanding the Russian Gas Pipeline Network
- Consult Maps: Utilize interactive maps to visualize the network’s routes and key infrastructure.
- Research Historical Context: Understanding the historical evolution of the network provides insights into its current state and future prospects.
- Follow Energy News: Stay updated on developments related to the network, including geopolitical tensions, energy diversification efforts, and environmental concerns.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives: Analyze the network’s impact on different stakeholders, including Russia, European countries, and energy companies.
Conclusion
The Russian gas pipeline network is a complex and multifaceted infrastructure that has shaped energy dynamics and geopolitical relations for decades. Its future trajectory will be influenced by a confluence of factors, including geopolitical tensions, energy diversification efforts, and the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. The network will continue to be a subject of intense scrutiny and debate as the global energy landscape undergoes significant transformation.


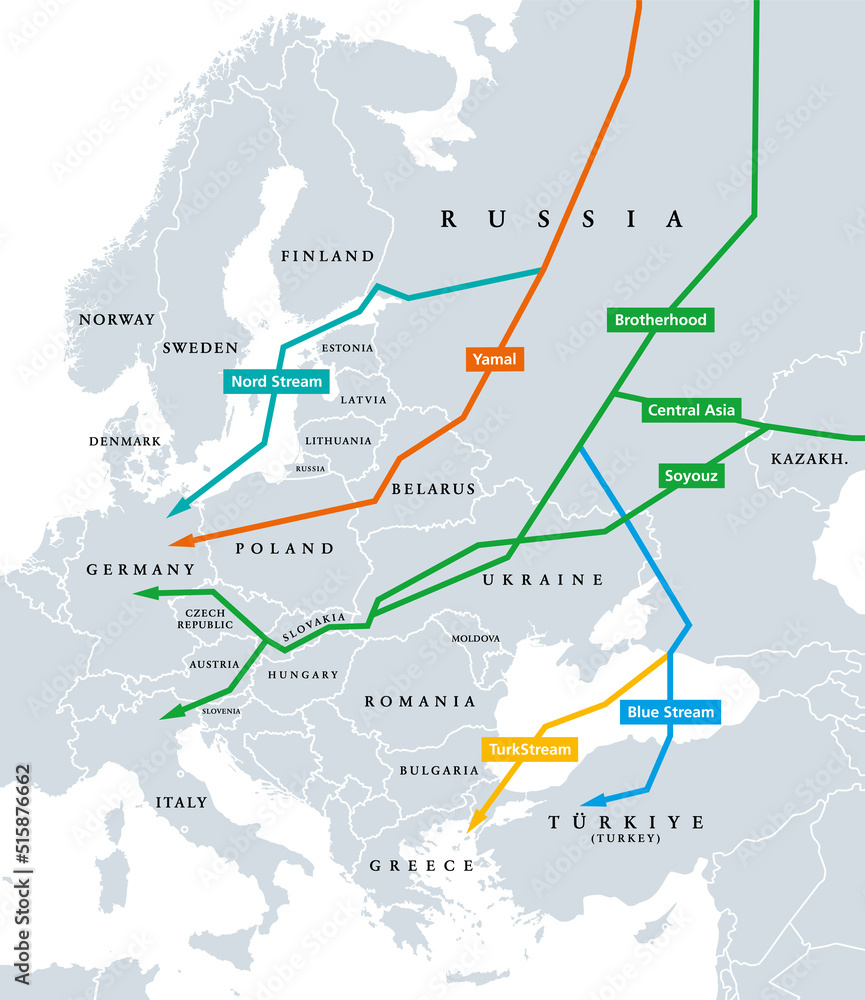
![Natural Gas pipelines from Russia into Europe (gif) [2252 x 1674] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/3n7EMsVzLTQO2hzghUro4n5-sFRG9JgxNk283KxIluo.gif?format=png8u0026s=fd5fc644a92c94a839468441b26be20bd4864647)
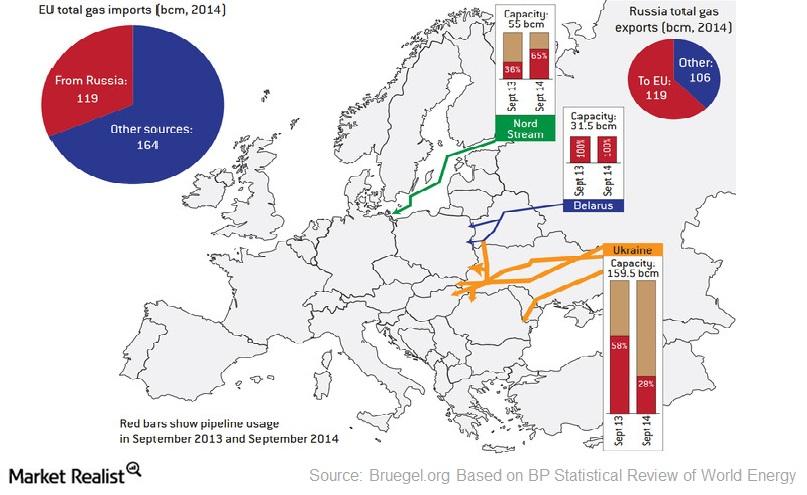

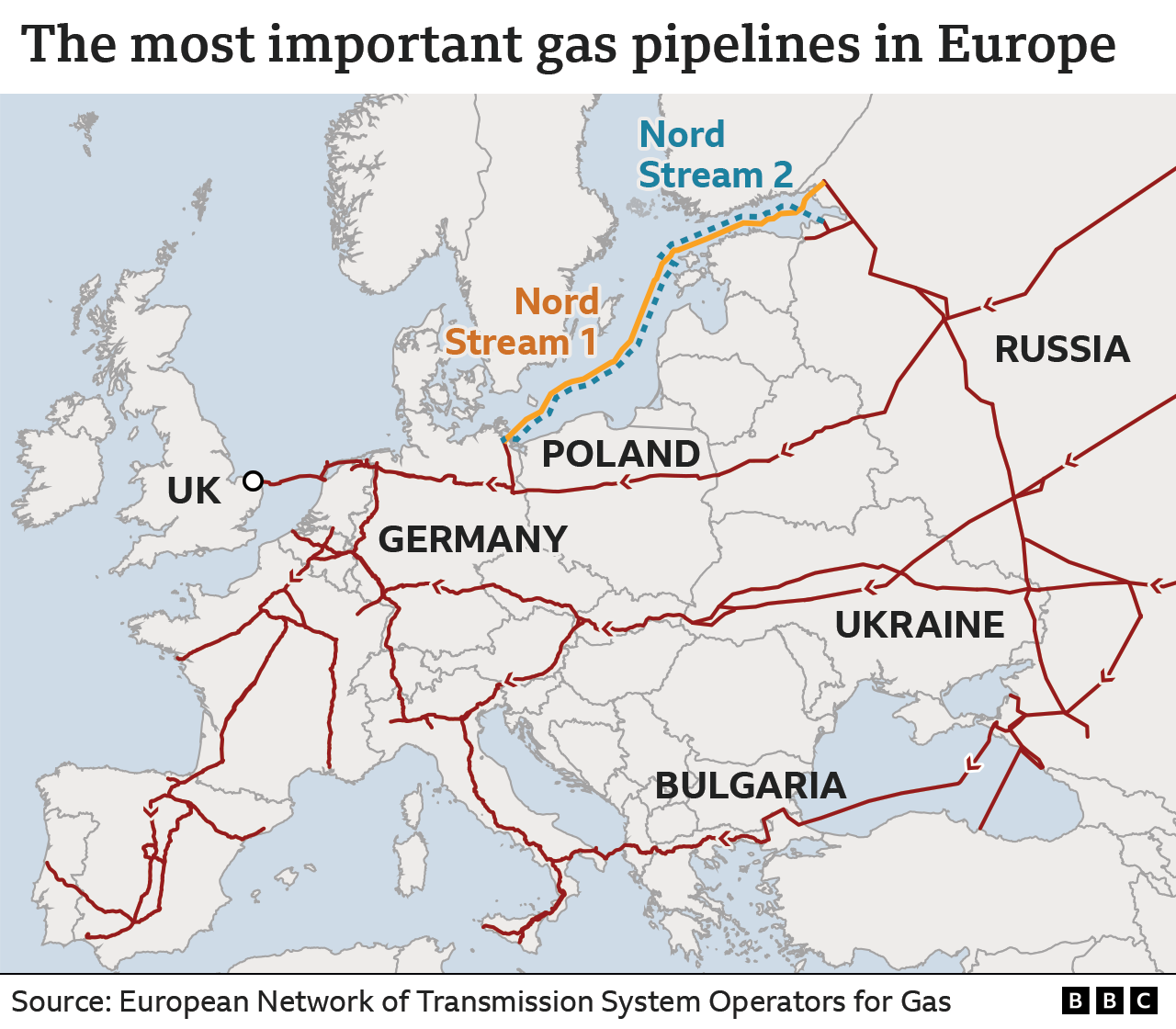
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Russian Gas Pipeline Network: A Lifeline to Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!