The Shifting Sands of Empire: Mapping Napoleon’s France
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Empire: Mapping Napoleon’s France
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Empire: Mapping Napoleon’s France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Empire: Mapping Napoleon’s France

The map of France under Napoleon Bonaparte is more than a mere geographical representation; it is a dynamic tapestry woven with ambition, conquest, and the shifting tides of power. This map is a testament to the extraordinary rise of a man who, from humble beginnings, transformed a nation into an empire that stretched across Europe. Examining its evolution reveals not only the scope of Napoleon’s conquests but also the profound impact these conquests had on the political, social, and cultural landscape of Europe.
From Republic to Empire: The Expansion of French Influence
Napoleon’s ascent to power began in the midst of the French Revolution, a period of upheaval that saw the dismantling of the monarchy and the establishment of the French Republic. As a brilliant military strategist and charismatic leader, Napoleon rose through the ranks of the French army, ultimately becoming First Consul in 1799. Under his rule, France embarked on a series of military campaigns that dramatically reshaped the map of Europe.
The Italian Campaigns (1796-1797): Napoleon’s early victories in Italy, culminating in the Treaty of Campo Formio, secured French control of the northern Italian peninsula. This region, previously under Habsburg rule, became a crucial strategic asset for France, providing access to the Mediterranean and resources for further expansion.
The Egyptian Campaign (1798-1801): Although ultimately unsuccessful, Napoleon’s expedition to Egypt aimed to disrupt British control of the Eastern Mediterranean and establish a French presence in this vital region. While the campaign failed to achieve its objectives, it significantly impacted the Napoleonic Wars, ultimately leading to a British naval victory and the strengthening of British maritime dominance.
The Consular Period (1799-1804): During this period, Napoleon consolidated his power in France, establishing a strong central government and implementing reforms that modernized the nation’s legal system, education, and economy. His focus on administrative efficiency and centralized power laid the groundwork for the expansion of French influence across Europe.
The Napoleonic Empire (1804-1814): In 1804, Napoleon crowned himself Emperor of France, marking the official transition from republic to empire. This period witnessed the pinnacle of Napoleon’s conquests, with France dominating much of Europe through a series of alliances, annexations, and military victories.
The Continental System (1806-1814): This economic blockade aimed to cripple Great Britain by preventing trade with continental Europe. Although ultimately unsuccessful, the Continental System significantly impacted European economies, leading to widespread hardship and contributing to the rise of nationalistic sentiments across Europe.
The Rise and Fall of the Napoleonic Empire:
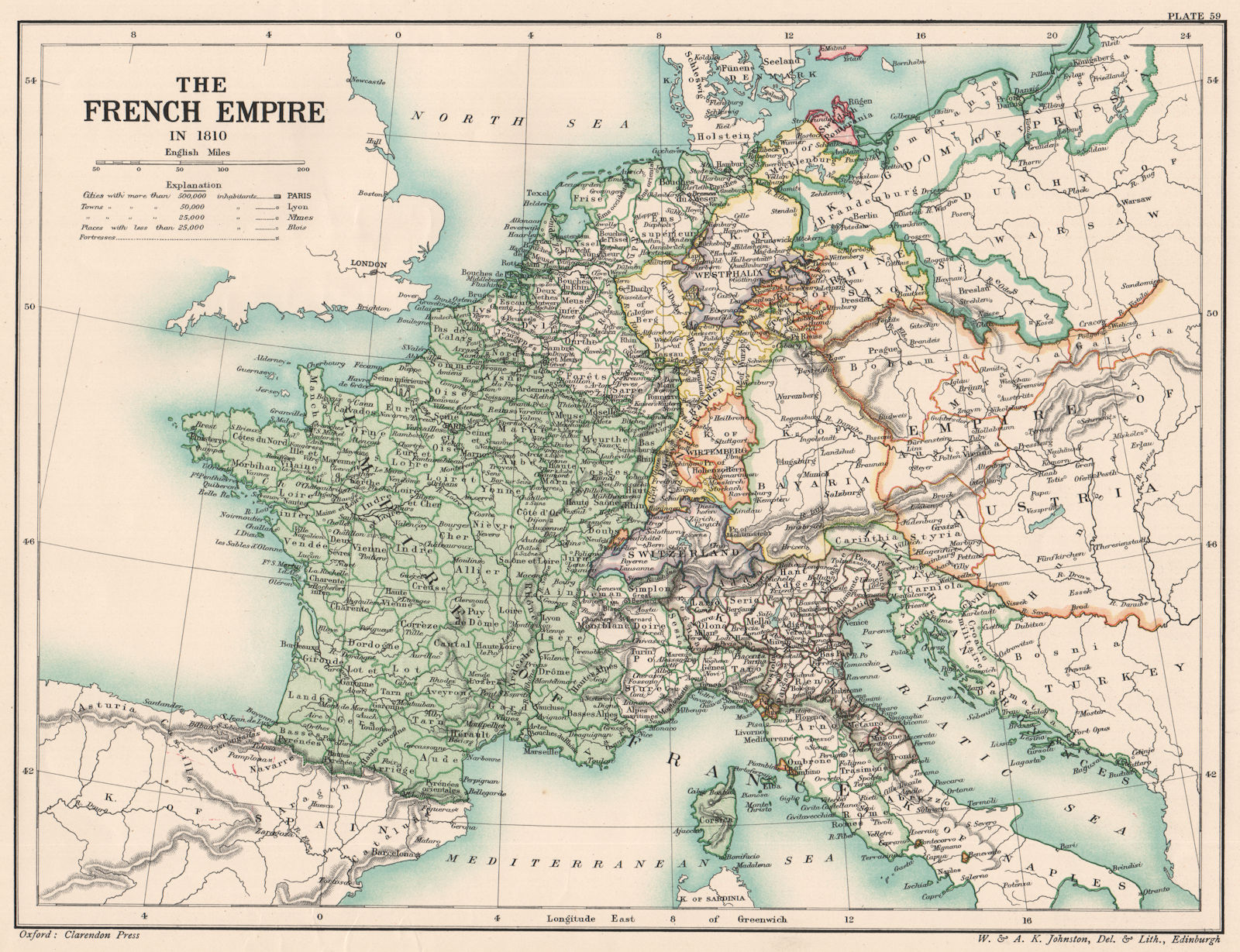
The map of France under Napoleon reached its zenith in 1810, encompassing a vast territory spanning from Spain and Portugal in the west to the Grand Duchy of Warsaw in the east. This seemingly invincible empire, however, was ultimately brought down by a combination of factors:
- The Rise of Nationalism: Napoleon’s conquests sparked resistance and nationalistic sentiment across Europe, fueling anti-French movements that ultimately contributed to his downfall.
- The Peninsular War (1808-1814): This protracted and costly conflict in Spain, aimed at securing the Iberian Peninsula, drained French resources and weakened Napoleon’s military power.
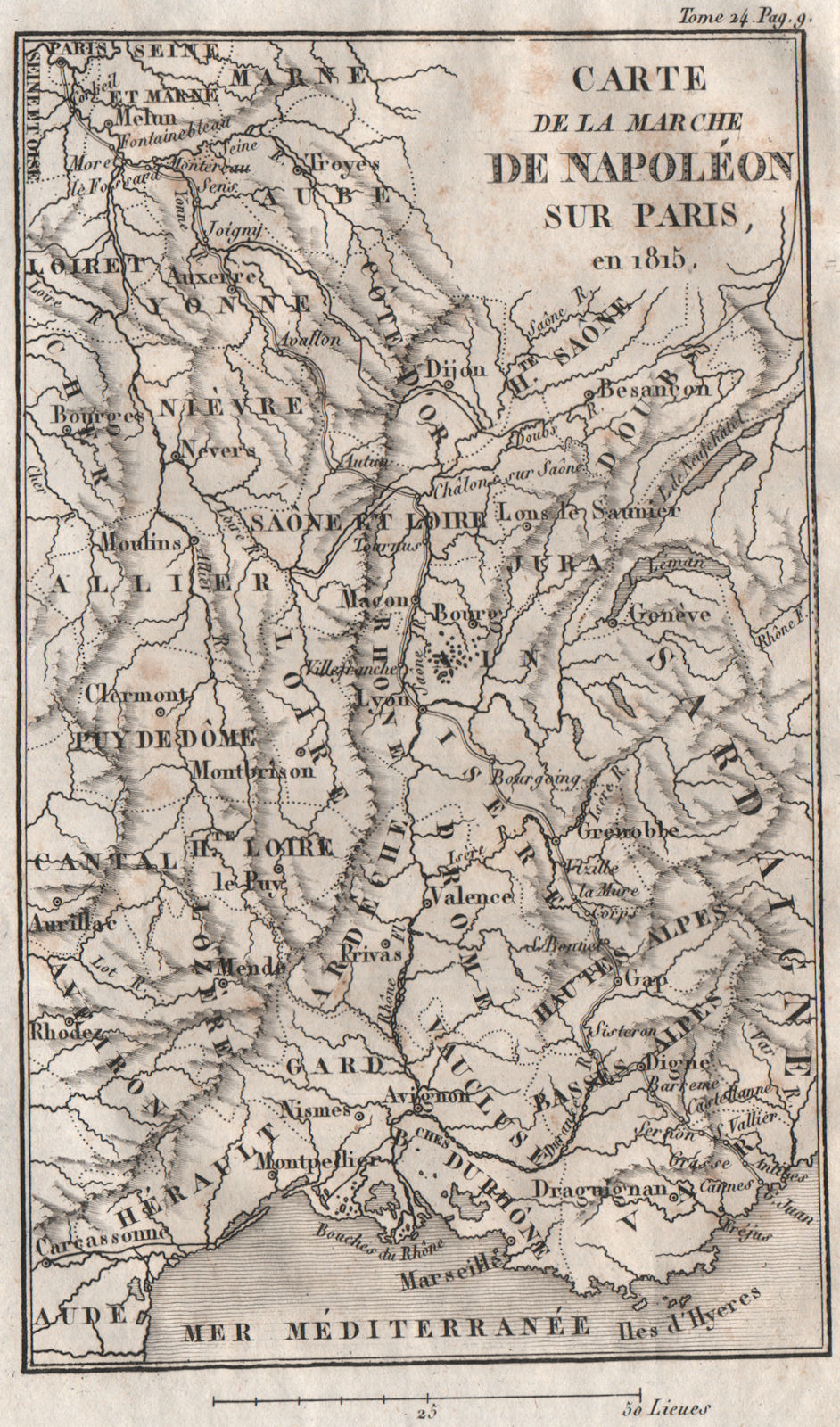
- The Invasion of Russia (1812): Napoleon’s disastrous campaign in Russia, marked by a devastating winter retreat and heavy losses, significantly weakened his army and undermined his authority.
- The Coalition of European Powers: The combined forces of Austria, Prussia, Russia, and Great Britain, united in their opposition to Napoleon, ultimately led to his defeat in the Napoleonic Wars.
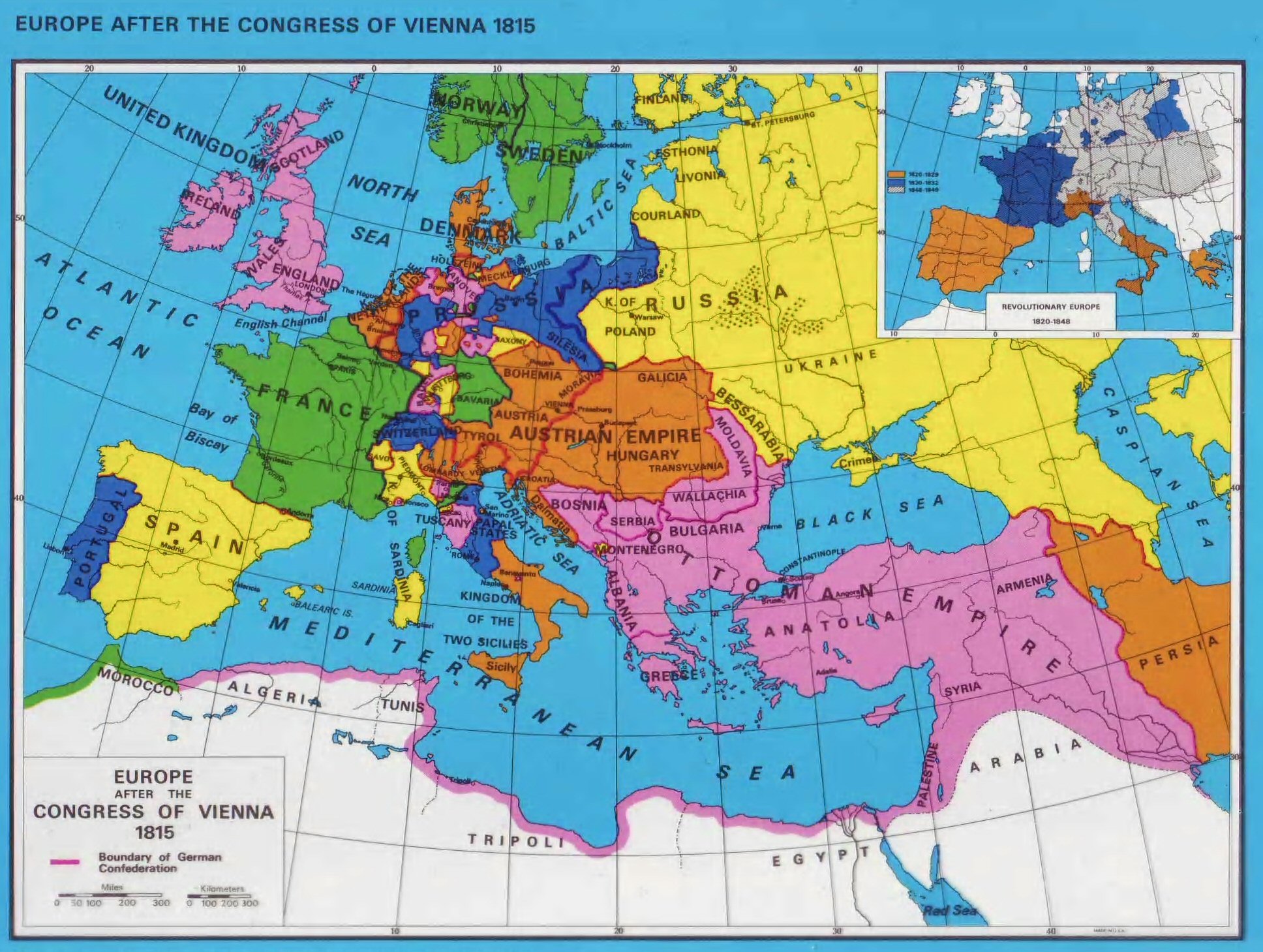
The Legacy of the Napoleonic Wars:
Despite its eventual collapse, the Napoleonic Empire left an enduring legacy on the map of Europe:
- The Spread of French Ideas: The Napoleonic Code, a comprehensive legal system that emphasized equality and individual rights, was adopted by many European nations, significantly impacting legal systems and societal structures.
- The Rise of Nationalism: The Napoleonic Wars fostered a sense of national identity and unity across Europe, contributing to the emergence of independent nation-states and the eventual decline of traditional empires.
- The Rise of Prussia and Russia: The Napoleonic Wars led to the rise of Prussia and Russia as major European powers, shifting the balance of power on the continent.
The Importance of the Map of France Under Napoleon:
The map of France under Napoleon is a powerful visual representation of the ambitions, conquests, and ultimately the limitations of one man’s vision. It serves as a reminder of the complexities of power, the importance of alliances and strategic planning, and the enduring impact of individual actions on the course of history.
FAQs about the Map of France Under Napoleon:
Q1. What were the main territories included in the map of France under Napoleon at its peak?
A1. At its peak, the map of France under Napoleon included France itself, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Italy (excluding Sicily and Sardinia), parts of Germany, Poland, and Spain.
Q2. What were the key factors that contributed to the downfall of the Napoleonic Empire?
A2. The downfall of the Napoleonic Empire was a result of a combination of factors, including the rise of nationalism across Europe, the costly Peninsular War, the disastrous invasion of Russia, and the eventual coalition of European powers against France.
Q3. How did the Napoleonic Wars impact the map of Europe?
A3. The Napoleonic Wars significantly reshaped the map of Europe, leading to the emergence of new nation-states, the redistribution of territories, and the rise of new powers such as Prussia and Russia.
Q4. What were the main innovations and reforms implemented by Napoleon in France?
A4. Napoleon introduced significant reforms in France, including the Napoleonic Code, which standardized the legal system, the establishment of a central bank, and the modernization of the educational system.
Q5. What were the main challenges faced by Napoleon in maintaining his empire?
A5. Napoleon faced numerous challenges in maintaining his empire, including the constant threat of coalition forces, the rise of nationalism across Europe, and the logistical difficulties of managing a vast and diverse territory.
Tips for Understanding the Map of France Under Napoleon:
- Focus on Key Territories: Pay attention to the core territories of the French Empire, including France itself, the Netherlands, Belgium, Italy, and parts of Germany.
- Track the Expansion and Contraction of the Empire: Trace the evolution of the map over time, noting the periods of expansion and contraction of French influence.
- Consider the Impact of Key Campaigns: Analyze the impact of significant campaigns such as the Italian Campaigns, the Egyptian Campaign, and the invasion of Russia on the map.
- Examine the Political and Economic Context: Understand the political and economic factors that shaped the map of France under Napoleon, such as the Continental System and the rise of nationalism.
Conclusion:
The map of France under Napoleon is a complex and fascinating testament to the ambition and legacy of one of history’s most influential figures. It reveals the dynamic nature of power, the intricate interplay of military conquest and political maneuvering, and the enduring impact of individual actions on the course of history. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped Europe in the early 19th century and the enduring legacy of the Napoleonic era.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Empire: Mapping Napoleon’s France. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
