The Shifting Sands of Power: A Deep Dive into the Napoleonic France Map
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Power: A Deep Dive into the Napoleonic France Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Power: A Deep Dive into the Napoleonic France Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Power: A Deep Dive into the Napoleonic France Map
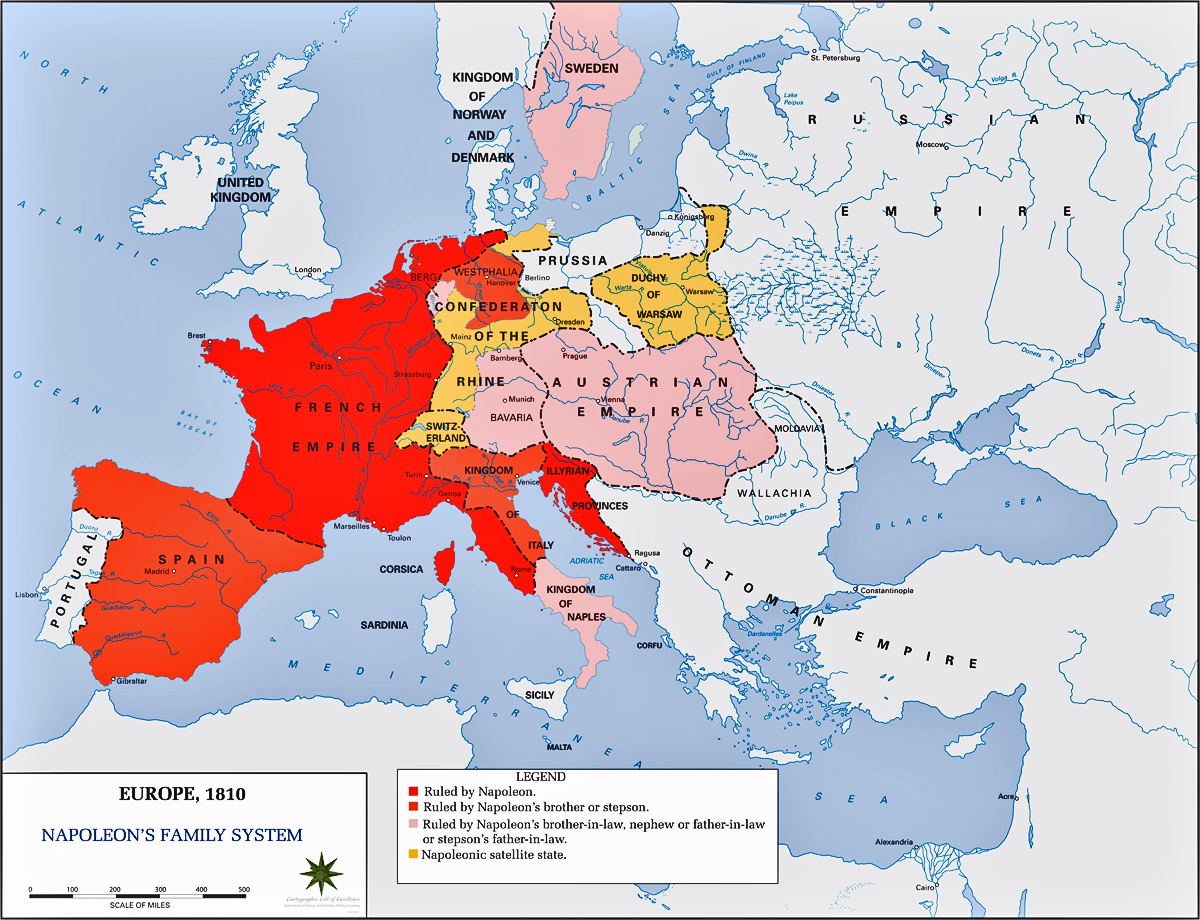
The Napoleonic Wars, a period of intense conflict spanning from 1803 to 1815, witnessed the rise and fall of an empire that reshaped Europe’s political landscape. At the heart of this tumultuous era lay the Napoleonic France map, a dynamic and ever-changing representation of the French Empire’s territorial ambitions and military prowess. This map, far more than a static depiction of borders, provides a crucial window into the strategic decisions, political machinations, and societal upheavals that defined the Napoleonic era.
From Republic to Empire: A Map of Expansion
In 1799, Napoleon Bonaparte seized power in France, establishing the Consulate and marking the beginning of his ascent to imperial status. The Napoleonic France map, initially encompassing the territories of the French Republic, soon began to expand, reflecting Napoleon’s relentless ambition to forge a European empire. Through a series of military campaigns, treaties, and annexations, the map grew to encompass vast swathes of Europe, including:
- Italy: By 1805, Napoleon had conquered the Italian peninsula, establishing the Kingdom of Italy under his control. The map reflects this expansion, incorporating regions like Lombardy, Piedmont, and Naples into the French sphere of influence.
- Germany: Napoleon’s victories in the War of the Third Coalition (1805) led to the establishment of the Confederation of the Rhine, a collection of German states under French protection. The map highlights this strategic move, incorporating significant parts of Germany into the French orbit.
- Spain: The Peninsular War (1808-1814) saw Napoleon attempt to install his brother Joseph Bonaparte as King of Spain. While ultimately unsuccessful, the map reflects the French occupation of Spain, marking a period of intense conflict and resistance.
- Netherlands: The Netherlands, under the control of Napoleon’s brother Louis, was incorporated into the French Empire, further expanding its territorial reach and solidifying its control over the North Sea coast.
- Poland: Napoleon’s influence extended to Poland, where he established the Duchy of Warsaw, a semi-autonomous state under French protection. The map illustrates this strategic move, showcasing the French presence in Eastern Europe.
Beyond Territorial Gain: The Map as a Tool of Control
The Napoleonic France map, however, was more than just a representation of geographical expansion. It served as a tool to exert control over conquered territories and influence the political landscape of Europe.
- Strategic Deployment: The map allowed Napoleon to strategically deploy his armies, ensuring swift communication and efficient movement across conquered territories. This was crucial for maintaining his military dominance and suppressing any potential uprisings.
- Political Control: The map served as a visual reminder of French power, intimidating potential rivals and consolidating Napoleon’s control over annexed regions. This was achieved through the establishment of puppet states, the imposition of French law, and the suppression of local autonomy.
- Economic Exploitation: The map facilitated the exploitation of conquered territories, allowing Napoleon to extract resources and manpower to fund his ambitious projects and sustain his war machine. This included imposing taxes, controlling trade routes, and requisitioning resources for the French military.
The Seeds of Discontent: The Map’s Limitations
While the Napoleonic France map initially represented a period of French dominance, it also sowed the seeds of its own downfall. The vast expansion of the empire strained its resources and led to widespread discontent among conquered populations.
- Nationalism: The Napoleonic Wars sparked a wave of nationalism across Europe, with conquered populations resisting French rule and demanding independence. The map, in its very representation of French control, became a symbol of oppression and fueled resistance movements.
- Economic Strain: The constant warfare and the need to maintain a large army placed immense pressure on French finances. The map, in its depiction of the vast empire, reflected the economic burden of maintaining such a vast and complex system.
- Military Overreach: Napoleon’s relentless pursuit of territorial expansion led to military overreach, forcing him to fight on multiple fronts and ultimately leading to his downfall. The map, in its depiction of the sprawling empire, became a symbol of Napoleon’s ambition and its eventual limitations.
The Legacy of the Napoleonic France Map
The Napoleonic France map, while a testament to Napoleon’s ambition and military prowess, ultimately became a symbol of his own undoing. The vast expansion of the empire fueled resistance, strained resources, and ultimately contributed to Napoleon’s downfall. Yet, the map continues to hold significant historical value, offering insights into the complexities of the Napoleonic era and its lasting impact on Europe.
- A Catalyst for Change: The Napoleonic Wars, reflected in the map’s constant evolution, served as a catalyst for political and social change in Europe. The map highlights the rise of nationalism, the spread of liberal ideas, and the emergence of new political structures.
- A Symbol of Ambition: The map serves as a reminder of Napoleon’s ambition, his desire to reshape Europe and create a French-dominated empire. It also illustrates the inherent limitations of such ambitions, highlighting the dangers of military overreach and the importance of maintaining internal stability.
- A Tool for Historical Analysis: The Napoleonic France map remains a valuable tool for historians, offering insights into the strategic decisions, political machinations, and societal upheavals that defined the era. It allows for a deeper understanding of the Napoleonic Wars, their impact on Europe, and the lasting legacy of Napoleon’s reign.
FAQs
Q: What was the largest extent of the Napoleonic France map?
A: The largest extent of the Napoleonic France map was reached around 1810-1812, encompassing most of Western and Central Europe, including France, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, parts of Germany, and the Duchy of Warsaw.
Q: How did the Napoleonic France map change over time?
A: The map constantly evolved through a series of conquests, treaties, and annexations. It grew rapidly during the early years of Napoleon’s reign, reaching its peak in 1810-1812. However, as Napoleon faced resistance and his military fortunes declined, the map began to shrink, culminating in its final reduction after the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
Q: What were the main factors that led to the decline of the Napoleonic France map?
A: The decline of the Napoleonic France map was attributed to several factors, including:
- Nationalism: Resistance from conquered populations fueled by nationalist sentiments.
- Economic Strain: The vast empire’s upkeep placed immense pressure on French finances.
- Military Overreach: Napoleon’s relentless pursuit of expansion led to military overreach and ultimately his downfall.
Q: What is the significance of the Napoleonic France map for understanding the Napoleonic era?
A: The Napoleonic France map offers a crucial window into the strategic decisions, political machinations, and societal upheavals that defined the Napoleonic era. It allows for a deeper understanding of Napoleon’s ambitions, the impact of his conquests, and the rise of nationalism and liberal ideas across Europe.
Tips
- Use the map as a visual aid: The Napoleonic France map is a powerful tool for understanding the spatial dynamics of the era. Use it to visualize the extent of Napoleon’s conquests, the strategic importance of key regions, and the movement of armies.
- Connect the map to historical events: Link the map to specific historical events, treaties, and campaigns to understand how territorial changes impacted the course of the Napoleonic Wars.
- Explore the map’s limitations: Recognize that the map is a representation of power, not a neutral depiction of reality. Consider the perspectives of conquered populations and the limitations of Napoleon’s ambitions.
- Compare the map to other historical maps: Compare the Napoleonic France map to maps of pre-Napoleonic Europe and post-Napoleonic Europe to understand the long-term impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the political landscape.
Conclusion
The Napoleonic France map, a testament to the ambition and military prowess of Napoleon Bonaparte, is a powerful visual representation of a pivotal period in European history. It captures the rise and fall of an empire, the complexities of war and conquest, and the enduring impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the political landscape of Europe. Studying the map, in its dynamic evolution, provides a unique lens through which to understand the strategic decisions, political machinations, and societal upheavals that shaped this turbulent era.

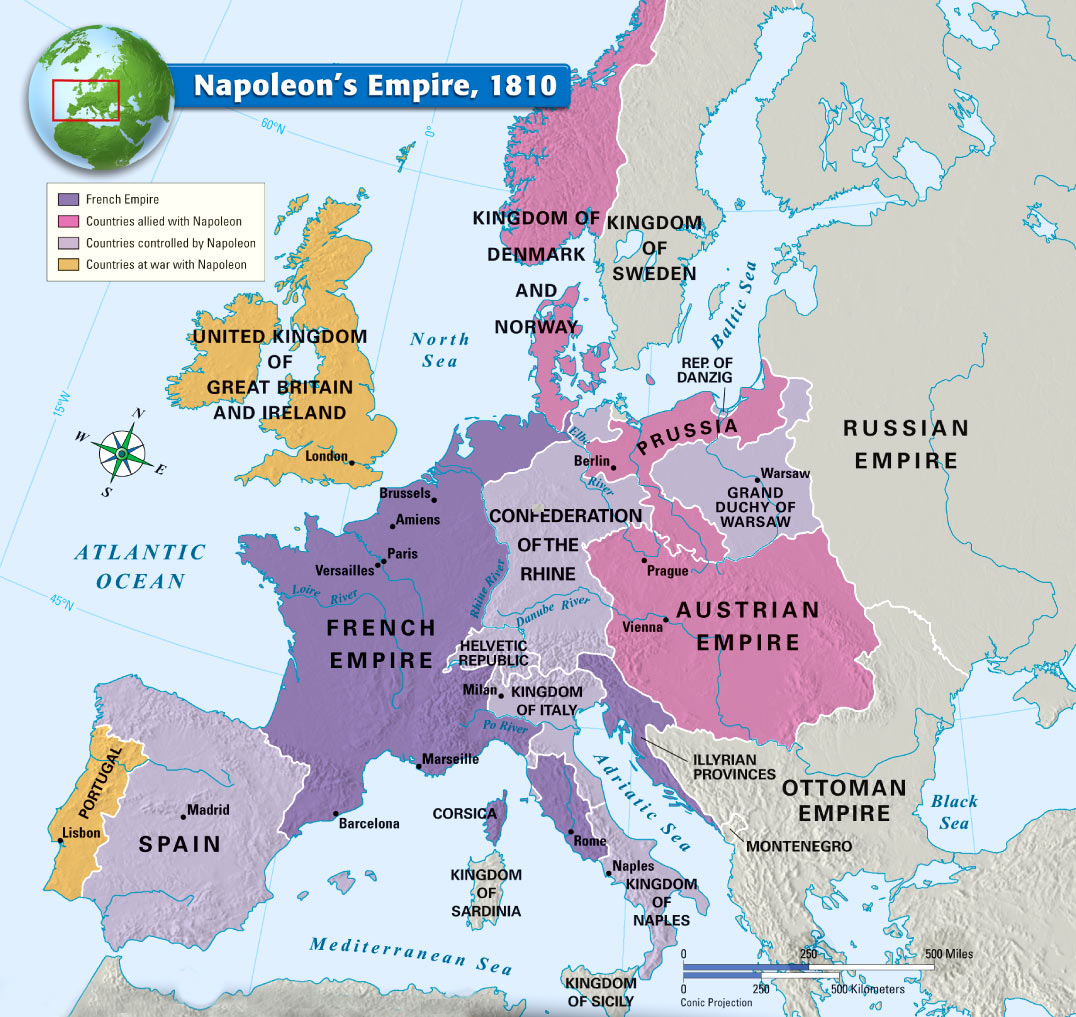



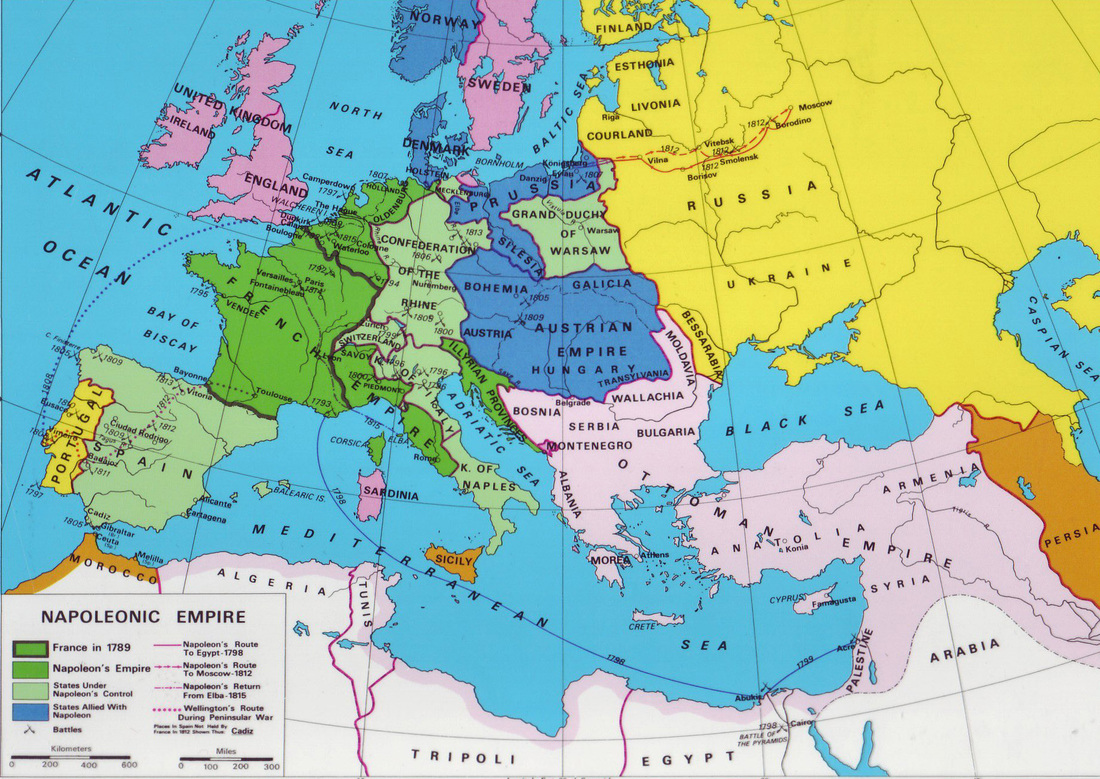


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Power: A Deep Dive into the Napoleonic France Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!