The Significance of Biogas: A Sustainable Energy Source
Related Articles: The Significance of Biogas: A Sustainable Energy Source
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Biogas: A Sustainable Energy Source. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Biogas: A Sustainable Energy Source
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1364560351-748f18a4056249faaff3c6e6810936d3.jpg)
Biogas, a renewable energy source derived from the breakdown of organic matter, has emerged as a crucial solution to global energy demands and environmental concerns. This article delves into the complexities of biogas production, its multifaceted applications, and its profound impact on various sectors.
Biogas: From Waste to Energy
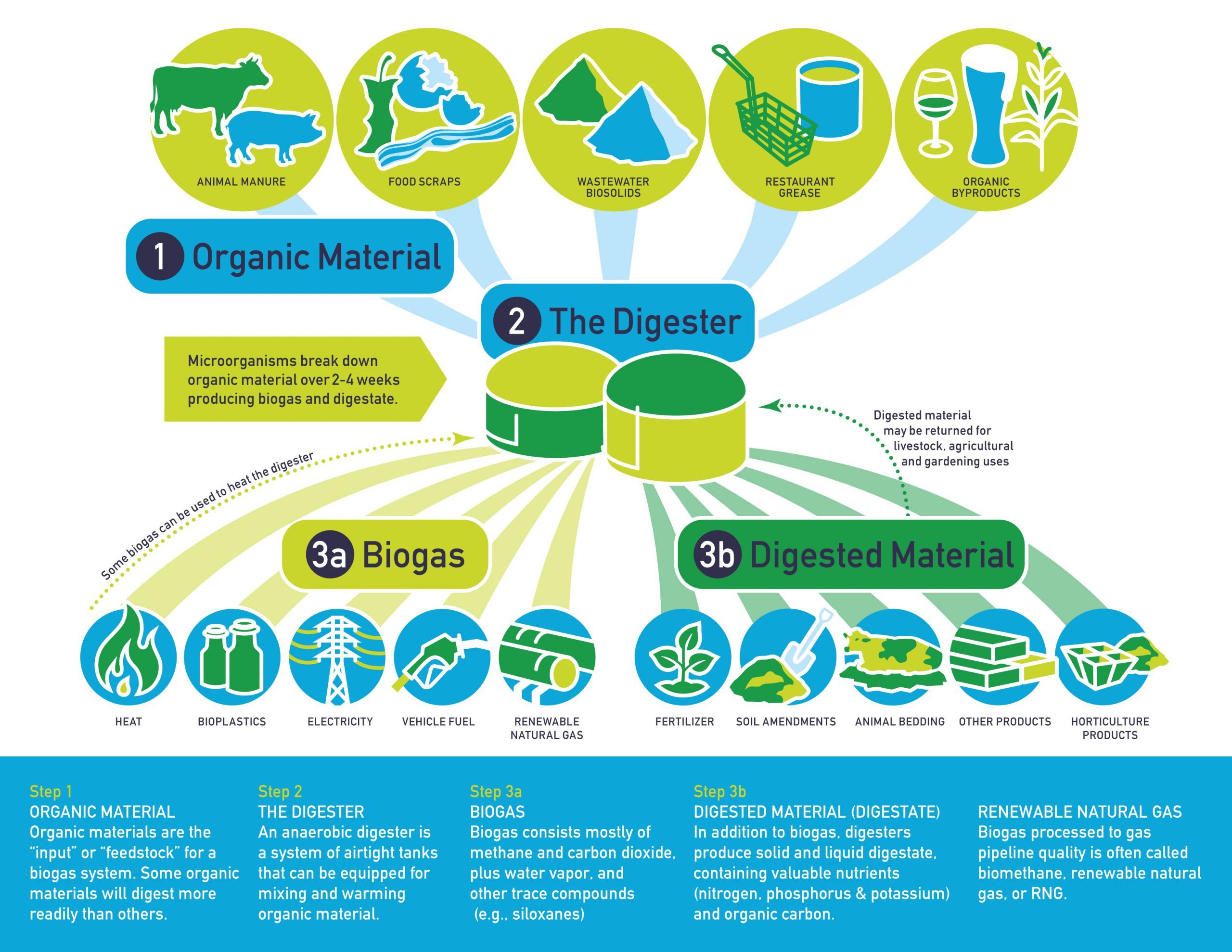
Biogas is a combustible gas primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), along with trace amounts of other gases. It is generated through anaerobic digestion, a biological process where microorganisms break down organic materials in the absence of oxygen. This process occurs naturally in landfills, sewage treatment plants, and animal manure, but can also be harnessed through controlled digestion in specialized biogas digesters.
The Biogas Production Process
The production of biogas involves several stages:
-
Pre-treatment: Organic feedstock, such as agricultural waste, food waste, or sewage sludge, undergoes pre-treatment to enhance its digestibility. This may involve size reduction, mixing, and separation of impurities.
-
Anaerobic Digestion: The pre-treated material is then introduced into a sealed digester, where anaerobic bacteria thrive in an oxygen-free environment. These bacteria break down the organic matter, producing biogas as a byproduct.
-
Gas Collection and Storage: The biogas produced is collected and stored in a holding tank. This gas can be used directly as fuel or further processed to remove impurities and increase its methane content.
-
Digestate Management: The remaining material, known as digestate, is rich in nutrients and can be used as a valuable fertilizer for agricultural purposes.
Applications of Biogas
Biogas has a wide range of applications, making it a versatile energy source:
-
Electricity Generation: Biogas can be combusted to generate electricity in power plants. This is particularly beneficial in rural areas where access to grid electricity is limited.
-
Heat Production: Biogas can be used directly as fuel for heating homes, businesses, and industrial processes.
-
Transportation Fuel: Biogas can be upgraded to biomethane, which can be used as a substitute for natural gas in vehicles.
-
Agricultural Applications: Biogas can be used to power agricultural equipment, such as tractors and irrigation systems.
-
Waste Management: Biogas production helps reduce the volume of organic waste in landfills, minimizing environmental impacts.
Environmental Benefits of Biogas
Biogas plays a vital role in mitigating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability:
-
Greenhouse Gas Reduction: By utilizing organic waste for energy production, biogas reduces the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere.
-
Renewable Energy Source: Biogas is a renewable energy source, meaning it is replenished naturally and does not contribute to finite fossil fuel reserves.
-
Waste Reduction and Recycling: Biogas production helps divert organic waste from landfills, reducing the need for landfilling and promoting resource recovery.
-
Improved Air Quality: By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, biogas contributes to cleaner air and improved public health.
Economic Benefits of Biogas
The use of biogas offers significant economic advantages:
-
Reduced Energy Costs: By generating electricity or heat from biogas, businesses and households can lower their energy bills.
-
New Economic Opportunities: The development of biogas infrastructure creates new job opportunities in the energy and agricultural sectors.
-
Increased Farm Income: Farmers can generate revenue by selling biogas or using it to power their operations, improving their profitability.
Challenges and Future Directions
While biogas offers a promising solution for sustainable energy and waste management, several challenges remain:
-
Feedstock Availability: Ensuring a consistent supply of organic feedstock is crucial for large-scale biogas production.
-
Technological Advancements: Continued research and development are needed to improve biogas digester efficiency and reduce production costs.
-
Policy Support: Government policies that incentivize biogas production and deployment are essential for driving its widespread adoption.
-
Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the benefits of biogas is crucial for its acceptance and integration into society.
FAQs about Biogas
Q: What are the different types of biogas digesters?
A: There are various types of biogas digesters, including batch digesters, continuous digesters, and plug flow digesters. Each type has specific advantages and disadvantages depending on the feedstock, scale of operation, and desired output.
Q: What are the safety considerations for using biogas?
A: Biogas is flammable and must be handled with caution. Proper ventilation, leak detection systems, and safety training are essential for safe biogas operation.
Q: What is the difference between biogas and biomethane?
A: Biogas is a raw gas mixture containing methane and other gases. Biomethane is a purified form of biogas with a high methane content, suitable for use as a transportation fuel.
Q: How can I get involved in biogas production?
A: Individuals, communities, and businesses can participate in biogas production by supporting local biogas projects, using biogas-derived products, and advocating for policies that promote biogas development.
Tips for Utilizing Biogas
-
Optimize Feedstock Selection: Choose feedstock that is readily available, cost-effective, and easily digestible.
-
Proper Digester Design: Select a digester design that is suitable for the specific feedstock and desired output.
-
Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance and cleaning of the digester to ensure optimal performance.
-
Gas Quality Control: Monitor the quality of biogas produced and upgrade it to biomethane if necessary.
-
Utilize Digestate: Use the digestate as a valuable fertilizer to enhance soil fertility.
Conclusion
Biogas, a sustainable and versatile energy source, holds immense potential to address global energy needs and environmental challenges. By harnessing the power of organic waste, biogas offers a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future. Through continued innovation, policy support, and public awareness, biogas can become a cornerstone of a cleaner and more energy-secure world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Biogas: A Sustainable Energy Source. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!