The Topography of France: A Detailed Exploration Through Maps
Related Articles: The Topography of France: A Detailed Exploration Through Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Topography of France: A Detailed Exploration Through Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Topography of France: A Detailed Exploration Through Maps
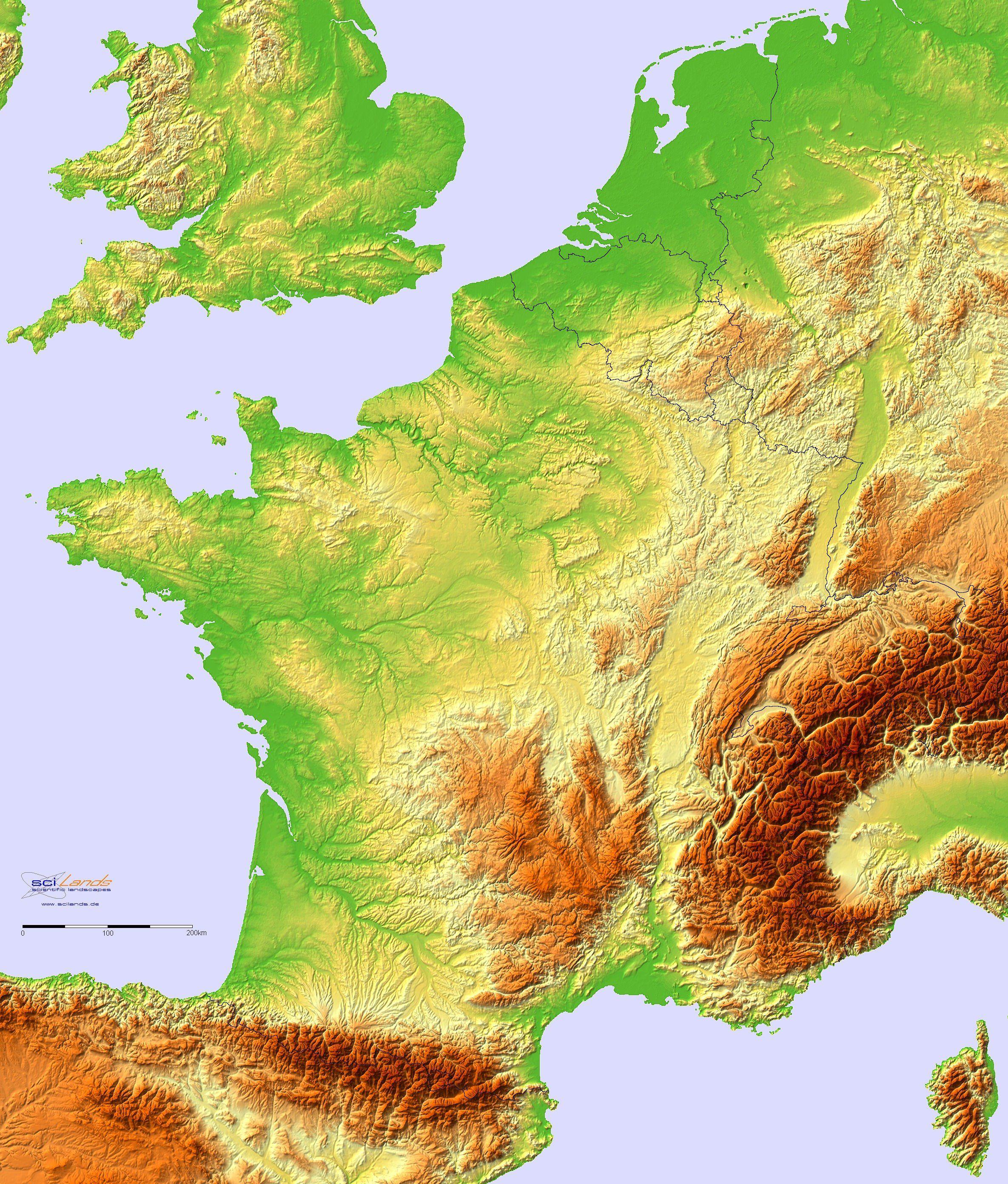
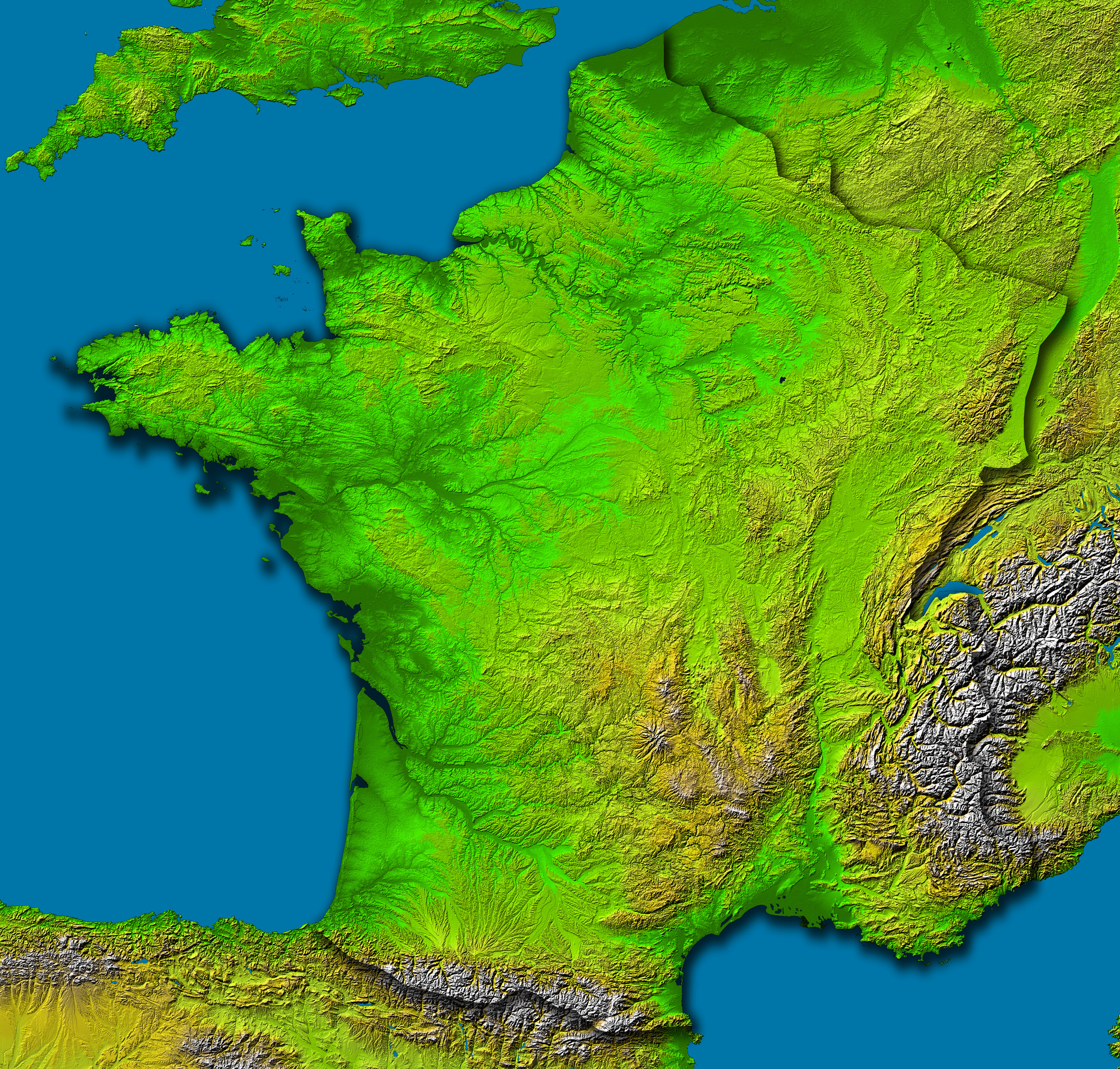
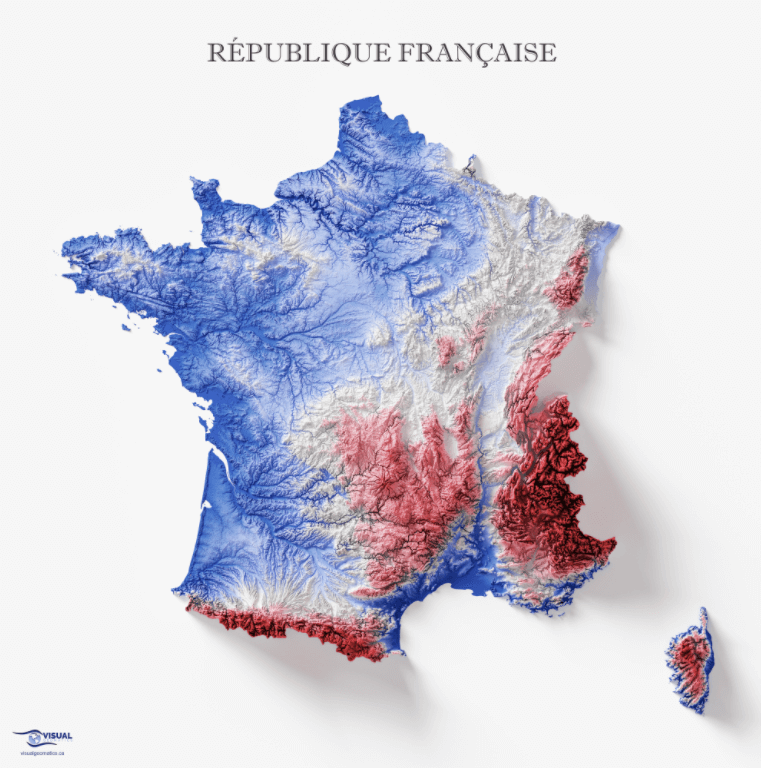
France, a nation celebrated for its diverse landscapes and cultural richness, boasts a topography as captivating as its history. Understanding the intricate interplay of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique character and the many activities it offers. Topographic maps, with their detailed representations of elevation and landforms, serve as invaluable tools for navigating, exploring, and comprehending the physical geography of France.
Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Topographic Maps
Topographic maps, unlike traditional road maps, go beyond mere location markers. They depict the Earth’s surface in three dimensions, revealing the subtle rises and falls of the terrain. Key elements of these maps include:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a visual representation of the land’s contours. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines signify gentle slopes or flat areas.
- Elevation: Numbers along contour lines or in specific locations indicate the height above sea level, providing a quantitative measure of elevation.
- Landforms: Topographic maps display various landforms like mountains, valleys, plateaus, and rivers, highlighting the geographic features that define a region.
- Symbols: A range of symbols represent natural and human-made features such as forests, lakes, roads, and buildings, enriching the map’s information content.
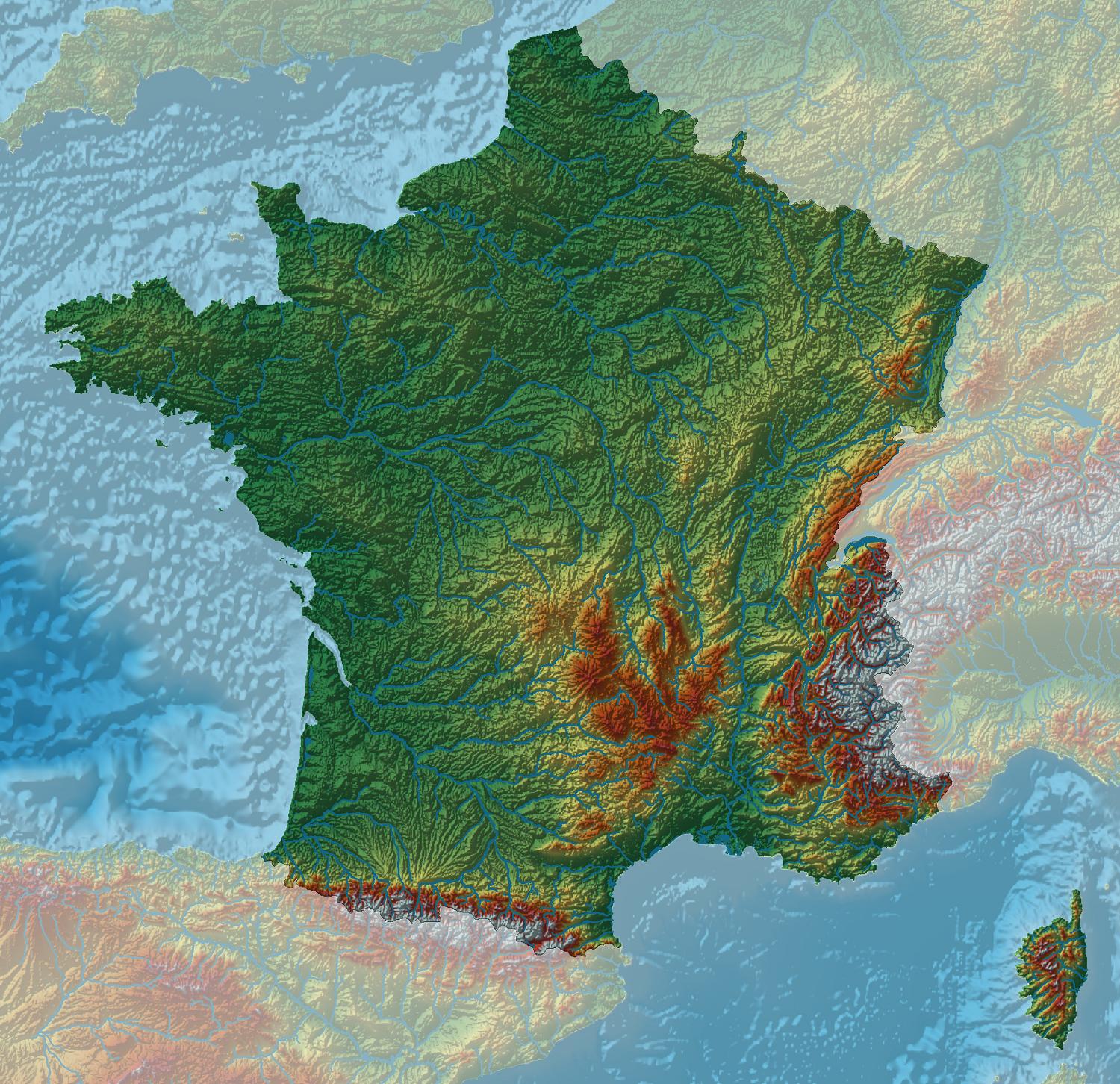
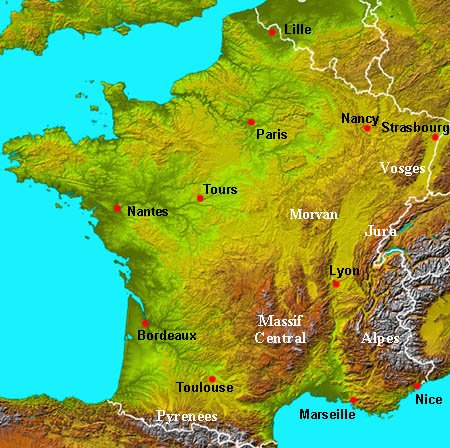
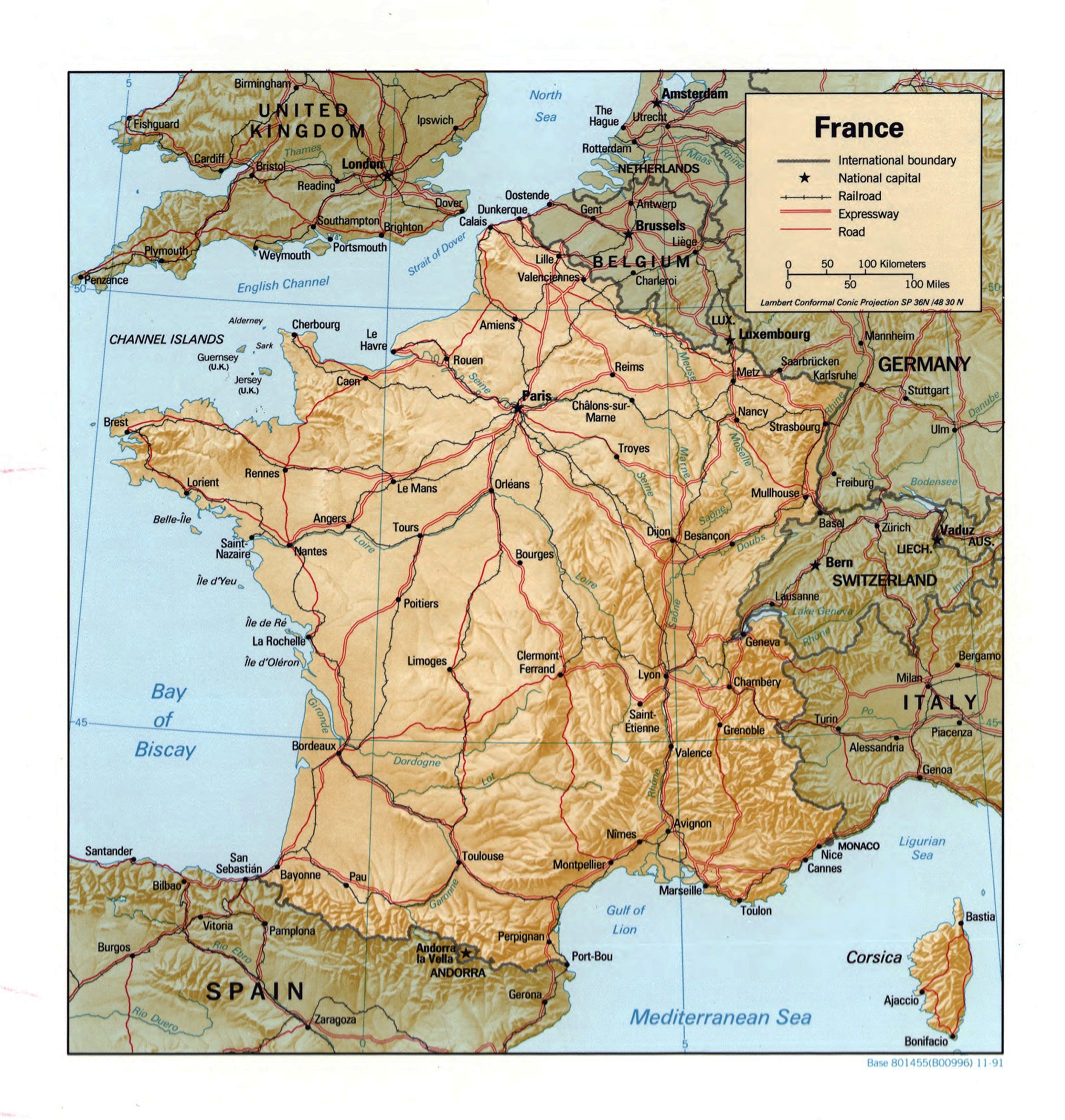
A Journey Through France’s Diverse Topography
The topographic map of France reveals a tapestry of contrasting landscapes, each with its own unique character and allure:
1. The Majestic Alps: France’s southeastern border is dominated by the towering Alps, a formidable mountain range that shapes the country’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural identity. The map vividly depicts the soaring peaks, deep valleys, and glacial lakes that characterize this region, making it a paradise for mountaineering, skiing, and hiking.
2. The rolling Massif Central: Occupying the heart of France, the Massif Central is a vast plateau punctuated by volcanic peaks, deep canyons, and verdant valleys. The map showcases the region’s diverse terrain, ranging from rugged mountains to fertile plains, fostering a rich agricultural tradition.
3. The fertile plains: North of the Massif Central lies a vast expanse of fertile plains, known as the Paris Basin. This region is characterized by gently rolling hills, fertile soil, and a network of rivers, making it a major agricultural hub and home to some of France’s most important cities.
4. The picturesque coastline: France’s extensive coastline, stretching from the rugged cliffs of Brittany to the sandy beaches of the Mediterranean, is a major draw for tourists. The map reveals the intricate details of the coastline, including bays, inlets, and islands, providing a visual representation of France’s maritime heritage.
5. The Vineyards and Wine Regions: France is renowned for its wine production, and the topographic map reveals the unique terroir of its various wine regions. The map highlights the rolling hills, fertile valleys, and temperate climate that contribute to the quality of French wines.
Beyond Navigation: The Importance of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are not merely navigational tools; they serve as essential resources for a wide range of disciplines and activities:
- Environmental Studies: Topographic maps provide crucial information for understanding land use, water resources, and environmental hazards. They are vital for environmental planning, conservation efforts, and disaster preparedness.
- Agriculture and Forestry: The maps reveal the terrain’s suitability for different agricultural practices and forestry activities, informing land management decisions and promoting sustainable resource utilization.
- Infrastructure Development: Topographic maps are essential for planning and constructing roads, railways, dams, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring efficient design and minimizing environmental impact.
- Military Operations: Topographic maps are indispensable for military planning and execution, providing critical information about terrain, elevation, and potential obstacles.
- Tourism and Recreation: Topographic maps empower hikers, cyclists, and outdoor enthusiasts to plan their adventures, navigate challenging terrain, and discover hidden gems.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Topographic Maps
1. What are the different types of topographic maps available?
Topographic maps come in various scales, ranging from large-scale maps that depict detailed information about small areas to small-scale maps that cover vast regions. The choice of scale depends on the intended use and the level of detail required.
2. How do I read a topographic map?
Reading a topographic map involves understanding the symbols, contour lines, and elevation information. Learning to interpret these elements allows for a comprehensive understanding of the terrain’s characteristics.
3. Where can I find topographic maps of France?
Topographic maps of France are available from various sources, including government agencies, online map services, and specialized map retailers.
4. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created using a combination of surveying techniques, aerial photography, and satellite imagery. These methods allow for accurate representation of the Earth’s surface.
5. What are the limitations of topographic maps?
Topographic maps are static representations of the terrain, and they may not reflect real-time changes in the environment. They also have limited accuracy in areas with dense vegetation or steep slopes.
Tips for Effective Use of Topographic Maps
- Study the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols, abbreviations, and scale used on the map.
- Use a compass: A compass is essential for navigating using topographic maps, especially in areas with limited landmarks.
- Plan your route carefully: Consider the elevation changes, terrain obstacles, and potential hazards before embarking on any journey.
- Carry a map and compass: Always have a backup map and compass in case of emergencies.
- Be aware of weather conditions: Topographic maps do not provide information about weather conditions, so check forecasts before setting out.
Conclusion: A Window into the Heart of France
Topographic maps are not just tools for navigation; they are windows into the heart of France, revealing the intricate interplay of its physical geography, cultural heritage, and human activities. Understanding the topography of France allows for a deeper appreciation of its landscapes, its history, and the unique challenges and opportunities it presents. By studying topographic maps, we gain a richer perspective on this fascinating country and its place in the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Topography of France: A Detailed Exploration Through Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!