The Vital Network: Understanding Gas Distribution Systems
Related Articles: The Vital Network: Understanding Gas Distribution Systems
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Vital Network: Understanding Gas Distribution Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Vital Network: Understanding Gas Distribution Systems
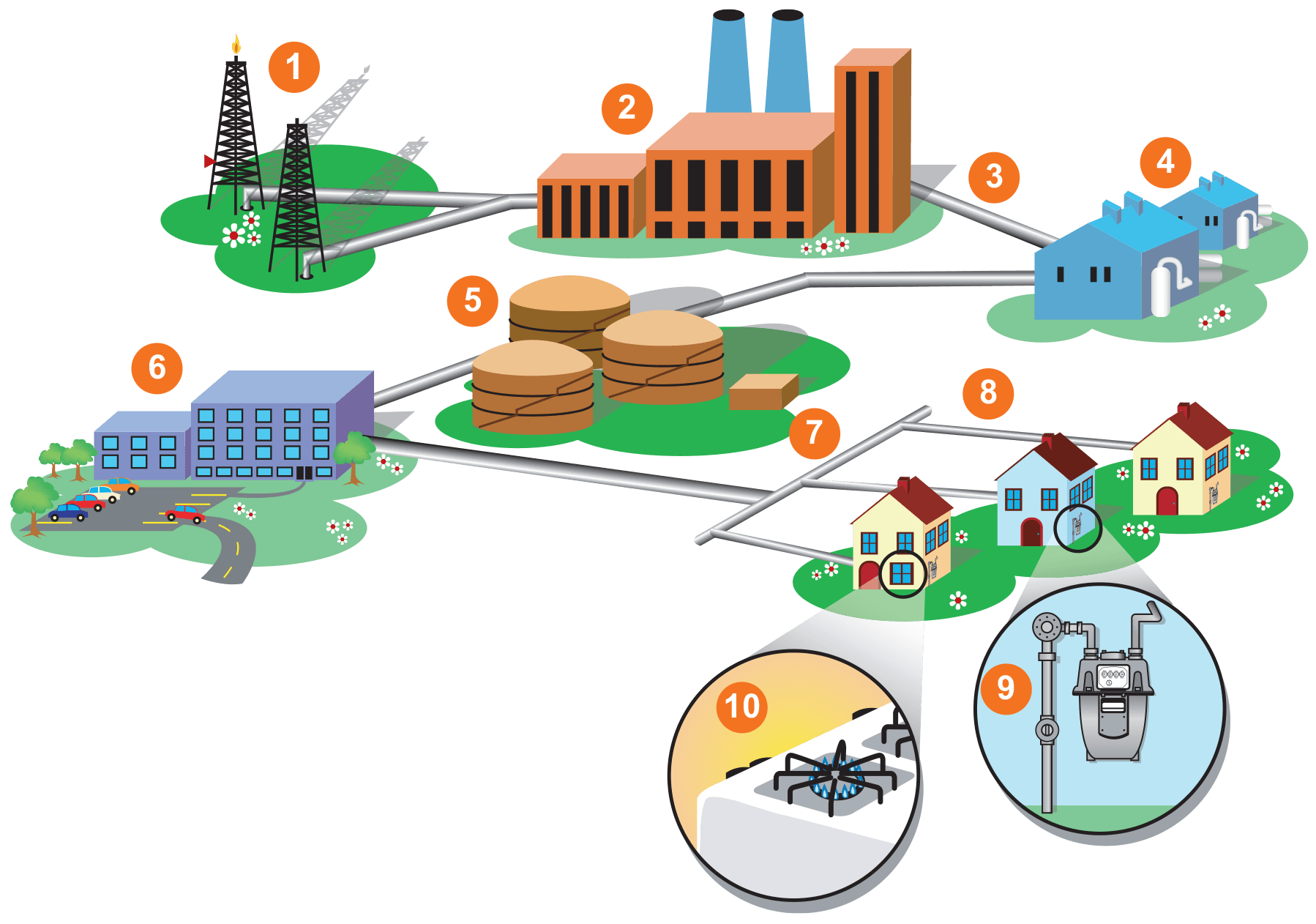
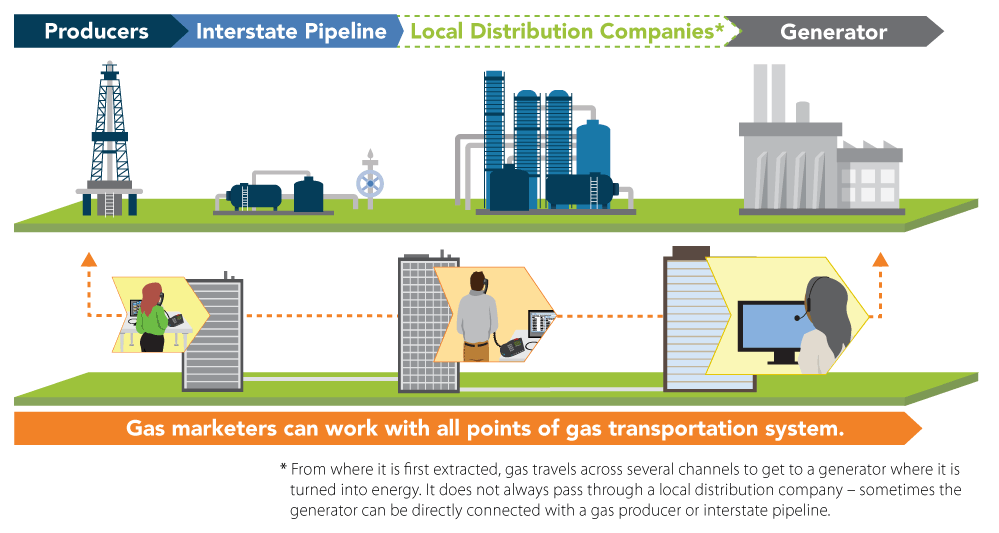
Natural gas, a clean and efficient energy source, plays a crucial role in modern society. Its widespread use for heating, cooking, and industrial processes necessitates a robust and reliable distribution network. This network, often referred to as a "gas distribution system," comprises a complex web of pipelines, regulators, and other equipment that safely and efficiently transports natural gas from its source to its final destination.
The Anatomy of a Gas Distribution System
The gas distribution system is a multi-layered network, typically divided into three main segments:
-
Transmission Pipelines: These large-diameter pipelines, often operating at high pressure, carry natural gas from production fields or processing facilities to major distribution centers. They traverse vast distances, crossing diverse terrains and often employing sophisticated technologies for safety and efficiency.
-
Distribution Pipelines: These smaller pipelines, branching out from transmission pipelines, deliver natural gas to local communities and industrial areas. They are typically constructed of steel or plastic, with varying diameters depending on the volume of gas being transported.
-
Service Lines: These are the final connections, extending from the distribution pipelines to individual homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. Service lines are typically made of smaller-diameter materials like copper or plastic, connecting directly to gas meters and appliances.
The Importance of Mapping Gas Lines
Accurate mapping of gas lines is crucial for several reasons:
-
Safety: Precise maps provide essential information for emergency responders, enabling them to quickly and efficiently identify the location of gas lines during accidents, leaks, or other incidents. This minimizes the risk of accidental damage to pipelines, preventing potential fires, explosions, and environmental harm.
-
Maintenance and Repairs: Maps facilitate the planning and execution of routine maintenance and repairs. By understanding the exact location and configuration of pipelines, crews can efficiently access and work on them, minimizing disruption to service and ensuring timely completion of tasks.
-
Expansion and Development: Accurate gas line maps are essential for planning future expansion of the distribution network. They provide valuable data for determining the optimal location of new pipelines, connections, and facilities, ensuring efficient and cost-effective growth of the system.
-
Environmental Protection: Maps contribute to environmental protection by allowing for the identification of potential leak points and other environmental risks. This enables proactive measures to be taken, preventing leaks and minimizing the release of greenhouse gases.
Methods for Mapping Gas Lines
Several methods are employed for mapping gas lines, each offering unique advantages:
-
Traditional Surveys: This method involves physically inspecting the ground, using tools like ground-penetrating radar or electromagnetic induction to locate buried pipelines. While effective, traditional surveys can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
-
Aerial Photography and LiDAR: These techniques utilize aircraft or drones equipped with high-resolution cameras or LiDAR sensors to capture detailed images of the terrain. By analyzing these images, it is possible to identify the location of gas lines and other infrastructure.
-
GIS (Geographic Information Systems): GIS software integrates various data sources, including aerial photographs, GPS coordinates, and historical records, to create comprehensive maps of the gas distribution system. GIS enables efficient analysis, visualization, and management of the network.
FAQs Regarding Gas Line Mapping
-
Q: How often are gas lines mapped?
-
A: The frequency of mapping depends on various factors, including the age and condition of the pipelines, the rate of development in the area, and regulatory requirements. In general, maps are updated regularly, with more frequent updates for areas experiencing significant growth or changes.
-
Q: Who is responsible for maintaining gas line maps?
-
A: Gas line maps are typically maintained by the gas distribution company responsible for operating the network. However, in some cases, local governments or regulatory agencies may also have access to or contribute to these maps.
-
Q: Are gas line maps publicly available?
-
A: The availability of gas line maps to the public varies depending on local regulations and policies. Some areas may require gas distribution companies to share map information with emergency responders and other authorized parties, while others may restrict access to protect the security of the network.
Tips for Ensuring Accurate and Up-to-Date Gas Line Maps
-
Regular Inspections: Conducting regular inspections of the gas distribution system is essential for identifying any changes or updates that need to be reflected in the maps.
-
Data Integration: Combining data from various sources, including aerial photography, GPS coordinates, and historical records, ensures a comprehensive and accurate representation of the network.
-
Collaboration with Stakeholders: Working with local governments, emergency responders, and other stakeholders helps to ensure that maps are accessible and used effectively by all relevant parties.
-
Technology Adoption: Utilizing advanced technologies like GIS and LiDAR enables efficient and accurate mapping, facilitating the creation and maintenance of up-to-date and comprehensive maps.
Conclusion
Gas line maps are an indispensable tool for ensuring the safe, reliable, and efficient operation of gas distribution systems. They provide critical information for emergency response, maintenance, expansion, and environmental protection. By employing accurate and up-to-date mapping techniques, gas distribution companies can effectively manage their networks, ensuring the continuous flow of natural gas to meet the needs of communities and industries.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Vital Network: Understanding Gas Distribution Systems. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
