Understanding IMAP: A Deep Dive into Gmail’s Email Access Protocol
Related Articles: Understanding IMAP: A Deep Dive into Gmail’s Email Access Protocol
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding IMAP: A Deep Dive into Gmail’s Email Access Protocol. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding IMAP: A Deep Dive into Gmail’s Email Access Protocol

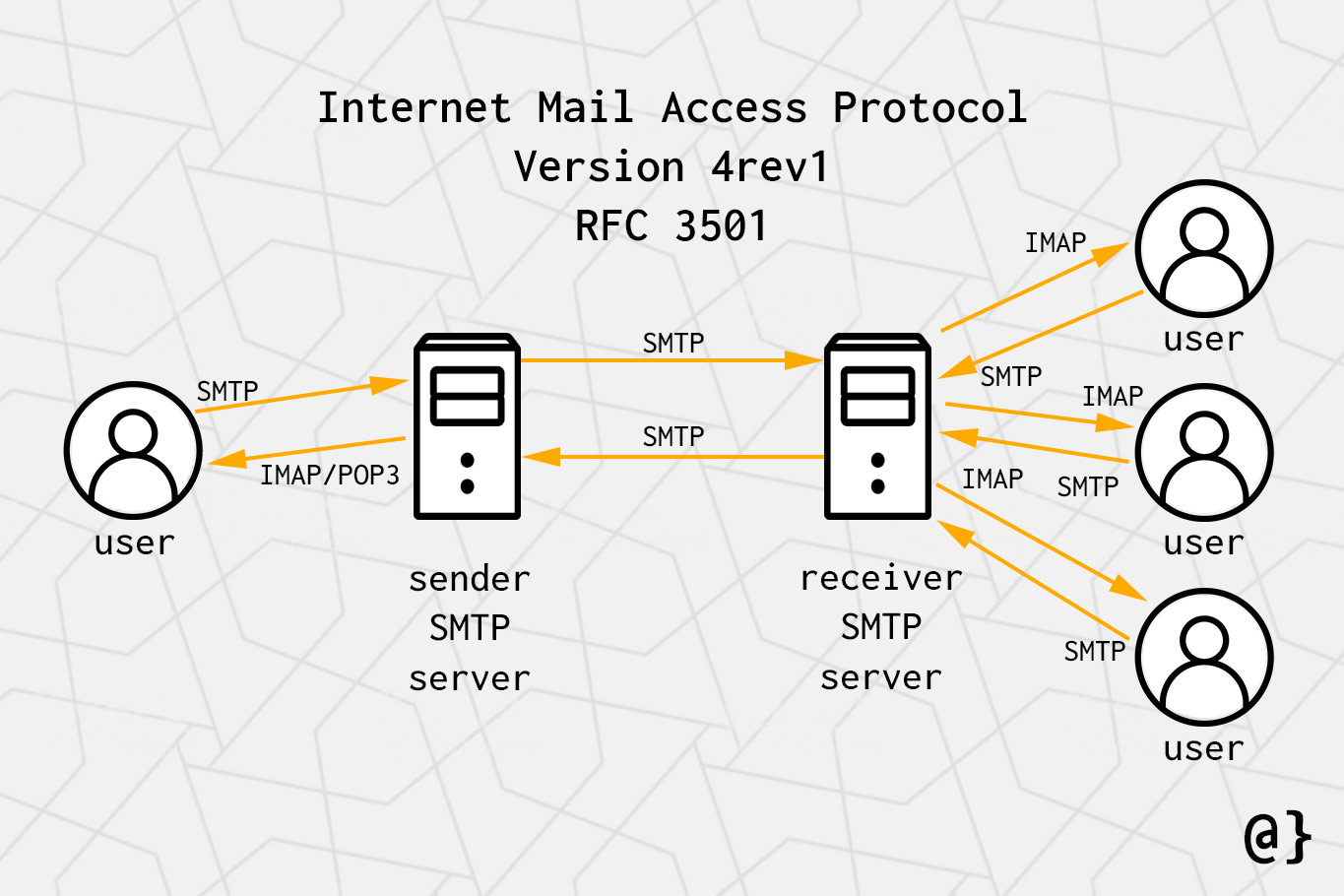
In the realm of email, the ability to manage and access messages from various devices seamlessly is paramount. This is where the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) emerges as a powerful tool, especially within the context of Gmail. IMAP, unlike its counterpart POP3, facilitates a dynamic and synchronized experience, allowing users to interact with their emails from multiple locations without compromising data integrity.
The Essence of IMAP
IMAP operates as a protocol, establishing a connection between an email client (such as Thunderbird, Outlook, or even the Gmail web interface) and a mail server. This connection enables users to access, manage, and manipulate their emails directly on the server, rather than downloading them entirely to their local device.
Key Features of IMAP in Gmail
-
Synchronization: IMAP’s core strength lies in its ability to synchronize email data across multiple devices. This means that any changes made to an email (such as marking it as read, deleting it, or moving it to a different folder) are reflected instantly on all connected devices. This eliminates the need for manual syncing and ensures data consistency.
-
Offline Access: While IMAP primarily focuses on server-side email management, it also facilitates offline access. When an email client is configured to utilize IMAP, it downloads a copy of the email headers and a limited amount of content locally. This allows users to view a preview of their emails even when they are not connected to the internet.
-
Flexible Folder Management: IMAP grants users the flexibility to create and manage folders directly on the server. This allows for a highly organized email system, with emails categorized and sorted according to individual preferences.
-
Multiple Client Support: IMAP is a widely adopted protocol, supported by numerous email clients, including popular options like Microsoft Outlook, Apple Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird. This ensures compatibility and allows users to choose the client that best suits their needs.
The Benefits of Utilizing IMAP with Gmail
-
Enhanced Collaboration: IMAP’s synchronization capabilities are particularly beneficial for collaborative environments. When multiple team members access the same shared email account, IMAP ensures that all actions are reflected across devices, maintaining a unified view of the inbox.
-
Centralized Data Management: By storing emails on the server, IMAP centralizes email management. This eliminates the need for multiple copies on different devices and reduces the risk of data loss.
-
Improved Security: IMAP offers a layer of security by allowing users to access and manage their emails directly on the server, without needing to download them to potentially vulnerable local devices.
-
Increased Efficiency: IMAP’s synchronization and offline access features streamline email management, allowing users to work efficiently from any location and device.
A Comparative Analysis: IMAP vs. POP3
While IMAP has become the preferred protocol for modern email management, it’s essential to understand its key differences from the older POP3 protocol.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3):
- Downloads emails to the local device, deleting them from the server by default.
- Offers limited synchronization capabilities.
- Does not support offline access (except for downloaded emails).
- Less secure, as emails are stored locally and potentially vulnerable.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol):
- Keeps emails on the server, allowing access from multiple devices.
- Offers robust synchronization capabilities.
- Supports offline access through header and partial content downloads.
- More secure, as emails are primarily stored on the server.
FAQs: IMAP and Gmail
Q1: How do I configure my email client to use IMAP with Gmail?
A1: The process varies slightly depending on the email client. However, the general steps involve:
- Opening the email client settings: Locate the account settings or configuration options within your chosen email client.
- Adding a new account: Select the option to add a new email account.
- Choosing IMAP: Select IMAP as the protocol for incoming mail.
- Entering Gmail details: Provide your Gmail address, password, and the server details (usually imap.gmail.com).
- Configuring outgoing mail: Set the outgoing mail server to smtp.gmail.com and ensure the correct port number (usually 587 or 465) is specified.
Q2: Can I use IMAP with multiple Gmail accounts simultaneously?
A2: Yes, you can configure your email client to use IMAP with multiple Gmail accounts concurrently. This allows you to manage all your accounts from a single interface.
Q3: Are there any limitations or drawbacks to using IMAP with Gmail?
A3: While IMAP offers numerous benefits, it’s important to note that:
- Larger storage requirements: IMAP requires more storage space on the server, as emails are not downloaded to the local device.
- Potential for slower performance: Depending on internet connection speed and server load, IMAP may result in slightly slower email access compared to POP3.
- Security concerns: While IMAP is generally considered secure, it’s crucial to use strong passwords and avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN.
Tips for Optimizing IMAP with Gmail
- Create folders for efficient organization: Leverage IMAP’s folder management capabilities to categorize emails based on topics, projects, or senders.
- Utilize filters and labels: Create filters to automatically move or label incoming emails, streamlining your inbox and reducing clutter.
- Enable IMAP access for mobile devices: Configure IMAP on your mobile phone or tablet to access your Gmail account seamlessly.
- Consider using a dedicated email client: Explore email clients like Thunderbird or Outlook, which offer advanced IMAP features and customization options.
- Regularly check for updates: Ensure that your email client and operating system are up-to-date to benefit from the latest security patches and performance improvements.
Conclusion
IMAP, in conjunction with Gmail, empowers users with a robust and flexible email management system. Its synchronization, offline access, and folder management features contribute to a seamless and efficient email experience. While IMAP does have certain limitations, its advantages far outweigh the drawbacks, making it the preferred protocol for modern email management. By understanding IMAP’s functionalities and adopting best practices, users can leverage this protocol to maximize their email productivity and maintain a well-organized inbox.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001-gmail-access-thunderbird-1173150-80fdab9339ec4fb9a6c58965db3b8b7b.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding IMAP: A Deep Dive into Gmail’s Email Access Protocol. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
