Unlocking the Secrets of Gas Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide to Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Gas Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide to Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Gas Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide to Multi-Component Gas Analyzers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Gas Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide to Multi-Component Gas Analyzers

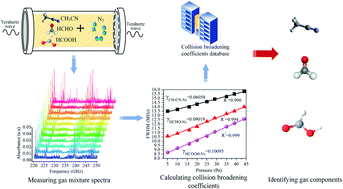
Gas mixtures are ubiquitous, playing crucial roles in numerous industrial processes, scientific research, and even our daily lives. From the precise composition of medical gases to the intricate blend of components in industrial manufacturing, understanding and controlling the composition of gas mixtures is paramount. This is where multi-component gas analyzers, often referred to as MAP gas analyzers, step in. These sophisticated instruments provide invaluable insights into the composition of gas mixtures, enabling precise control, safety optimization, and process efficiency.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
Multi-component gas analyzers, or MAP gas analyzers, are analytical instruments designed to measure the concentration of multiple gases within a sample simultaneously. They are essential tools for various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Process optimization, quality control, and emissions monitoring.
- Healthcare: Medical gas purity analysis, ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy.
- Environmental monitoring: Atmospheric analysis, pollution control, and climate research.
- Research and development: Gas mixture analysis for chemical reactions, material science, and environmental studies.
Key Components and Operational Principles of MAP Gas Analyzers
MAP gas analyzers typically employ a combination of advanced technologies to achieve accurate and reliable gas analysis. These components include:
- Sampling System: This component extracts a representative sample of the gas mixture from the process stream or environment.
-
Separation System: This system separates the individual components of the gas mixture based on their physical or chemical properties. Common separation techniques include:
- Chromatography: This technique separates components based on their affinity for a stationary phase.
- Spectroscopy: This technique utilizes the interaction of light with the gas molecules to identify and quantify different components.
-
Detection System: This component measures the concentration of each separated gas component. Various detection methods are employed, such as:
- Thermal Conductivity Detectors (TCDs): These detectors measure the change in thermal conductivity of a gas, providing a signal proportional to the concentration of the analyte.
- Flame Ionization Detectors (FIDs): These detectors measure the ionization current produced when organic compounds are burned in a hydrogen flame.
- Photoionization Detectors (PIDs): These detectors use ultraviolet (UV) light to ionize the analyte molecules, generating a signal proportional to the concentration.
- Data Processing Unit: This component processes the signals from the detection system, converting them into meaningful concentration values for each gas component.
Types of Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
MAP gas analyzers are available in a wide range of configurations, each suited for specific applications. Common types include:
- Gas Chromatography (GC) Systems: These systems employ chromatography for separating gas components, offering high resolution and sensitivity.
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometers: These systems use infrared spectroscopy to identify and quantify various gas components.
- Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometers: These systems utilize near-infrared light to analyze gas mixtures, offering rapid and non-destructive analysis.
- Mass Spectrometers (MS): These systems separate ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, providing comprehensive information about the composition of the gas mixture.
Advantages of Utilizing Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
Employing MAP gas analyzers offers several advantages, significantly impacting various industries and research fields:
- Accurate and Precise Analysis: These instruments provide highly accurate and precise measurements of gas composition, crucial for ensuring product quality, safety, and process optimization.
- Simultaneous Measurement: MAP gas analyzers can measure multiple gas components simultaneously, saving time and resources compared to individual analyzers.
- Real-time Monitoring: Some MAP gas analyzers offer real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling continuous tracking of gas composition and timely adjustments to processes.
- Versatile Applications: The versatility of MAP gas analyzers allows their application in diverse industries and research fields, from manufacturing and healthcare to environmental monitoring and scientific research.
- Improved Process Control: Precise gas composition analysis enables better control of manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved product quality.
- Enhanced Safety: Monitoring the composition of gas mixtures in critical applications like healthcare and industrial processes ensures safety and prevents potential hazards.
- Environmental Compliance: MAP gas analyzers play a crucial role in monitoring emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
Q1: What are the typical operating conditions for MAP gas analyzers?
A: Operating conditions vary depending on the specific analyzer and application. Factors like temperature, pressure, and flow rate need to be considered. Manufacturers provide detailed specifications and operating parameters for each model.
Q2: How often should MAP gas analyzers be calibrated?
A: Calibration frequency depends on the application, the instrument’s sensitivity, and the stability of the gas mixture being analyzed. Regular calibration ensures accurate and reliable measurements.
Q3: What are the common maintenance requirements for MAP gas analyzers?
A: Regular maintenance includes cleaning, replacing filters, checking for leaks, and calibrating the instrument. Manufacturers provide specific maintenance schedules and guidelines.
Q4: What are the limitations of MAP gas analyzers?
A: Limitations include the potential for interference from other gases, the need for calibration, and the complexity of operating some models.
Q5: How do I choose the right MAP gas analyzer for my application?
A: Consider factors like the specific gases to be analyzed, required accuracy, sensitivity, operating conditions, and budget. Consulting with experts and manufacturers can help select the most suitable analyzer.
Tips for Effective Utilization of Multi-Component Gas Analyzers
- Proper Installation: Ensure the analyzer is installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions, considering environmental factors and proper ventilation.
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate the analyzer regularly using certified gas standards to maintain accuracy and reliability.
- Preventative Maintenance: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to minimize downtime and ensure optimal performance.
- Data Management: Utilize appropriate software and systems for data acquisition, analysis, and reporting.
- Training and Expertise: Ensure operators are adequately trained to operate and maintain the analyzer effectively.
Conclusion
Multi-component gas analyzers are indispensable tools for numerous industries and research fields. Their ability to provide accurate and precise measurements of gas composition is vital for process optimization, safety assurance, environmental compliance, and scientific advancement. Understanding the key components, operational principles, and application-specific considerations of MAP gas analyzers enables effective utilization and maximizes their benefits. As technology continues to evolve, MAP gas analyzers will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of gas analysis and related applications.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Gas Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide to Multi-Component Gas Analyzers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!