Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of the Eastern Seaboard: A Deep Dive into the East Coast Fault Lines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of the Eastern Seaboard: A Deep Dive into the East Coast Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of the Eastern Seaboard: A Deep Dive into the East Coast Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of the Eastern Seaboard: A Deep Dive into the East Coast Fault Lines

The eastern seaboard of the United States, often perceived as a haven of stability, is not immune to the powerful forces of plate tectonics. Beneath the bustling cities and serene landscapes lies a network of ancient fault lines, remnants of a turbulent geological past. While less active than their counterparts on the West Coast, these faults represent a potential seismic hazard, demanding careful study and preparedness.
This article delves into the intricate tapestry of East Coast fault lines, exploring their geological origins, activity levels, potential risks, and the critical role they play in shaping the region’s landscape and future.
A Journey Through Time: The Formation of East Coast Fault Lines
The story of East Coast fault lines begins millions of years ago, when the supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart. This tectonic dance, driven by the relentless forces of mantle convection, resulted in the formation of the Atlantic Ocean and the gradual separation of North America and Africa.
As these landmasses drifted apart, the crust along the eastern edge of North America experienced significant stretching and thinning. This process created numerous faults, some of which are still active today. These faults, classified as normal faults, are characterized by the hanging wall (the block above the fault plane) moving down relative to the footwall (the block below).
The most prominent fault system along the East Coast is the Coastal Plain Fault System, stretching from South Carolina to New York. This system comprises several interconnected fault zones, including the Charleston Fault, the Brevard Fault Zone, and the Eastern Piedmont Fault System.
Understanding the Fault Lines: A Closer Look at Activity and Potential Risks
While the East Coast is generally considered less seismically active than the West Coast, the presence of these ancient fault lines cannot be ignored. While most of these faults are currently dormant, some exhibit signs of recent activity, hinting at the possibility of future earthquakes.
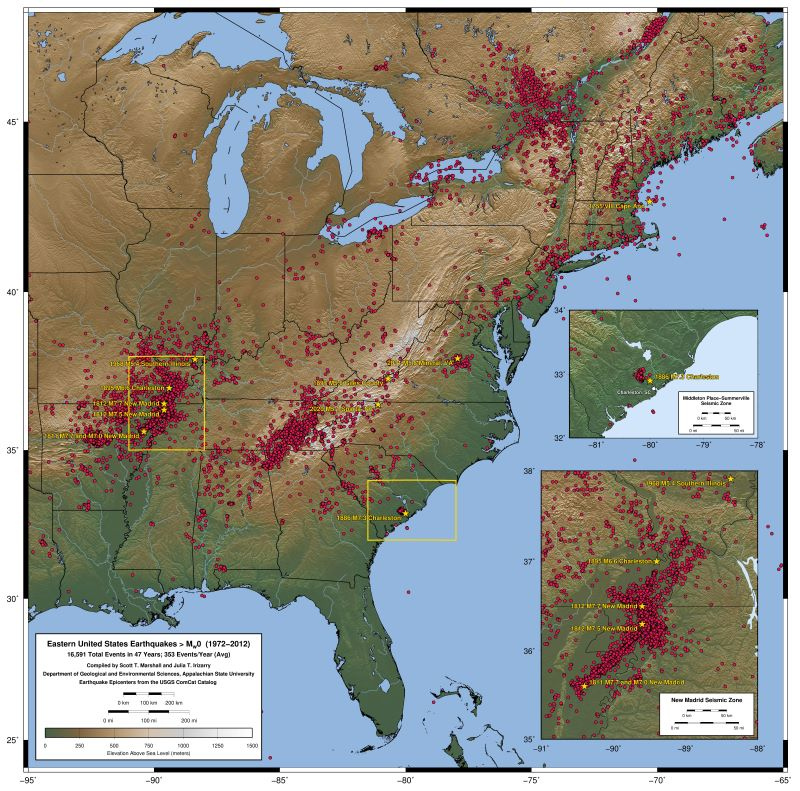
The most notable example is the Charleston Fault, responsible for the devastating 1886 Charleston earthquake, which remains the strongest recorded earthquake in the eastern United States. This earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 7.0, caused widespread damage and loss of life, highlighting the potential for significant seismic events in the region.
Another significant fault zone is the Brevard Fault Zone, running parallel to the Appalachian Mountains. While this fault is considered inactive at present, evidence suggests that it was active in the past, potentially generating earthquakes of moderate magnitude.
Mapping the Unseen: Importance of Fault Line Mapping and Research
Understanding the location and activity of these fault lines is crucial for mitigating potential seismic risks. Detailed geological mapping, combined with advanced geophysical techniques such as seismic reflection surveys, helps scientists identify and characterize these faults.
This information is then used to develop seismic hazard maps, which provide valuable insights into the likelihood and potential impacts of earthquakes in specific areas. These maps serve as essential tools for:
- Infrastructure Design and Construction: Architects and engineers use seismic hazard maps to design buildings and infrastructure capable of withstanding potential earthquakes.
- Emergency Planning: Local authorities rely on these maps to develop effective emergency response plans, ensuring swift and efficient aid in the event of an earthquake.
- Land Use Planning: Understanding seismic risk can influence land use decisions, minimizing development in areas prone to significant earthquake activity.
Beyond the Maps: The Broader Implications of East Coast Fault Lines
The presence of fault lines on the East Coast has implications beyond seismic hazards. These geological features play a significant role in shaping the region’s landscape and influencing its natural resources.
- Geological Formations: Fault lines often act as conduits for underground fluids, leading to the formation of mineral deposits and geothermal resources.
- Groundwater Resources: Fault zones can create pathways for groundwater movement, affecting the availability and quality of water resources.
- Landslide Potential: The presence of faults can increase the risk of landslides, especially in areas with steep slopes and heavy rainfall.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions about East Coast Fault Lines
Q: Are earthquakes common on the East Coast?
A: While earthquakes are less frequent on the East Coast than on the West Coast, they are not uncommon. Historical records document numerous earthquakes, including the devastating 1886 Charleston earthquake.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur on the East Coast?
A: The frequency of earthquakes varies depending on the location and specific fault zone. However, smaller earthquakes are relatively common, while larger events are less frequent.
Q: Are East Coast earthquakes as powerful as West Coast earthquakes?
A: While East Coast earthquakes generally have lower magnitudes than those on the West Coast, they can still cause significant damage due to the older and more brittle nature of the eastern crust.
Q: What are the most seismically active areas on the East Coast?
A: The most seismically active areas on the East Coast include the Charleston Fault Zone, the Brevard Fault Zone, and the Eastern Piedmont Fault System.
Q: What steps are being taken to prepare for potential earthquakes on the East Coast?
A: Efforts to prepare for potential earthquakes on the East Coast include:
- Seismic hazard mapping and risk assessment
- Building codes and regulations that incorporate seismic design standards
- Public education and outreach programs to raise awareness about earthquake preparedness
- Emergency response planning and training for first responders
Tips for Staying Safe in an Earthquake
- Secure heavy objects: Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Have an emergency plan: Develop a family emergency plan, including designated meeting points and communication methods.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Learn how to drop, cover, and hold on: During an earthquake, drop to the ground, cover your head and neck, and hold on to a sturdy object.
- Stay informed: Monitor local news and weather reports for earthquake warnings and updates.
Conclusion: Embracing the Dynamic Nature of the East Coast
The East Coast fault lines, though less active than their West Coast counterparts, represent a tangible reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet. Understanding these geological features is not just about mitigating seismic risks but also about appreciating the complex and fascinating history of the Earth’s crust. By continuing to study and map these fault lines, we can gain valuable insights into the region’s geological past, present, and future, ultimately contributing to safer and more resilient communities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of the Eastern Seaboard: A Deep Dive into the East Coast Fault Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!