Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: A Deep Dive into NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission
Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: A Deep Dive into NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: A Deep Dive into NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: A Deep Dive into NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission
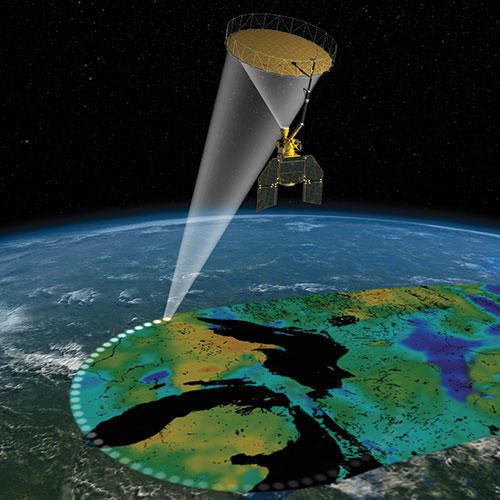
The Earth’s soil, a seemingly mundane element, holds profound influence over our planet’s climate, water cycle, and ecosystems. Understanding its moisture content, a critical variable in these processes, is paramount for predicting weather patterns, managing water resources, and ensuring food security. To unlock this knowledge, NASA launched the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission in 2015, a groundbreaking endeavor to map global soil moisture with unprecedented detail and accuracy.
A Dual-Approach to Soil Moisture Mapping:
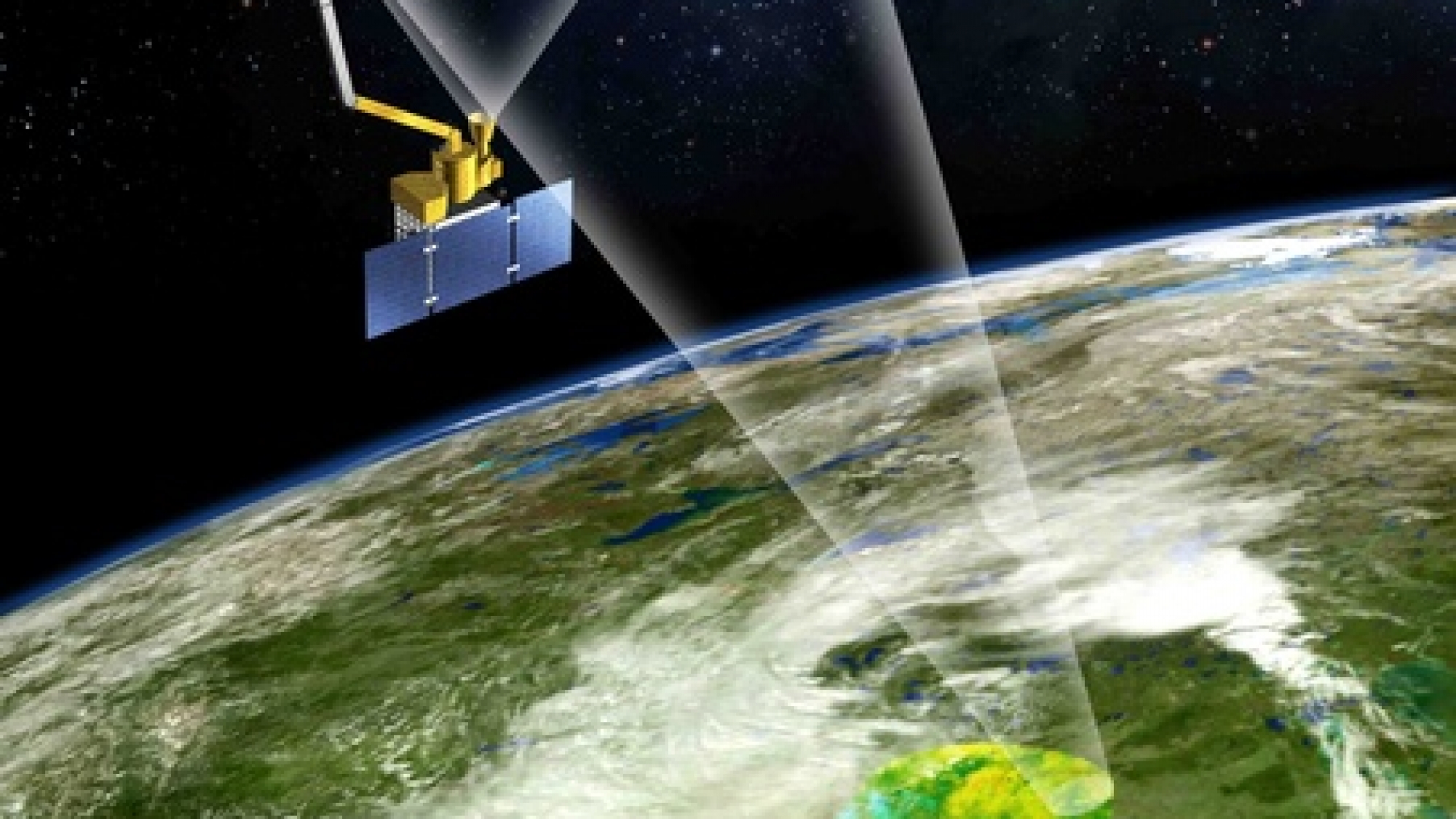
SMAP employs a unique dual-frequency radar and radiometer system to measure soil moisture. The radar, operating at L-band, penetrates the vegetation canopy and soil surface, providing insights into moisture levels beneath the surface. The radiometer, also operating at L-band, measures the brightness temperature of the soil, revealing information about its moisture content at the surface. Combining these two methods allows for a comprehensive picture of soil moisture, encompassing both surface and subsurface conditions.
Global Coverage and High-Resolution Data:
SMAP’s orbit, a near-polar sun-synchronous path, ensures global coverage every two to three days. This frequent revisiting allows for the monitoring of dynamic changes in soil moisture, capturing the nuances of seasonal variations and extreme weather events. The mission’s high spatial resolution, achieving a footprint of approximately 40 kilometers, provides a detailed map of soil moisture across diverse landscapes, from arid deserts to lush forests.
Unlocking the Power of Data:
The data collected by SMAP has revolutionized our understanding of soil moisture dynamics. It provides invaluable insights for numerous applications, including:
- Weather Forecasting: Accurate soil moisture data improves weather forecasting models, leading to more reliable predictions of rainfall, drought, and other extreme weather events.
- Water Resource Management: By monitoring soil moisture levels, water managers can optimize irrigation practices, minimize water waste, and ensure sustainable water use.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Understanding soil moisture conditions allows farmers to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and fertilizer application, enhancing crop yields and food security.
- Climate Modeling: Soil moisture plays a crucial role in the Earth’s climate system. SMAP data improves climate models, leading to a better understanding of climate change impacts and future projections.
- Disaster Mitigation: Soil moisture data is crucial for predicting and mitigating the effects of natural disasters, such as floods and droughts.
Beyond Soil Moisture: Expanding the Scope of SMAP
While soil moisture is the primary focus, SMAP data also provides valuable information about other environmental variables, including:
- Frozen Soil: SMAP’s radar can detect frozen soil, offering insights into the extent and dynamics of permafrost.
- Vegetation Water Content: The radiometer can measure vegetation water content, providing information about plant health and biomass.
- Surface Roughness: SMAP data can be used to map surface roughness, which is important for understanding the flow of water and sediment.
SMAP’s Legacy and Future:
Since its launch, SMAP has provided a wealth of data, revolutionizing our understanding of soil moisture and its role in Earth’s systems. The mission’s success has paved the way for future advancements in soil moisture monitoring, with the development of new technologies and instruments.
FAQs about NASA’s SMAP Mission:
Q: What is the primary objective of the SMAP mission?
A: The primary objective of SMAP is to map global soil moisture with unprecedented detail and accuracy, providing insights into the distribution, dynamics, and variability of soil moisture.
Q: How does SMAP measure soil moisture?
A: SMAP employs a dual-frequency radar and radiometer system. The radar penetrates the vegetation canopy and soil surface, measuring subsurface moisture, while the radiometer measures the brightness temperature of the soil, revealing surface moisture.
Q: What is the spatial resolution of SMAP data?
A: SMAP data has a spatial resolution of approximately 40 kilometers, providing a detailed map of soil moisture across diverse landscapes.
Q: How often does SMAP revisit the same location?
A: SMAP revisits the same location every two to three days, allowing for the monitoring of dynamic changes in soil moisture.
Q: What are the applications of SMAP data?
A: SMAP data has numerous applications, including weather forecasting, water resource management, agriculture, climate modeling, and disaster mitigation.
Q: What are the benefits of SMAP data?
A: SMAP data provides valuable insights into soil moisture dynamics, improving our understanding of weather patterns, water resources, climate change, and natural disasters.
Tips for Utilizing SMAP Data:
- Data Access and Processing: NASA provides free access to SMAP data through its Earthdata portal. Users can download and process the data using various software tools.
- Data Visualization and Analysis: Various software tools, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and R, can be used to visualize and analyze SMAP data, creating maps, graphs, and other visualizations.
- Data Integration and Applications: SMAP data can be integrated with other datasets, such as weather data, land cover data, and agricultural data, to create more comprehensive insights and applications.
- Collaboration and Research: SMAP data is a valuable resource for researchers and scientists working in various fields, including hydrology, agriculture, climate science, and disaster management.
Conclusion:
NASA’s SMAP mission stands as a testament to the power of space-based observation in understanding our planet. By providing unprecedented insights into soil moisture, SMAP has transformed our ability to monitor and manage Earth’s vital resources, contributing to a more sustainable future. As technology continues to advance, future missions building upon SMAP’s legacy will further enhance our understanding of soil moisture and its role in shaping our world.
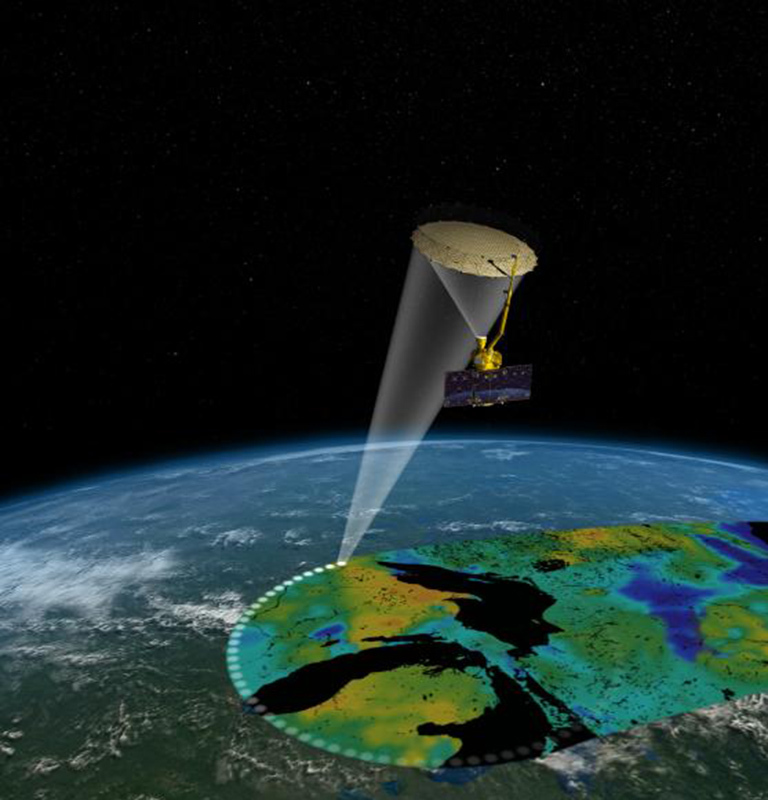

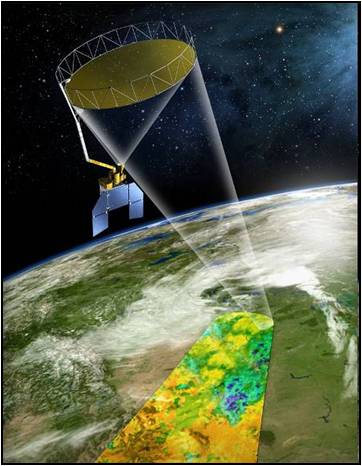





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: A Deep Dive into NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!