Unveiling Earth’s UV Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Earth UV Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s UV Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Earth UV Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Earth’s UV Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Earth UV Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Earth’s UV Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Earth UV Map

The Earth’s atmosphere acts as a protective shield, filtering out harmful radiation from the sun. However, some ultraviolet (UV) radiation penetrates this barrier, reaching the Earth’s surface and impacting life in various ways. Understanding the distribution and intensity of this UV radiation is crucial for safeguarding human health, protecting ecosystems, and informing various scientific endeavors. This is where the Earth UV map comes into play, providing a comprehensive picture of the global UV landscape.
The Significance of UV Radiation:
UV radiation, though essential for vitamin D synthesis, can be detrimental at high levels. Excessive exposure can lead to skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues. It can also harm plants and marine life, affecting ecosystems and food chains. Monitoring and understanding UV levels are vital for implementing protective measures and mitigating potential risks.
Introducing the Earth UV Map:
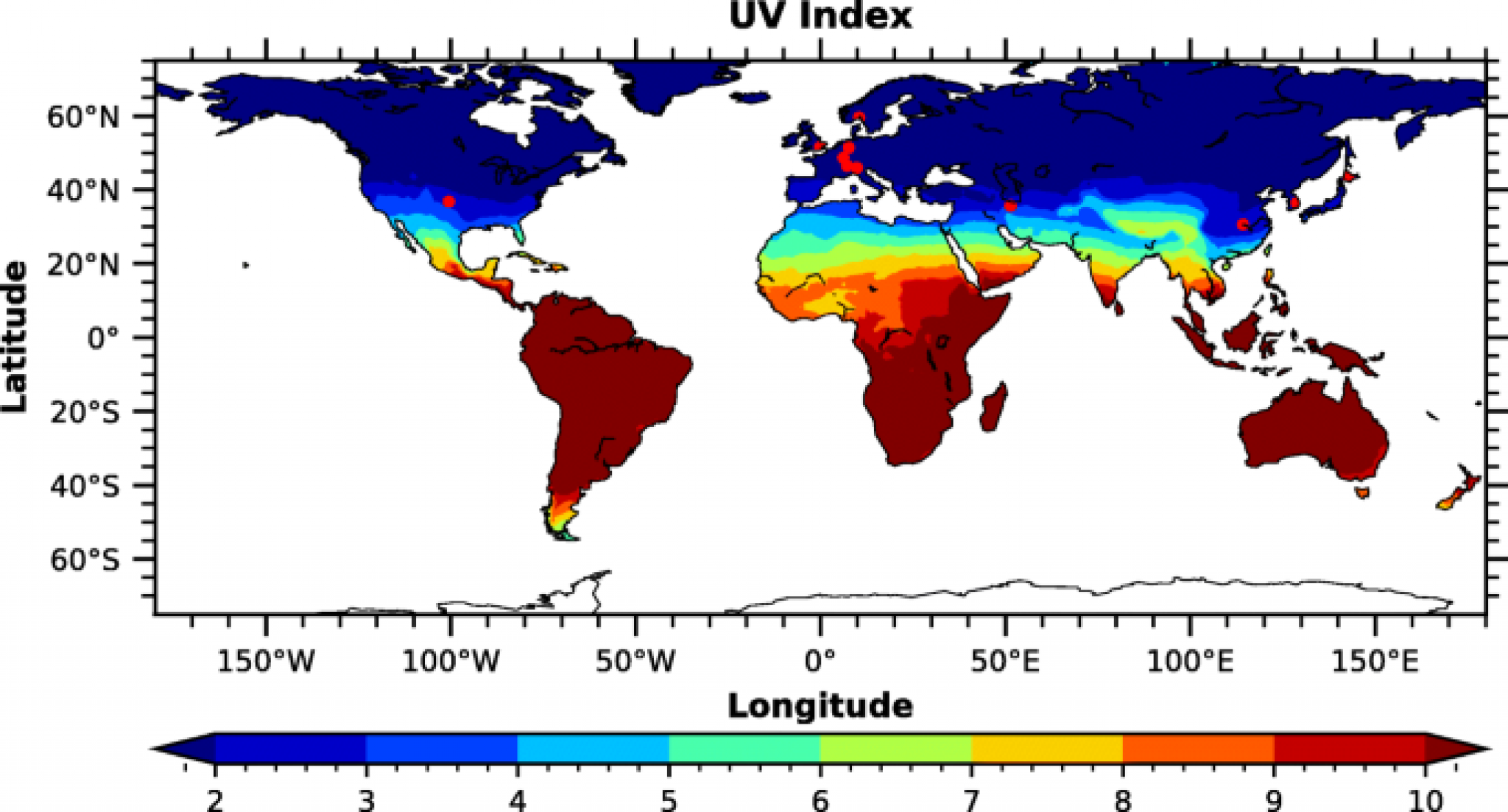
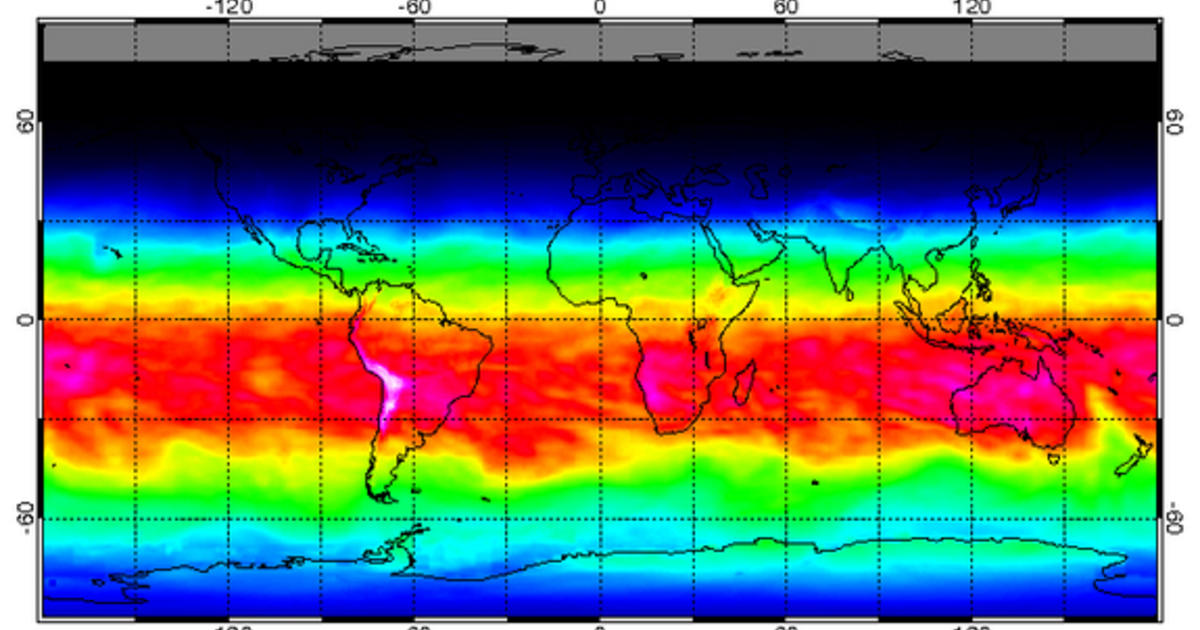
The Earth UV map is a visualization tool that displays the current and forecasted UV index values across the globe. It provides a geographically comprehensive overview of UV radiation intensity, allowing users to identify areas with high or low UV exposure. This information serves as a valuable resource for individuals, researchers, and policymakers alike.
How the Earth UV Map Works:
The Earth UV map relies on sophisticated algorithms and data from various sources:
- Satellite Observations: Satellites equipped with UV sensors continuously monitor the Earth’s atmosphere, measuring the amount of UV radiation reaching the surface.
- Atmospheric Models: Advanced computer models simulate atmospheric conditions, including ozone levels and cloud cover, to predict UV intensity.
- Ground-Based Measurements: Specialized instruments located at various locations worldwide provide real-time UV readings, supplementing satellite data.
These data sources are combined and processed to generate the Earth UV map, providing a dynamic and up-to-date picture of global UV levels.
Benefits of the Earth UV Map:
The Earth UV map offers a wide range of benefits, contributing to various aspects of our lives:
- Public Health: Individuals can use the map to assess UV risk in their area and take appropriate precautions, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and limiting exposure during peak UV hours.
- Environmental Monitoring: The map assists scientists in understanding the impact of UV radiation on ecosystems, allowing them to monitor changes in plant and animal life and develop strategies for conservation.
- Agriculture: Farmers can use the map to optimize crop production, as UV radiation affects plant growth and development.
- Climate Research: The map provides valuable data for climate modeling, helping researchers understand the impact of climate change on UV levels and its consequences for the planet.
- Space Exploration: The map is used in space exploration to assess the UV environment faced by astronauts and spacecraft, ensuring their safety and mission success.
Understanding the UV Index:
The UV index is a standardized measurement of the strength of UV radiation at a particular time and location. It ranges from 0 to 11+, with higher values indicating stronger UV radiation. The UV index is used on the Earth UV map to depict the intensity of UV exposure across the globe.
Factors Influencing UV Levels:
Several factors contribute to variations in UV levels:
- Latitude: UV radiation is more intense at lower latitudes closer to the equator, where the sun’s rays hit the Earth at a more direct angle.
- Altitude: UV levels increase with altitude, as the atmosphere becomes thinner and offers less protection.
- Time of Day: UV radiation is strongest during midday hours, typically between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Cloud Cover: Clouds can block UV radiation, reducing its intensity at the surface.
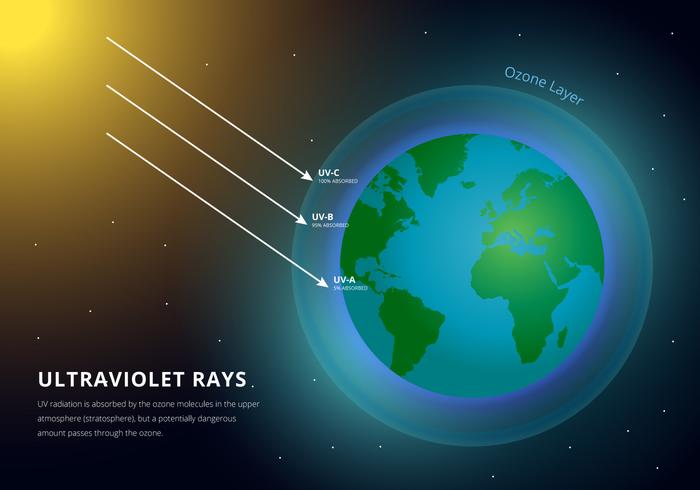
- Ozone Layer: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs most of the harmful UV radiation, but depletion of this layer can lead to increased UV levels at the surface.
Using the Earth UV Map Effectively:
The Earth UV map is a powerful tool, but it is crucial to understand its limitations and use it responsibly:
- Local Variations: The map provides a general overview, but local factors like cloud cover and elevation can significantly influence UV levels.
- Specific Needs: Individuals with sensitive skin or medical conditions should consult with healthcare professionals for specific UV exposure recommendations.
- Dynamic Nature: UV levels can change rapidly due to weather conditions, so it is essential to check the map regularly for the most up-to-date information.
FAQs about the Earth UV Map:
Q: What is the difference between the UV index and UV radiation?
A: The UV index is a measure of the strength of UV radiation, while UV radiation itself refers to the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. The UV index provides a practical scale for understanding the intensity of UV radiation and its potential health effects.
Q: How accurate is the Earth UV map?
A: The accuracy of the Earth UV map depends on the quality and availability of data from various sources, including satellites, models, and ground-based measurements. While the map provides a reliable estimate of UV levels, local variations and dynamic atmospheric conditions can influence actual UV exposure.
Q: What are the health risks associated with high UV exposure?
A: Excessive UV exposure can lead to various health problems, including:
- Skin Cancer: UV radiation damages DNA in skin cells, increasing the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
- Cataracts: UV radiation can damage the lens of the eye, leading to cataracts and other vision problems.
- Immune Suppression: UV exposure can suppress the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections.
- Premature Aging: UV radiation can accelerate skin aging, leading to wrinkles, age spots, and other signs of premature aging.
Q: How can I protect myself from UV radiation?
A: To minimize UV exposure and protect your health, follow these recommendations:
- Limit Exposure During Peak Hours: Avoid prolonged outdoor activities between 10 am and 4 pm, when UV radiation is strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover as much skin as possible with long sleeves, pants, and wide-brimmed hats.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher liberally and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses that block 99% or more of UVA and UVB rays.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, seek shade under trees or umbrellas to reduce UV exposure.
Tips for Using the Earth UV Map:
- Check the map regularly: UV levels can change quickly, so it is important to check the map before going outdoors, especially during peak UV hours.
- Consider local conditions: The map provides a general overview, but local factors like cloud cover and elevation can influence actual UV exposure.
- Share the information: Encourage others to use the Earth UV map to protect themselves from UV radiation.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest information about UV radiation and its health effects.
Conclusion:
The Earth UV map is a valuable tool for understanding the global UV landscape and mitigating the risks associated with excessive UV exposure. By providing comprehensive and up-to-date information on UV levels, it empowers individuals, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions and protect themselves and their communities from the harmful effects of UV radiation. As our understanding of UV radiation and its impact on Earth continues to evolve, the Earth UV map will play an increasingly crucial role in safeguarding human health, protecting ecosystems, and promoting sustainable development.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Earth’s UV Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Earth UV Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!