Unveiling France: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Geography Through Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling France: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Geography Through Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling France: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Geography Through Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling France: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Geography Through Maps
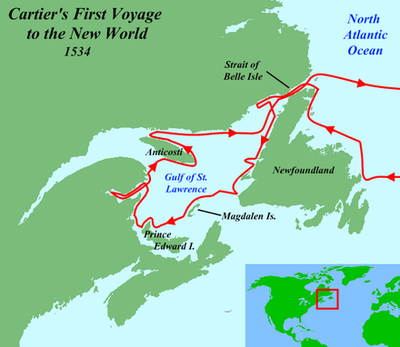
The study of France, a nation brimming with history, culture, and breathtaking landscapes, is significantly enhanced by the use of maps. These visual tools offer a profound understanding of the country’s geography, its diverse regions, and the intricate connections that shape its identity. This article delves into the importance of using maps to explore France, particularly for students in the ninth grade, providing a comprehensive overview of the subject.
Understanding France’s Physical Geography:
Maps are instrumental in visualizing the physical features of France, a country characterized by a diverse and captivating topography.
- Mountain Ranges: The iconic Alps, Pyrenees, and Massif Central dominate the landscape, offering stunning vistas and challenging terrain. Maps allow students to identify these ranges, their relative locations, and the impact they have on climate and human settlements.
- River Systems: The Loire, Rhone, and Seine rivers, among others, are vital arteries, shaping the country’s agricultural landscape and facilitating trade and transportation. Maps provide a clear understanding of these river systems, their tributaries, and their historical significance.
- Coastal Regions: France boasts extensive coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the English Channel. Maps highlight the varied coastal features, including beaches, cliffs, and estuaries, and their influence on the country’s economy and culture.
- Landform Variations: From the rolling hills of Normandy to the plains of the Paris Basin, France displays a remarkable diversity of landforms. Maps enable students to identify these variations and understand their impact on agricultural practices, population distribution, and regional identity.
Exploring Regional Diversity:
Maps are invaluable tools for understanding the distinct regions of France, each with its unique cultural heritage, language, and traditions.
- Metropolitan France: The mainland portion of France is divided into 18 administrative regions, each with its own distinctive characteristics. Maps illustrate the boundaries of these regions, allowing students to pinpoint key cities, landmarks, and geographical features that define them.
- Overseas Territories: France also possesses overseas territories scattered across the globe, offering a glimpse into the country’s colonial past and its diverse cultural tapestry. Maps provide a visual representation of these territories, their locations, and their unique characteristics.
- Historical Significance: Maps can highlight the historical evolution of France, tracing the boundaries of former kingdoms, empires, and provinces. This allows students to understand the historical context of the country’s current political and cultural landscape.
- Cultural Landscapes: Maps can be used to explore the cultural landscapes of France, identifying regions known for their specific cuisines, architectural styles, or artistic traditions. This allows students to appreciate the richness and diversity of French culture.
Practical Applications in the Classroom:
The use of maps in the ninth-grade classroom offers numerous benefits, fostering a deeper understanding of France and its geography.
- Active Learning: Maps encourage active learning by engaging students in visual analysis, interpretation, and critical thinking. They become active participants in the learning process, rather than passive recipients of information.
- Spatial Reasoning: Maps enhance spatial reasoning skills, helping students develop a sense of direction, distance, and scale. This is crucial for understanding the world around them and for navigating information effectively.
- Problem-Solving: Maps can be used to solve problems related to geography, such as identifying the shortest route between two cities, analyzing population distribution, or understanding the impact of environmental factors on human settlements.
- Global Connections: Maps help students understand the interconnectedness of the world, recognizing that France’s geography and history are intertwined with those of its neighbors and the wider global community.
FAQs on Using Maps to Study France:
Q: What types of maps are most helpful for studying France?
A: A variety of maps can be utilized, including physical maps, political maps, thematic maps (e.g., climate, population density), and historical maps. The choice depends on the specific learning objectives.
Q: How can students utilize maps effectively?
A: Students can engage in activities such as map reading, map analysis, map labeling, creating their own maps, and using maps in conjunction with other resources like text and images.
Q: How can maps be integrated into the curriculum?
A: Maps can be incorporated into various classroom activities, including lectures, discussions, projects, presentations, and assessments.
Q: What are some examples of map-based activities for ninth-grade students?
A: Students can create timelines based on historical maps, design travel itineraries using road maps, research and present on specific regions using thematic maps, or analyze population trends using population density maps.
Tips for Using Maps to Study France:
- Encourage map exploration: Provide students with opportunities to explore maps independently, fostering curiosity and self-directed learning.
- Use a variety of map types: Introduce students to different types of maps to broaden their understanding of geographical concepts.
- Connect maps to real-world applications: Show students how maps are used in everyday life, such as navigation, planning, and decision-making.
- Integrate maps into interdisciplinary projects: Combine map studies with other subjects, such as history, literature, art, or social studies.
- Utilize online mapping tools: Explore interactive online maps and mapping software to enhance engagement and provide real-time data.
Conclusion:
Maps are essential tools for understanding the geography of France, providing a visual framework for exploring its physical features, regional diversity, and historical evolution. By incorporating maps into the ninth-grade curriculum, educators can foster active learning, enhance spatial reasoning skills, and create engaging learning experiences that connect students to the world around them. The study of France through maps empowers students to become informed citizens, capable of understanding the complexities of the world and appreciating the rich cultural heritage of this remarkable country.
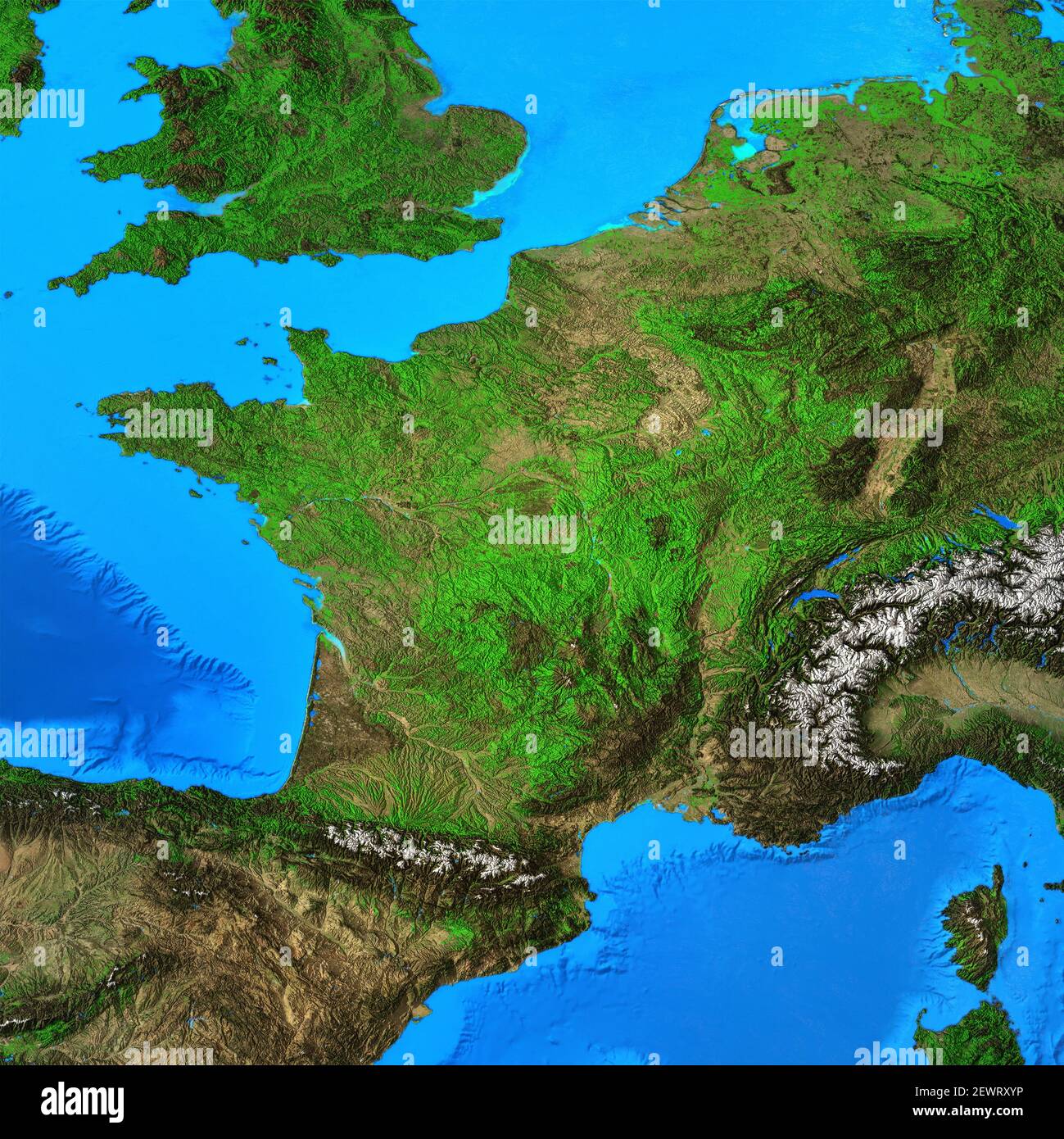
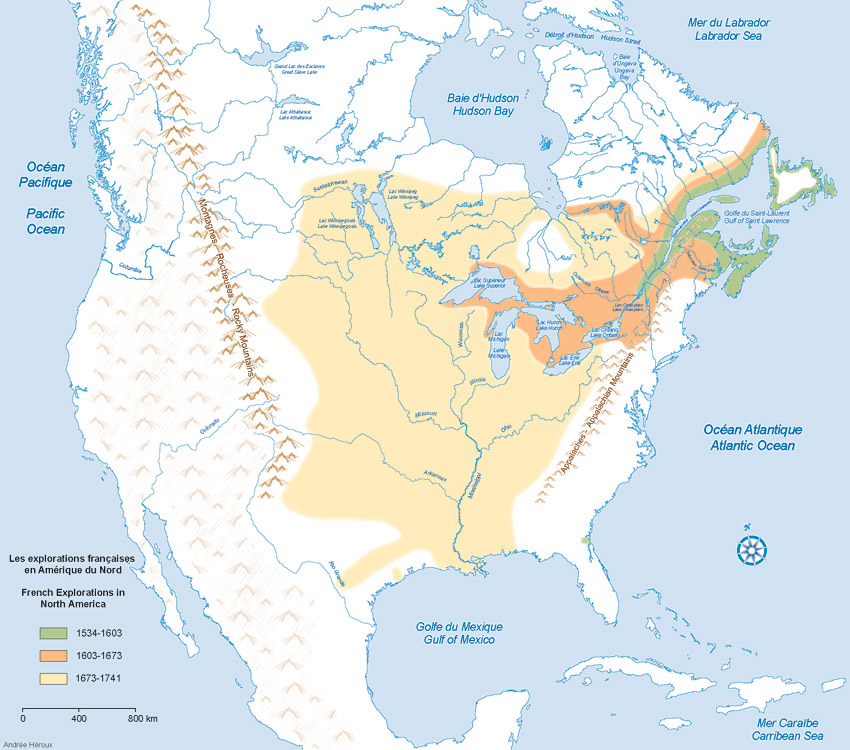
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-163113170-5c4f1e6346e0fb00014c3781.jpg)
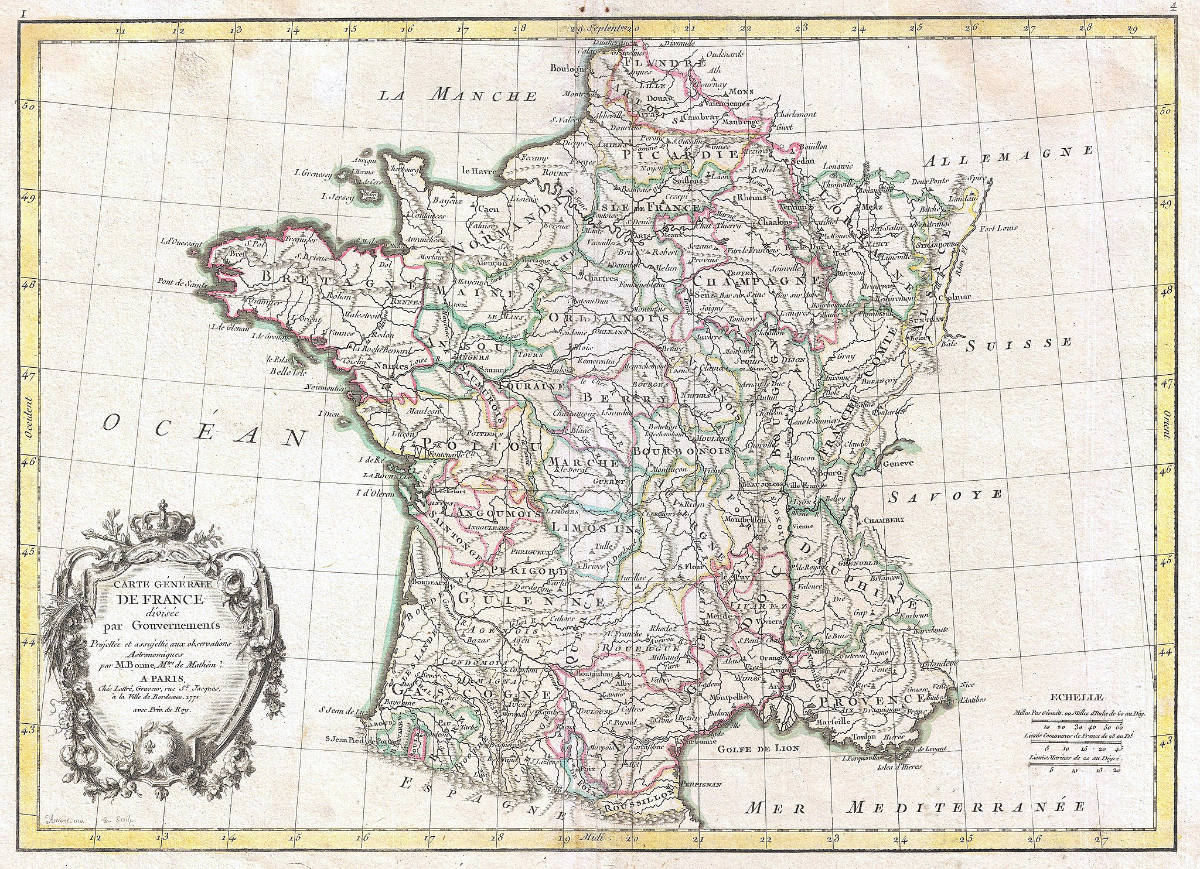



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling France: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Geography Through Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!