Unveiling Network Services: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap’s Stealth Scan
Related Articles: Unveiling Network Services: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap’s Stealth Scan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Network Services: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap’s Stealth Scan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Network Services: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap’s Stealth Scan
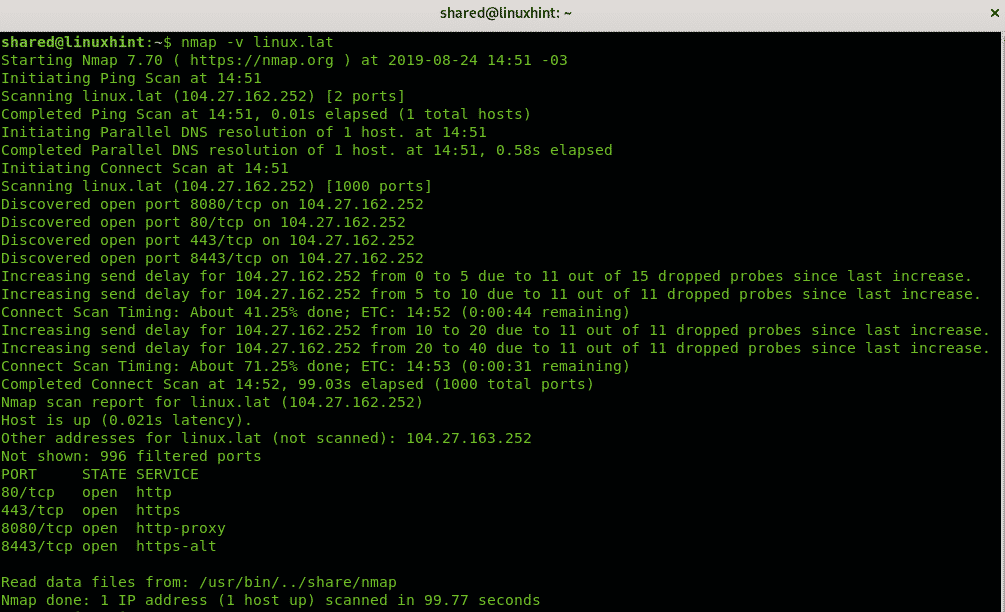
Network scanning is a fundamental practice in cybersecurity and network administration. It allows for a comprehensive understanding of network infrastructure, identifying active hosts, open ports, and running services. Among the numerous tools available for this purpose, Nmap stands out as a powerful and versatile scanner, offering a wide array of options to tailor scans to specific needs.
This article delves into one such option, a stealth scan capability within Nmap that prioritizes discretion and reduces the likelihood of detection by firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS). By employing this technique, security professionals and network administrators can conduct comprehensive network assessments while minimizing the risk of triggering security alerts.
Understanding Stealth Scans
In the realm of network scanning, stealth is paramount. When conducting a scan, the goal is to gather information without raising alarms. Traditional Nmap scans, while effective, can be noisy, emitting a multitude of packets that may trigger security mechanisms. This is where the concept of stealth scans comes into play.
Stealth scans, often referred to as "SYN scans" or "half-open scans," are designed to minimize the footprint of the scanning process, making it less likely to be detected. They achieve this by manipulating the TCP handshake, the three-way communication process that establishes a connection between two devices.
The Mechanics of Stealth Scans
The TCP handshake involves three stages:
- SYN (Synchronization): The client sends a SYN packet to the server, initiating a connection request.
- SYN-ACK (Synchronization-Acknowledgment): The server responds with a SYN-ACK packet, acknowledging the request and signaling its willingness to establish a connection.
- ACK (Acknowledgment): The client sends an ACK packet to the server, confirming the connection establishment.
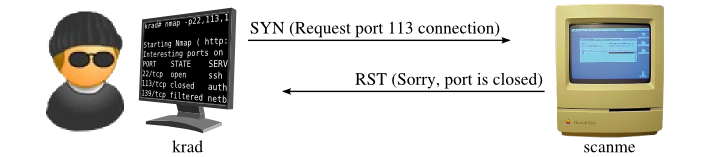
In a traditional TCP scan, the client completes the handshake by sending the ACK packet, thereby establishing a full connection. However, in a stealth scan, the client only sends the SYN packet and waits for the server’s response. If the server responds with a SYN-ACK packet, it indicates that the port is open. If the server does not respond or sends a RST (Reset) packet, it indicates that the port is closed.
Nmap’s Stealth Scan Flag: A Powerful Tool for Discretion
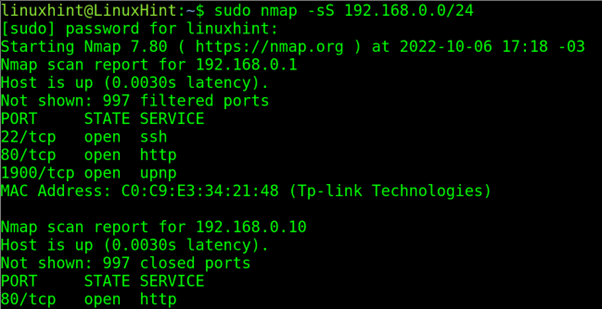
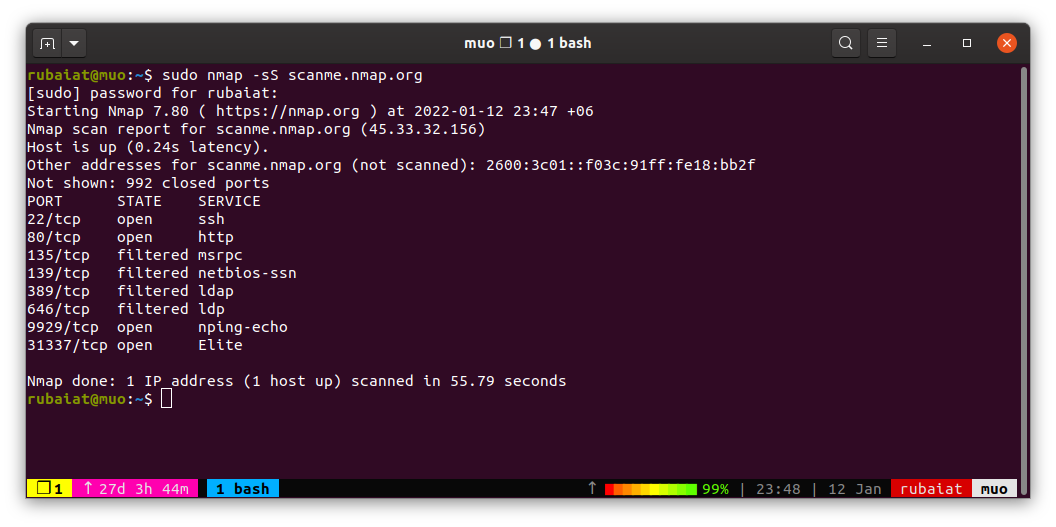
Nmap provides the -sS flag to execute a stealth scan. This flag instructs Nmap to perform a SYN scan, sending only a SYN packet and waiting for the server’s response. By omitting the ACK packet, the scan remains half-open, reducing its visibility and minimizing the risk of detection.
Benefits of Stealth Scans
- Reduced Detection: Stealth scans are less likely to trigger firewalls and intrusion detection systems, allowing for a more discreet network assessment.
- Improved Accuracy: By avoiding the full handshake, stealth scans reduce the risk of false positives, leading to more accurate scan results.
- Enhanced Security: Stealth scans minimize the potential for unintended consequences, such as accidental port scans or disruptions to network services.
- Flexibility: Nmap’s stealth scan capability can be integrated with other scan options, allowing for a comprehensive and tailored approach to network analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are stealth scans always undetectable?
A: While stealth scans are designed to be discreet, they are not foolproof. Advanced firewalls and intrusion detection systems may still detect the scanning activity. Additionally, the sheer volume of SYN packets sent during a large-scale scan can raise suspicions.
Q: When should I use a stealth scan?
A: Stealth scans are particularly useful in situations where discretion is paramount, such as:
- Penetration testing: Stealth scans help avoid triggering security alerts and allow for a more thorough assessment of the target network.
- Network monitoring: Stealth scans can be used to identify and analyze suspicious activity without alerting potential attackers.
- Vulnerability assessments: Stealth scans provide a more accurate picture of open ports and services, facilitating vulnerability identification and remediation.
Q: Are there any drawbacks to stealth scans?
A: While stealth scans offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain drawbacks:
- Slower scan speeds: Stealth scans rely on the server’s response, which can be slower than traditional TCP scans.
- Limited information: Stealth scans provide only basic information about open ports, such as their status. Further investigation may be required to gather detailed information about the services running on those ports.
Tips for Using Stealth Scans Effectively
- Target specific hosts: Focus on scanning specific IP addresses or ranges, rather than entire networks, to reduce the volume of traffic and minimize detection.
- Use a low scan rate: Adjust the scan rate to minimize the number of SYN packets sent per second, further reducing the risk of detection.
-
Employ other Nmap options: Combine stealth scans with other Nmap options, such as
-Pn(no ping scan) and-T4(aggressive timing), to further enhance discretion and efficiency. - Analyze scan results carefully: Thoroughly review the scan results to identify potential security vulnerabilities and ensure accurate interpretation of the data.
Conclusion
Nmap’s stealth scan capability, represented by the -sS flag, is a valuable tool for network security professionals and administrators. By employing this technique, they can conduct comprehensive network assessments while minimizing the risk of detection by firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Stealth scans provide a discreet and effective means of gaining insight into network infrastructure, enabling proactive security measures and optimized network management. However, it’s crucial to use stealth scans responsibly and ethically, adhering to relevant legal and ethical guidelines. Understanding the nuances of stealth scans and their limitations is essential for maximizing their effectiveness while mitigating potential risks.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Network Services: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap’s Stealth Scan. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!