Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Heat Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Heat Maps
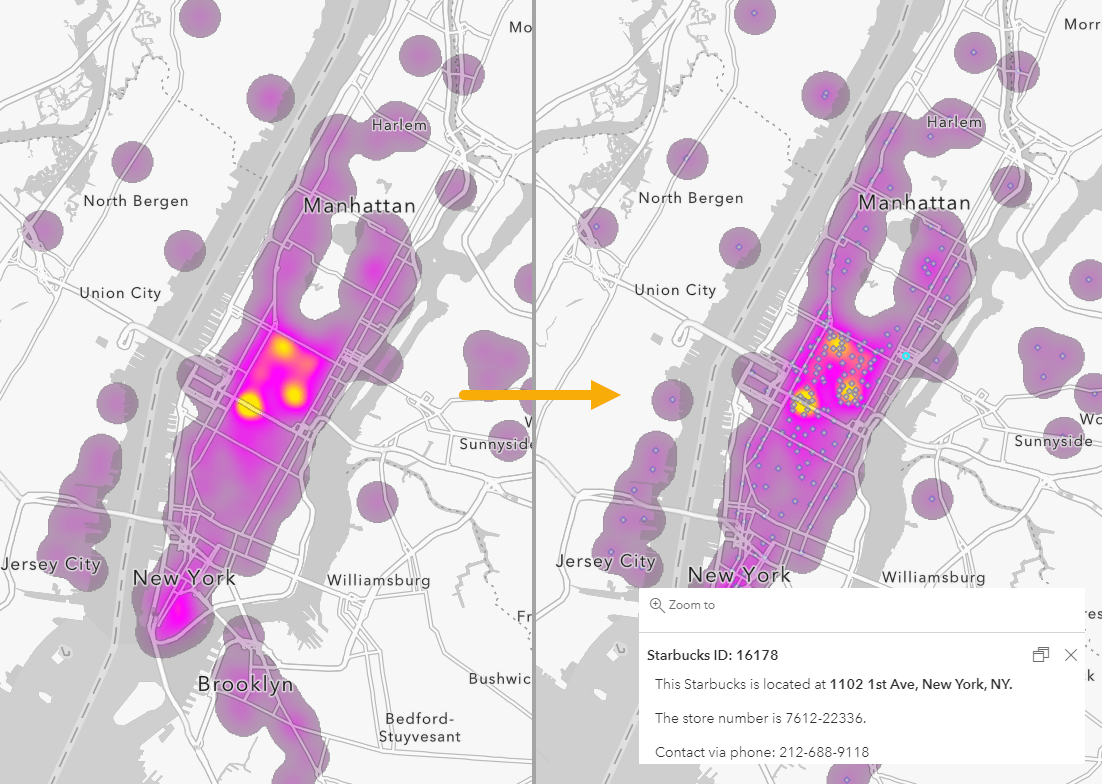
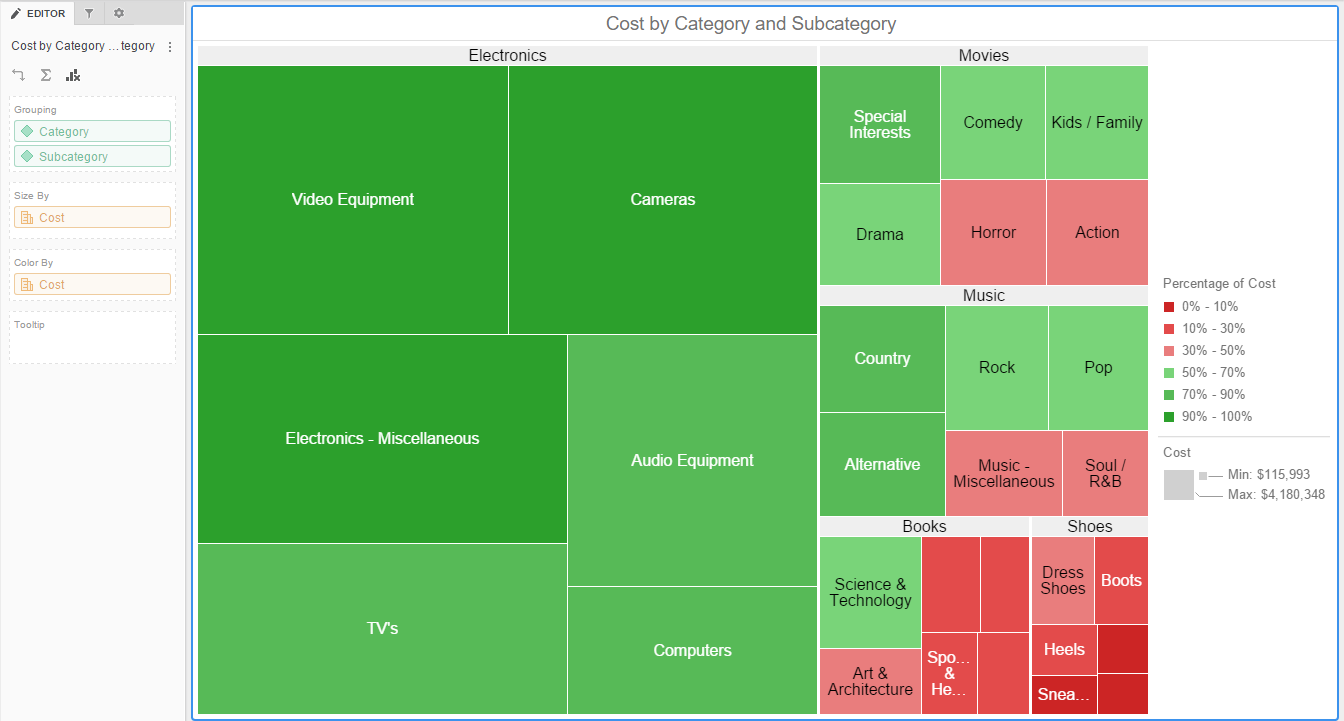
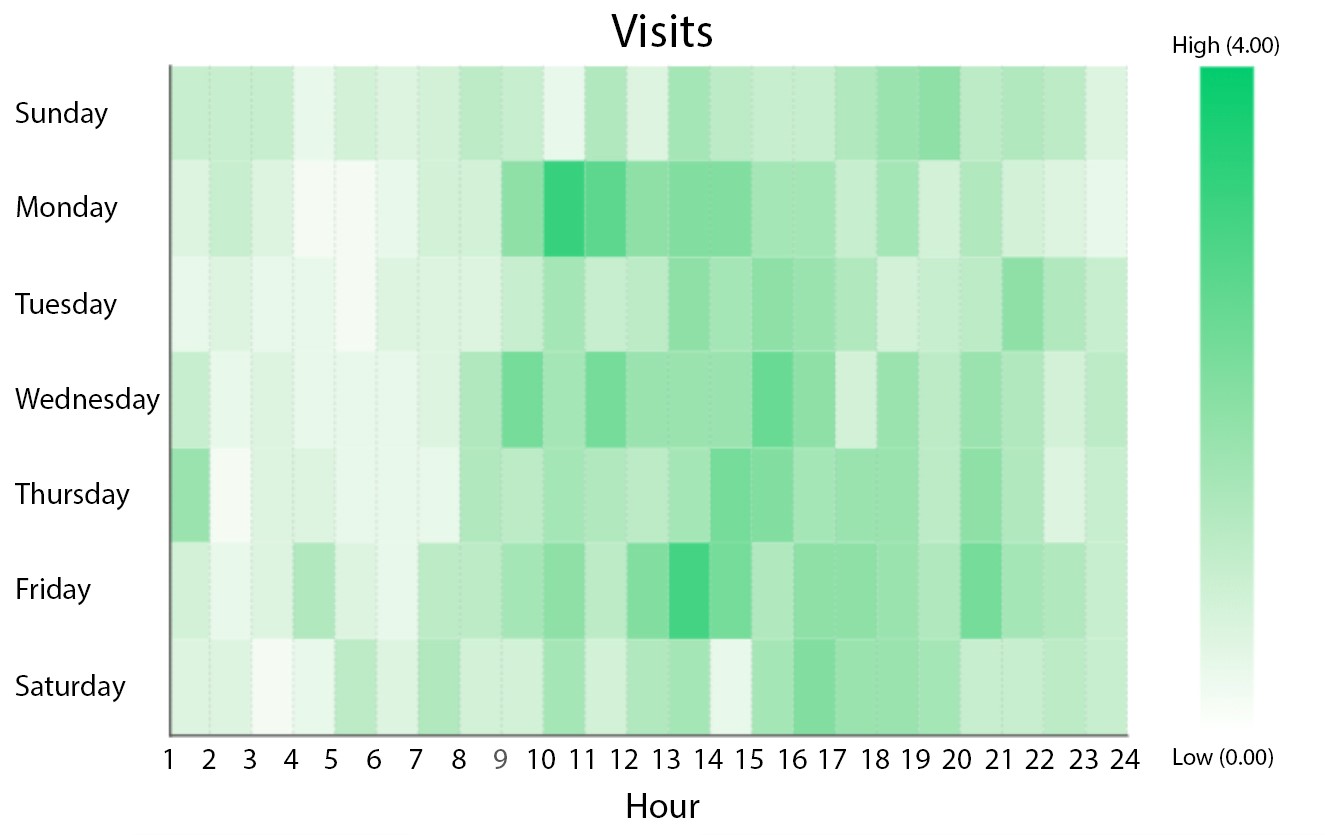
In the realm of data visualization, where complex information is transformed into readily digestible insights, map heat maps stand as a powerful tool. By employing a color gradient to represent varying densities or intensities of data points across a geographic area, these maps offer a compelling visual representation of spatial patterns, trends, and anomalies.
The Essence of Map Heat Maps
Imagine a bustling city, with areas of intense activity and others comparatively quiet. A map heat map would visually capture this dynamic, using a spectrum of colors to highlight areas of high activity (often represented by warmer hues like red or orange) and areas of low activity (represented by cooler hues like blue or green). This visual representation, often referred to as a "heat map," allows users to instantly grasp the distribution and concentration of data points within a defined geographic space.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Dive into Functionality
The power of map heat maps extends far beyond simple visual representation. These maps serve as a potent analytical tool, enabling users to:
- Identify Hotspots and Coldspots: By pinpointing areas of high and low data concentration, map heat maps reveal critical insights into spatial patterns. For instance, identifying areas with a high concentration of crime incidents can guide police resource allocation, while understanding areas with low customer density can inform business expansion strategies.
- Analyze Spatial Relationships: Beyond simple density, map heat maps can be used to analyze the relationship between different data sets. For example, overlaying a map of population density with a map of air pollution levels can reveal how population distribution correlates with environmental factors.
- Track Trends and Changes Over Time: By creating a series of heat maps for different time periods, users can observe how data distribution evolves over time. This allows for the identification of emerging trends, shifts in activity, and potential anomalies.
Applications Across Industries: A Wide Spectrum of Use Cases
The versatility of map heat maps makes them indispensable across a vast array of industries and applications:
- Business and Marketing: Understanding customer demographics, identifying optimal store locations, analyzing marketing campaign effectiveness, and pinpointing areas of high demand.
- Urban Planning and Development: Visualizing population density, identifying areas of high traffic congestion, planning infrastructure development, and analyzing the impact of urban renewal projects.
- Environmental Science: Mapping air pollution levels, tracking deforestation rates, monitoring animal migration patterns, and analyzing the impact of climate change.
- Public Health: Identifying areas with high disease prevalence, tracking the spread of epidemics, evaluating the effectiveness of public health interventions, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Law Enforcement and Security: Analyzing crime patterns, identifying high-risk areas, deploying resources effectively, and predicting future crime hotspots.
Constructing a Map Heat Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Building a map heat map involves several key steps:
- Data Collection and Preparation: Gathering relevant data, ensuring its accuracy, and formatting it in a compatible format for mapping software.
- Choosing a Mapping Platform: Selecting a suitable platform based on data type, desired level of detail, and available features. Popular options include Google Maps, ArcGIS, Tableau, and QGIS.
- Defining the Geographic Area: Specifying the region of interest, including boundaries, zoom levels, and specific locations.
- Setting the Color Gradient: Choosing a color palette that effectively represents the data range, ensuring clarity and visual appeal.
- Overlaying Data Points: Mapping the data points onto the chosen geographic area, ensuring accurate placement and visualization.
- Adjusting Parameters: Fine-tuning the heat map settings, such as opacity, smoothing, and aggregation methods, to achieve the desired level of detail and visual impact.
- Interpreting and Communicating Results: Analyzing the generated heat map, drawing meaningful conclusions, and communicating insights effectively through reports, presentations, or interactive dashboards.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. What data types are suitable for map heat maps?
Map heat maps can be used to visualize various data types, including:
- Numerical data: This includes data that can be measured or counted, such as population density, crime rates, or sales figures.
- Categorical data: This includes data that represents distinct groups or categories, such as different types of businesses, land use classifications, or disease prevalence rates.
- Temporal data: This includes data that changes over time, such as traffic congestion patterns, weather conditions, or the spread of an epidemic.
2. What are the benefits of using map heat maps?
Map heat maps offer several advantages:
- Visual clarity: They provide an intuitive and easily understandable representation of spatial patterns.
- Data exploration: They facilitate the identification of trends, anomalies, and relationships within data sets.
- Decision support: They provide insights that can inform strategic planning, resource allocation, and problem-solving.
- Communication effectiveness: They present complex data in a visually engaging and readily digestible manner.
3. What are some common challenges associated with map heat maps?
Despite their advantages, map heat maps can present certain challenges:
- Data quality: The accuracy of the heat map relies on the quality and completeness of the underlying data.
- Data aggregation: The aggregation of data points can obscure individual locations and potentially mask important details.
- Visual interpretation: Interpreting the heat map requires an understanding of the chosen color gradient and data aggregation methods.
- Ethical considerations: Using map heat maps to visualize sensitive data requires careful consideration of privacy and potential bias.
Tips for Creating Effective Map Heat Maps
- Choose a clear and informative color gradient: Use a palette that effectively represents the data range, avoiding overly complex or distracting schemes.
- Optimize data aggregation: Choose appropriate aggregation methods to balance the need for clarity with the preservation of detail.
- Include relevant context: Provide clear labels, legends, and annotations to enhance understanding and interpretation.
- Consider user experience: Design the map for easy navigation and interaction, ensuring accessibility for diverse audiences.
- Validate and iterate: Test the map with different data sets and user feedback to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Insights
Map heat maps have emerged as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, offering a clear and intuitive way to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within geographic spaces. By embracing their versatility and understanding their limitations, users can leverage map heat maps to gain valuable insights, inform decision-making, and effectively communicate complex information. As data collection and analysis continue to evolve, map heat maps will undoubtedly remain a vital tool for unlocking the power of spatial data and driving informed action.
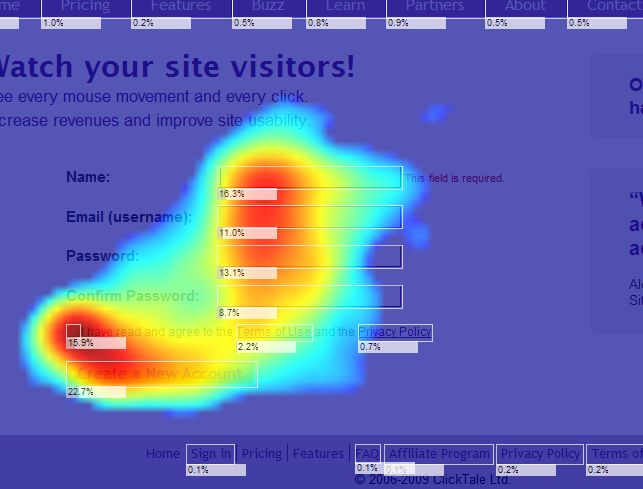



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!