Unveiling the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Journey Through the Tectonic Plates Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Journey Through the Tectonic Plates Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Journey Through the Tectonic Plates Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Journey Through the Tectonic Plates Map

The Earth, seemingly a solid and stable sphere, is in fact a dynamic and ever-changing entity. Its surface, far from being a static canvas, is composed of a mosaic of giant, interlocking pieces known as tectonic plates. These plates, constantly in motion, are responsible for a plethora of geological phenomena, shaping the Earth’s landscape and influencing its climate and life forms. Understanding the intricate dance of these plates is crucial for comprehending the Earth’s past, present, and future.
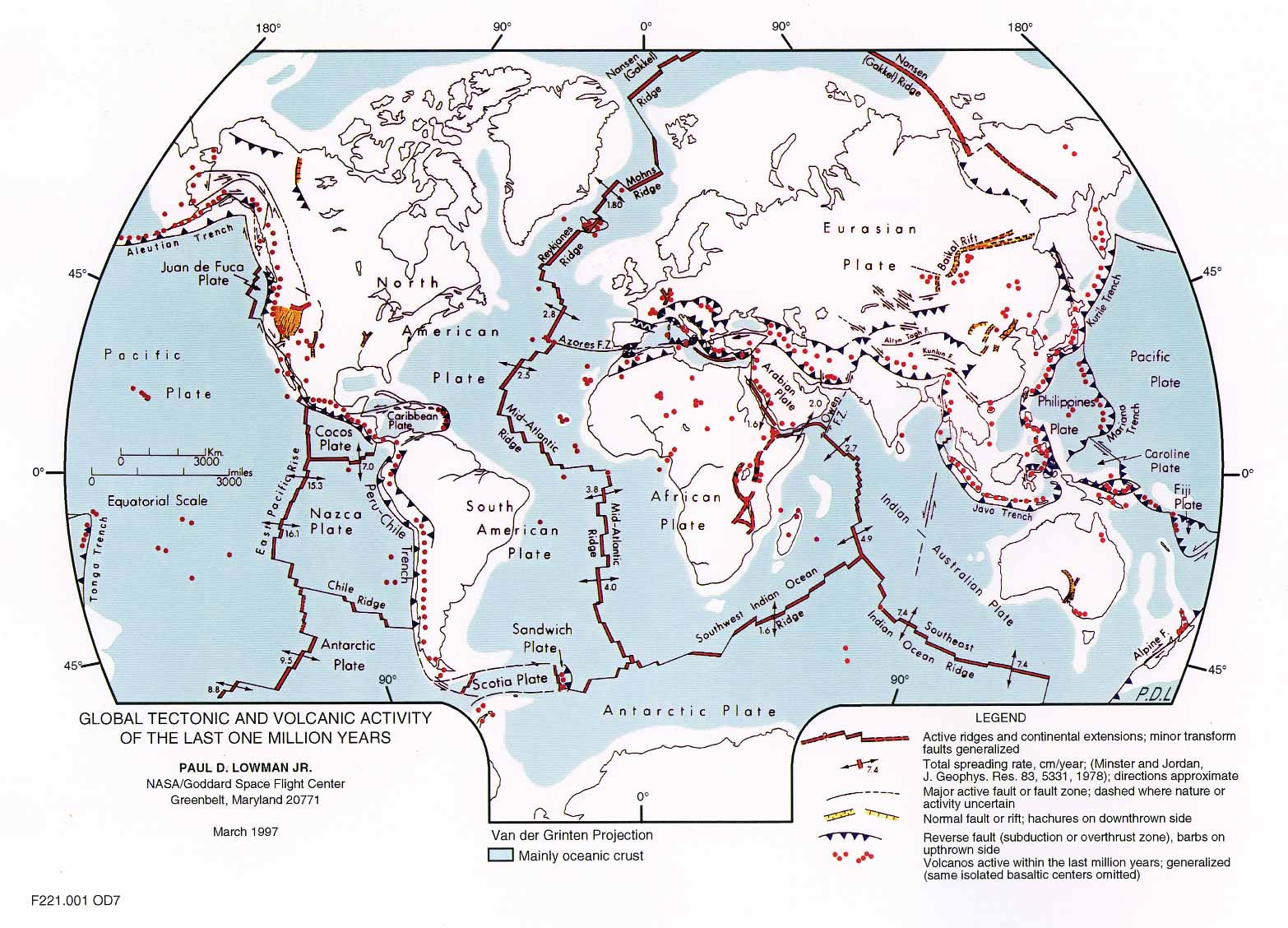
The tectonic plates map, a visual representation of these dynamic pieces, is a powerful tool for unraveling the Earth’s complex geological history. It provides a framework for understanding the distribution of mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes, and other geological features, highlighting the interconnectedness of these phenomena.
The Fabric of the Earth: Understanding Tectonic Plates
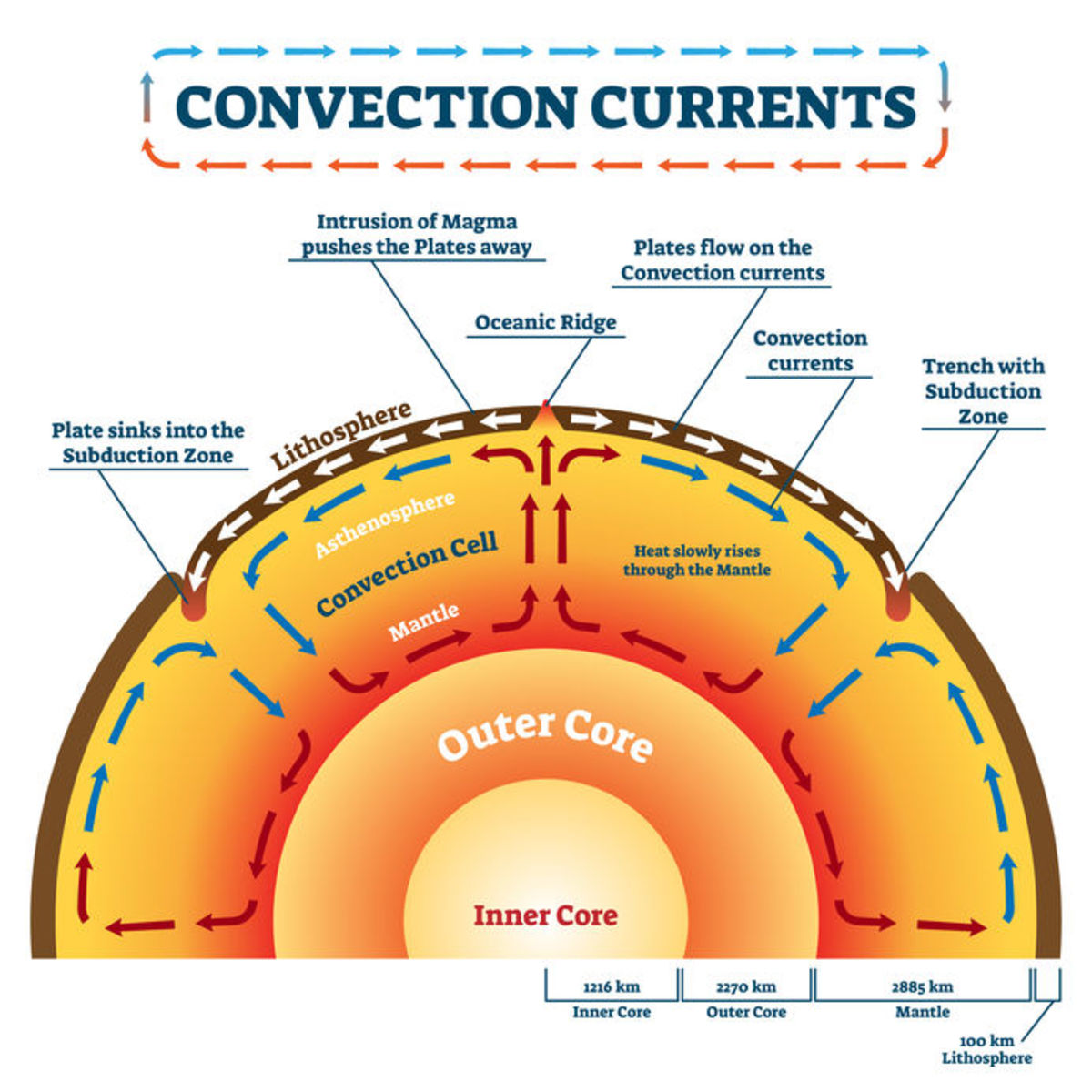
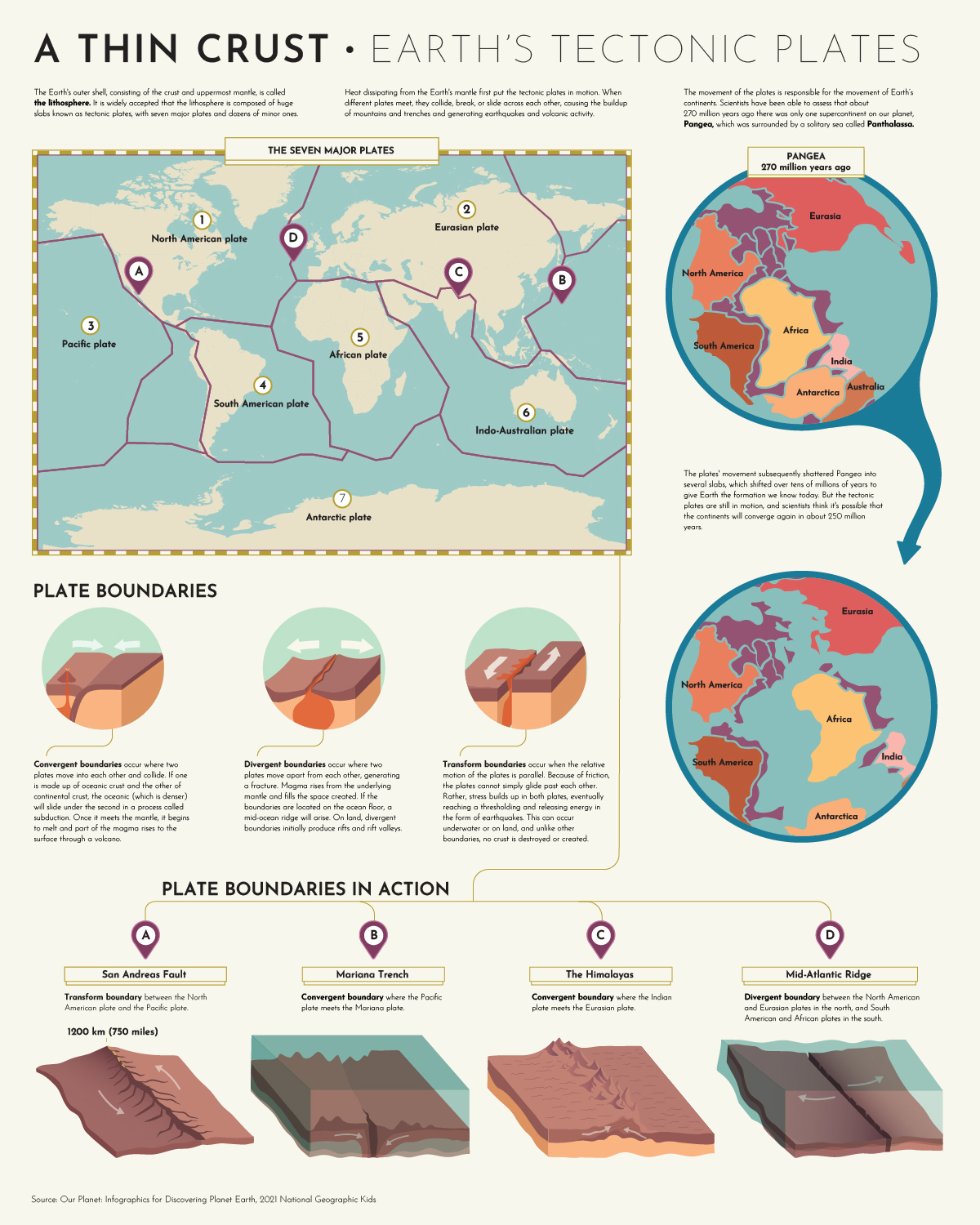
The Earth’s outer layer, the lithosphere, is divided into about 15 major tectonic plates and numerous smaller ones. These plates are not fixed but constantly move, albeit slowly, at a rate of a few centimeters per year. This movement is driven by the convection currents within the Earth’s mantle, a layer of hot, viscous rock beneath the lithosphere.
The tectonic plates map illustrates the boundaries between these plates, delineating three primary types of interactions:
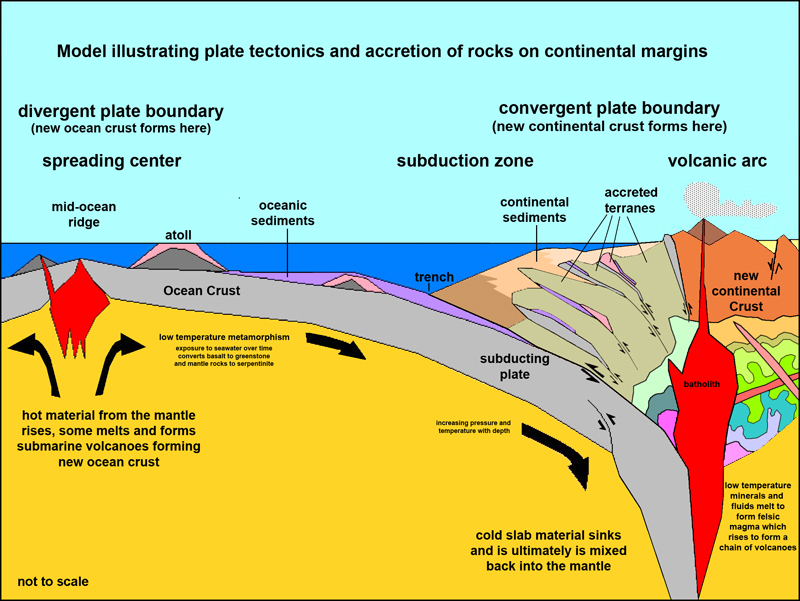
- Convergent Boundaries: When two plates collide, the denser plate subducts beneath the less dense one, leading to the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and deep ocean trenches. The Himalayan Mountains, for instance, are a result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Divergent Boundaries: When two plates move apart, magma rises from the mantle, creating new oceanic crust. This process, known as seafloor spreading, occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where volcanic activity is prevalent. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a prominent underwater mountain range, is a prime example.
- Transform Boundaries: When two plates slide past each other horizontally, the resulting friction can trigger earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault in California, a notorious earthquake-prone zone, is a prime example of a transform boundary.
The Tectonic Plates Map: A Window into the Earth’s Past and Future
The tectonic plates map is not merely a static representation of the Earth’s surface. It is a dynamic tool that allows us to understand the Earth’s past geological evolution and predict future events. By studying the movement and interactions of these plates, scientists can:
- Reconstruct Past Continents: The map reveals that continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea, which subsequently broke apart, leading to the formation of the modern continents. This understanding has revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s history and the evolution of life.
- Predict Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions: The map identifies areas prone to seismic activity and volcanic eruptions, allowing for better preparedness and mitigation strategies. By understanding the locations of plate boundaries, scientists can forecast potential earthquake zones and volcanic hotspots.
- Unravel the Formation of Mountains and Oceans: The map explains the formation of mountain ranges, ocean basins, and other geological features. It helps us understand the processes that shape the Earth’s surface and the distribution of natural resources.
Beyond the Map: Applications and Implications
The tectonic plates map is not merely a scientific tool but has significant implications for various fields:
- Resource Exploration: Understanding the geological processes associated with plate tectonics aids in the exploration of natural resources, such as oil, gas, and minerals. The map helps identify areas with high potential for resource deposits.
- Environmental Studies: The map helps understand the distribution of volcanoes, earthquakes, and other geological hazards that can impact human populations and ecosystems. This information is crucial for environmental management and disaster preparedness.
- Climate Change Research: Plate tectonics plays a significant role in shaping the Earth’s climate. The movement of plates influences ocean currents, atmospheric circulation, and the distribution of landmasses, all of which impact global climate patterns.
FAQs about the Tectonic Plates Map
1. How often is the tectonic plates map updated?
The tectonic plates map is constantly being updated as scientists gather new data from GPS measurements, seismic activity, and other sources. However, major updates are typically made every few years, incorporating new findings and refining the understanding of plate movements.
2. Can the tectonic plates map predict the exact time and location of earthquakes?
While the tectonic plates map helps identify earthquake-prone zones, it cannot predict the exact time and location of an earthquake. Earthquakes are complex events influenced by various factors, and predicting their occurrence remains a significant challenge.
3. What is the impact of tectonic plate movement on human civilization?
Tectonic plate movement has profound implications for human civilization. It shapes the landscape, creates resources, and poses hazards. Understanding these processes is crucial for planning, development, and disaster mitigation.
4. How does the tectonic plates map help in understanding the Earth’s history?
The tectonic plates map provides a framework for understanding the Earth’s past, revealing the history of continents, oceans, and mountain ranges. It helps trace the movement of continents over millions of years, providing insights into the Earth’s evolution.
5. What are the future implications of tectonic plate movement?
The ongoing movement of tectonic plates will continue to shape the Earth’s surface, creating mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Understanding these processes is crucial for predicting future events and mitigating their impact.
Tips for Understanding the Tectonic Plates Map
- Focus on Plate Boundaries: The boundaries between tectonic plates are the most active areas, where earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain formation occur. Pay attention to the types of boundaries (convergent, divergent, transform) and their associated geological features.
- Consider the Scale: The tectonic plates map represents a vast and complex system. Remember that the movement of plates is slow and occurs over millions of years.
- Connect the Dots: The tectonic plates map is a powerful tool for understanding the interconnectedness of geological phenomena. Recognize how the movement of one plate can influence events in other parts of the world.
- Engage with Visualizations: Utilize interactive maps, animations, and visualizations to gain a deeper understanding of the dynamic nature of tectonic plates.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Ever-Changing Earth
The tectonic plates map is a testament to the Earth’s dynamic nature. It reveals a planet in constant motion, a canvas sculpted by the forces of plate tectonics. This understanding is not only essential for comprehending the Earth’s past and present but also crucial for shaping our future, guiding our efforts in resource management, environmental protection, and disaster preparedness. As we continue to explore the depths of the Earth, the tectonic plates map will remain an invaluable tool, guiding our understanding of this ever-changing and fascinating planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Journey Through the Tectonic Plates Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!