Unveiling the Earth’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Topographic Maps

Google Earth, a powerful tool for exploring the planet, offers more than just satellite imagery. Its topographic map feature provides a detailed and interactive representation of the Earth’s surface, showcasing its elevation and contours. This article delves into the intricacies of Google Earth’s topographic maps, highlighting their functionalities, benefits, and applications.
Understanding the Topography: A Visual Representation of Elevation
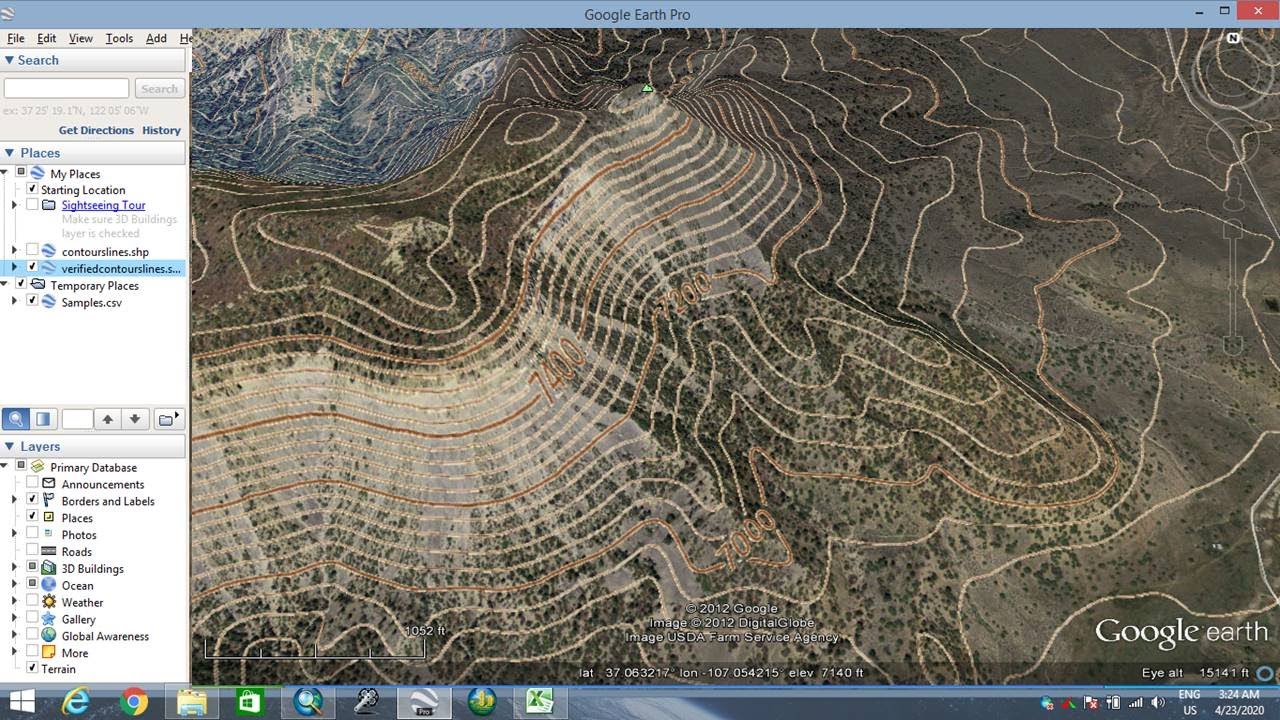
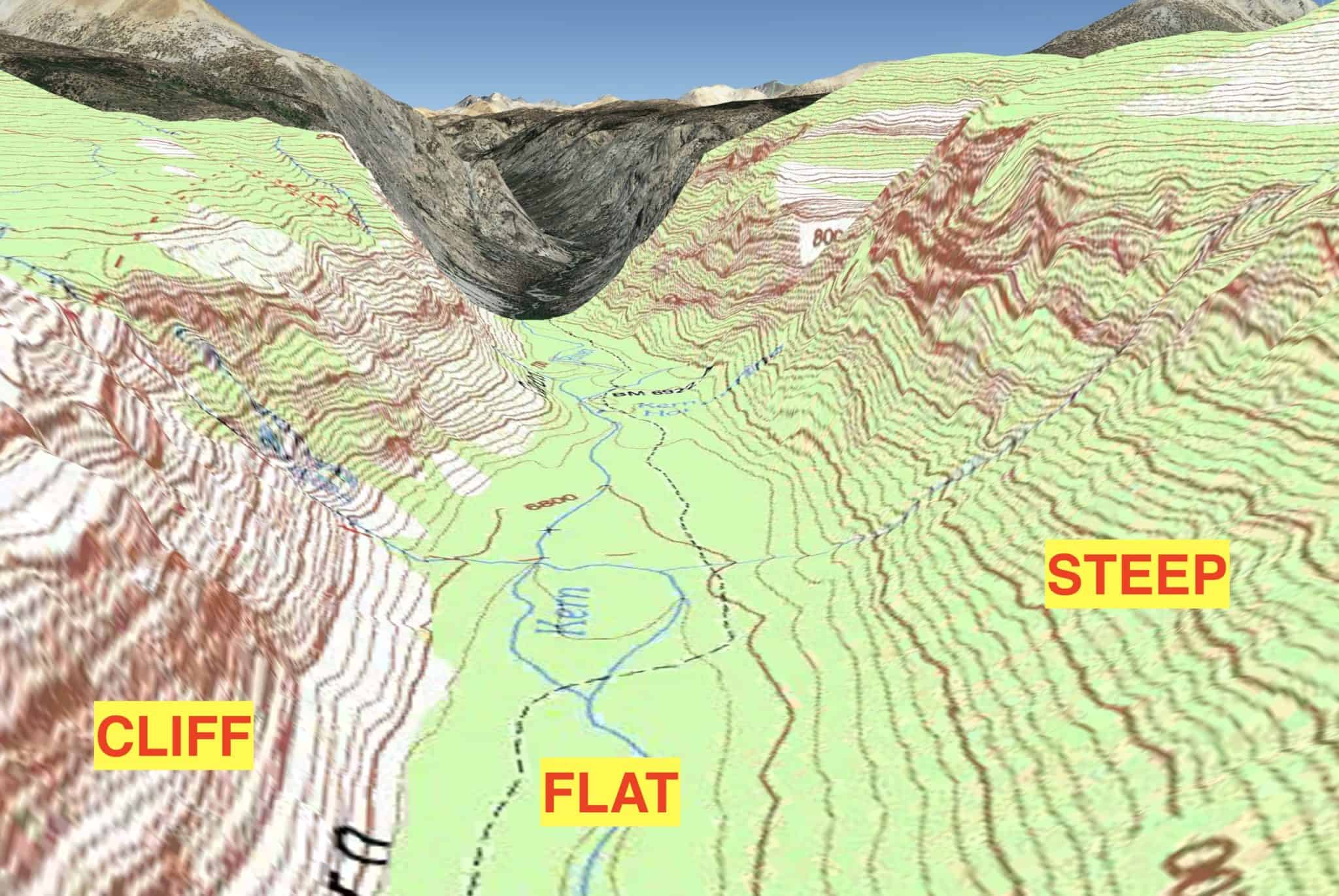
Topographic maps, often referred to as contour maps, depict the Earth’s surface by using lines to connect points of equal elevation. These lines, known as contour lines, provide a visual representation of the terrain’s slopes, valleys, peaks, and other features. Google Earth integrates this traditional mapping technique into its platform, offering a dynamic and interactive experience for users.
Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Features and Functionality
Google Earth’s topographic map functionality allows users to seamlessly navigate and explore the Earth’s terrain. Here’s a breakdown of its key features:
- Elevation Data: The topographic map displays elevation data, providing users with a clear understanding of the height of different areas. This information is crucial for various applications, from planning hiking trips to understanding potential environmental risks.
- Contour Lines: The map utilizes contour lines, which are lines connecting points of equal elevation. These lines provide a visual representation of the terrain’s slopes, allowing users to easily identify steep inclines, gentle slopes, and flat areas.
- Terrain Shading: Google Earth employs terrain shading to enhance the visualization of the topography. By applying a subtle shading effect, it accentuates the contours and provides a more realistic representation of the terrain.
- 3D View: Google Earth allows users to switch to a 3D view, providing a more immersive and realistic experience. This feature enables users to virtually explore the terrain, gaining a better understanding of its shape and features.
- Measurement Tools: The platform offers various measurement tools, including distance, area, and elevation measurements. These tools enable users to obtain precise measurements of terrain features, supporting planning and analysis activities.
Applications Beyond Exploration: The Importance of Topographic Maps
Google Earth’s topographic maps extend far beyond recreational exploration, offering valuable insights and functionalities for various sectors:
- Environmental Studies: Researchers and environmental scientists utilize topographic maps to analyze terrain features, understand hydrological patterns, assess potential flood risks, and model climate change impacts.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners rely on topographic maps to assess site suitability for development projects, identify potential challenges related to terrain, and optimize infrastructure planning.
- Civil Engineering: Civil engineers use topographic maps for road and bridge design, evaluating terrain conditions for construction projects, and optimizing infrastructure development.
- Military Operations: Military planners utilize topographic maps for strategic planning, identifying terrain advantages and disadvantages, and developing optimal deployment strategies.
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps for navigation, route planning, and assessing terrain challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Google Earth’s Topographic Maps
1. How accurate are Google Earth’s topographic maps?
The accuracy of Google Earth’s topographic maps varies depending on the data source and the location. While the platform utilizes high-resolution satellite imagery and advanced processing techniques, data accuracy can be affected by factors such as terrain complexity, vegetation cover, and data availability.
2. Can I download topographic data from Google Earth?
Google Earth does not directly offer the ability to download topographic data in its raw format. However, users can access elevation data for specific areas through the platform’s measurement tools or export 3D models for further analysis.
3. How can I customize the appearance of the topographic map?
Google Earth offers various customization options for the topographic map. Users can adjust the display of contour lines, terrain shading, and other visual elements to enhance the map’s clarity and focus on specific features.
4. What are the limitations of Google Earth’s topographic maps?
While Google Earth’s topographic maps offer valuable insights, they have limitations. The platform’s data is primarily derived from satellite imagery, which may not capture all terrain details, especially in densely vegetated areas or mountainous regions.
5. What alternative resources are available for topographic data?
Several alternative resources provide topographic data, including government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). These resources offer high-resolution topographic maps and elevation data for various regions.
Tips for Utilizing Google Earth’s Topographic Maps Effectively
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define the purpose of using the topographic map, whether for planning a hiking trip, analyzing environmental data, or conducting a site assessment.
- Explore the Customization Options: Experiment with the map’s settings to enhance its clarity and focus on the desired features.
- Utilize the Measurement Tools: Take advantage of the platform’s measurement tools to obtain precise data on distances, areas, and elevations.
- Compare with Other Data Sources: Cross-reference Google Earth’s topographic data with other sources, such as government agencies or specialized mapping platforms, to ensure data accuracy.
- Consider the Limitations: Recognize the inherent limitations of Google Earth’s topographic data, especially in areas with limited data availability or complex terrain.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Exploring and Understanding the Earth
Google Earth’s topographic map functionality provides a valuable tool for exploring, understanding, and analyzing the Earth’s terrain. By combining traditional cartographic techniques with advanced technology, it offers an interactive and user-friendly experience for individuals and professionals alike. From planning outdoor adventures to conducting scientific research, Google Earth’s topographic maps empower users to gain a deeper understanding of the planet’s physical features and their significance. While recognizing its limitations, Google Earth’s topographic maps remain an indispensable resource for navigating and interpreting the Earth’s diverse landscapes.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Google Earth’s Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!