Unveiling the Earth’s Tremors: A Comprehensive Look at World Earthquake Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Tremors: A Comprehensive Look at World Earthquake Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Tremors: A Comprehensive Look at World Earthquake Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Tremors: A Comprehensive Look at World Earthquake Maps

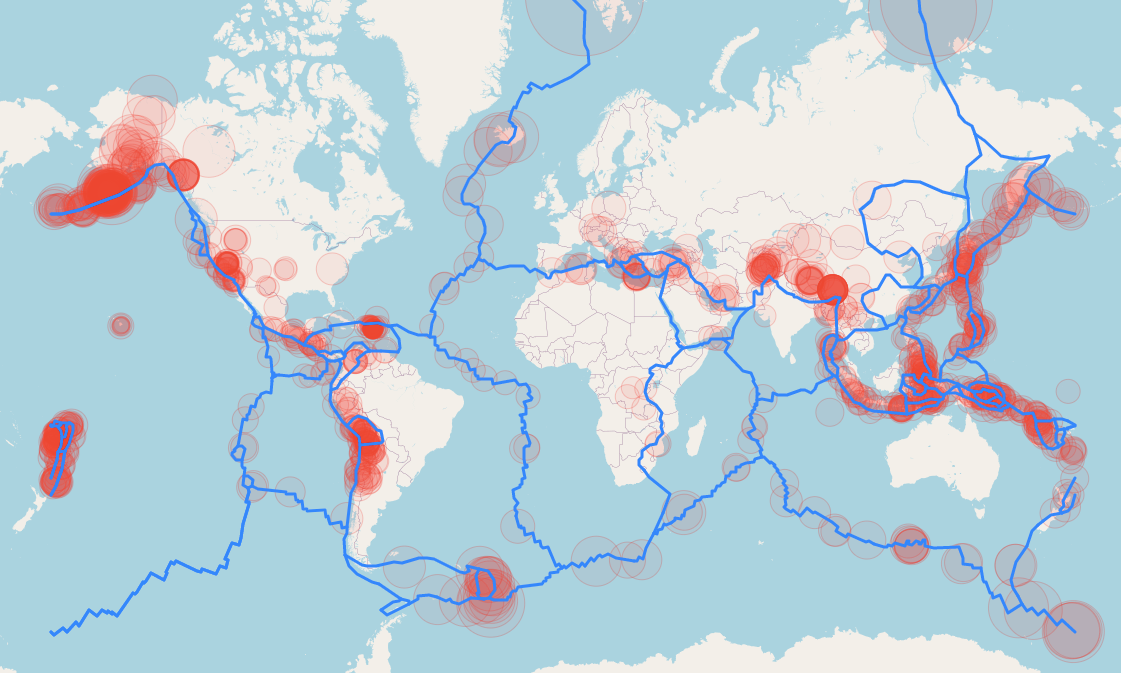
The Earth’s surface is a dynamic and ever-changing landscape. Beneath the seemingly stable ground, tectonic plates constantly shift and collide, generating immense forces that manifest as earthquakes. These seismic events can range from barely perceptible tremors to catastrophic disasters, leaving a trail of destruction and human suffering. Understanding the distribution and frequency of these events is crucial for mitigating their impact and ensuring the safety of populations. This is where world earthquake maps play a vital role.
A Visual Representation of Seismic Activity:
World earthquake maps are visual representations of global seismic activity. They depict the locations of past earthquakes, often using color-coding to indicate the magnitude and depth of each event. These maps are invaluable tools for scientists, engineers, and policymakers, providing insights into:
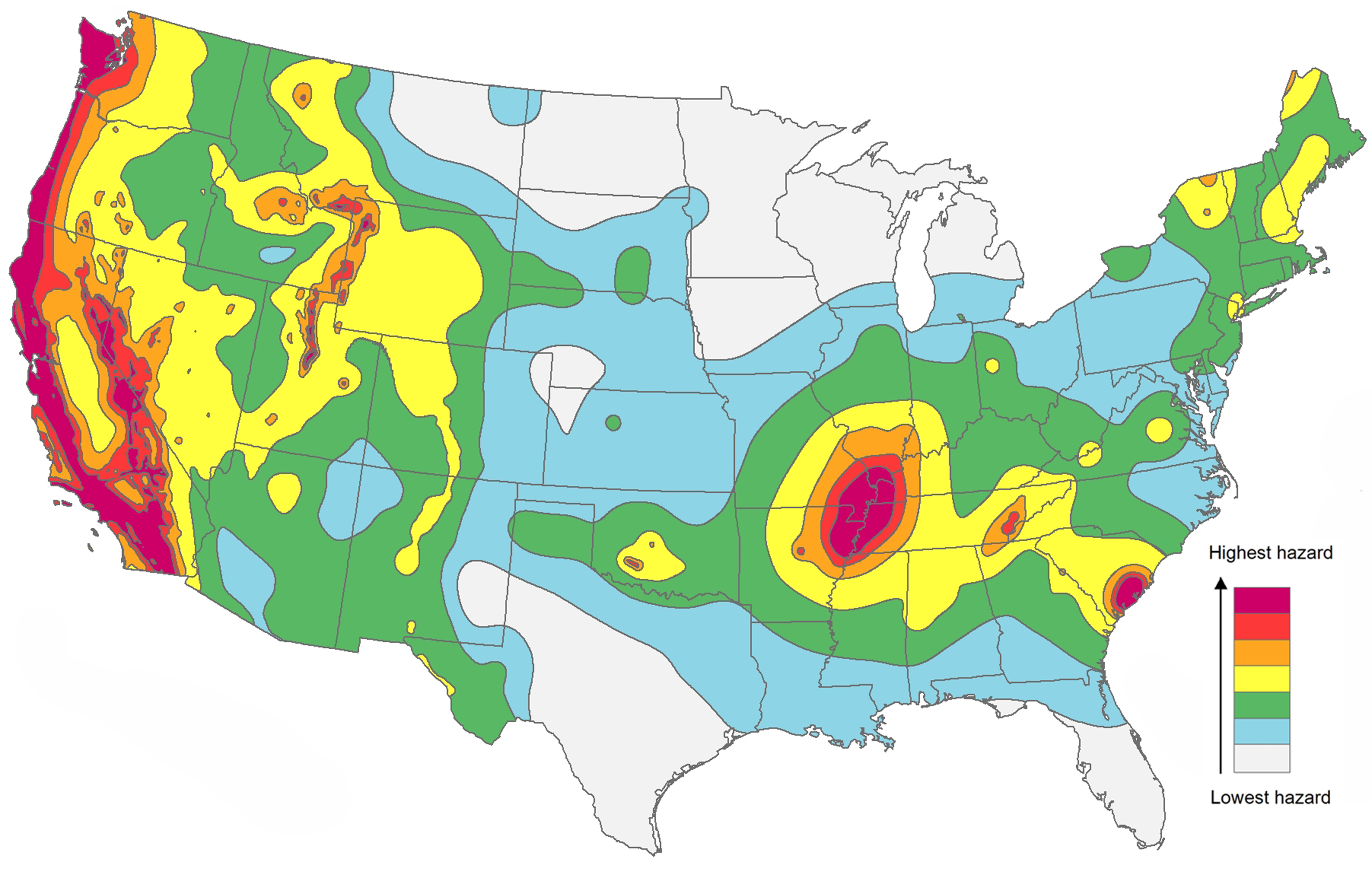
- Seismic Zones: Identifying areas prone to earthquakes, known as seismic zones, helps pinpoint regions where earthquake-resistant infrastructure and building codes are essential.
- Earthquake Frequency and Magnitude: Mapping earthquake occurrences over time reveals patterns in seismic activity, allowing researchers to assess the likelihood and potential intensity of future events.
- Tectonic Plate Boundaries: The distribution of earthquakes aligns remarkably well with the boundaries of tectonic plates. These maps visually illustrate the concept of plate tectonics and the forces driving seismic activity.
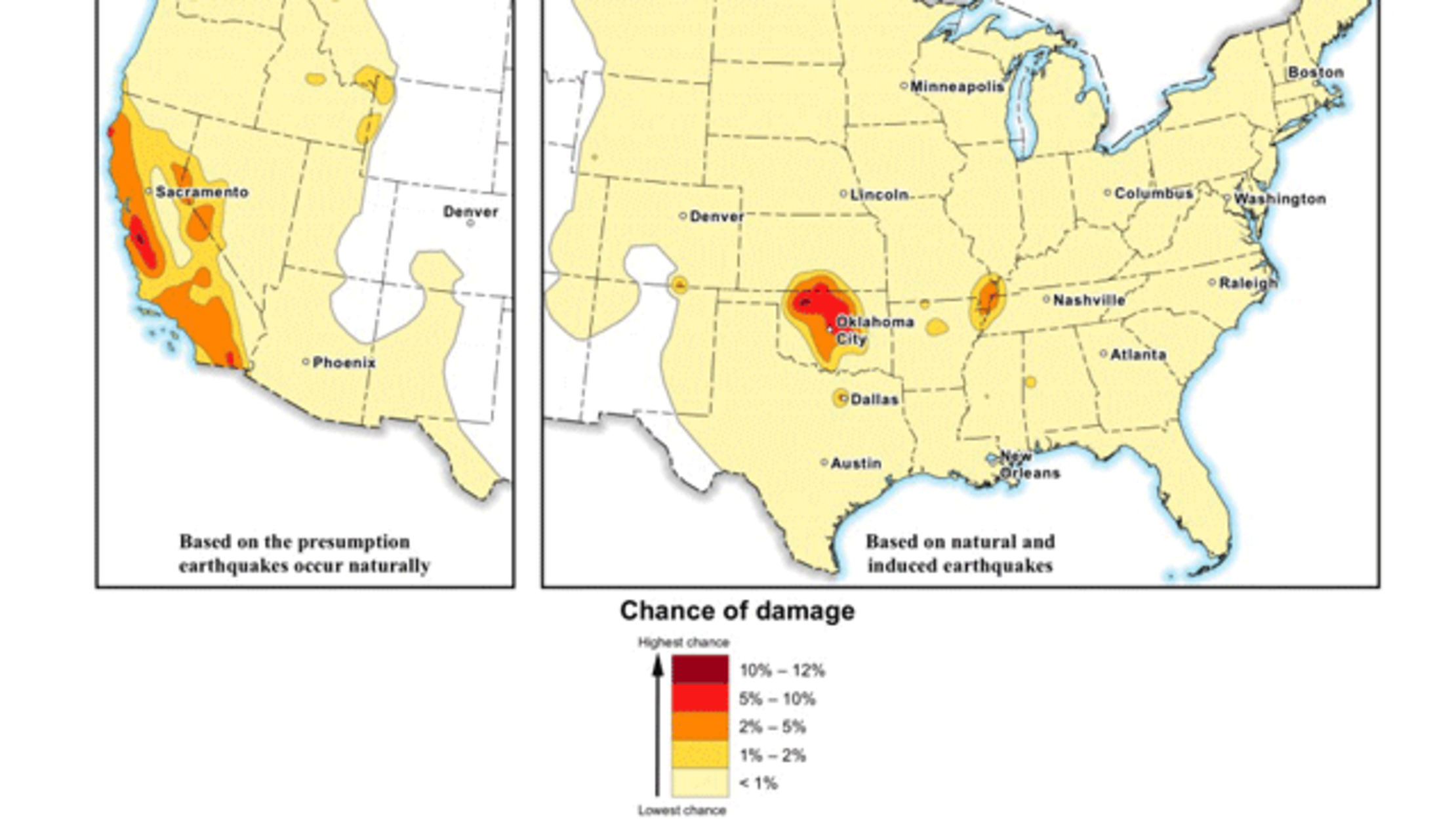
- Earthquake Risk Assessment: Combining earthquake occurrence data with population density and vulnerability assessments allows for comprehensive earthquake risk analysis, informing disaster preparedness plans and mitigation strategies.
Building a Foundation for Preparedness:
World earthquake maps serve as the foundation for numerous applications aimed at minimizing the impact of earthquakes:
- Building Codes and Infrastructure Design: By understanding the seismic hazard of a region, engineers can design buildings and infrastructure that can withstand the forces generated by earthquakes.
- Early Warning Systems: Seismic networks and real-time monitoring systems rely on earthquake maps to pinpoint the location and magnitude of an earthquake, enabling rapid alerts and potentially saving lives.
- Disaster Response and Relief Efforts: Knowing the areas most affected by an earthquake allows for efficient allocation of resources, ensuring timely and effective relief efforts.
- Public Education and Awareness: Visualizing earthquake activity on a global scale raises awareness about the risks and importance of preparedness, empowering individuals to take proactive steps to protect themselves.
Beyond the Visual: A Deeper Dive into Data Analysis:
While visually compelling, world earthquake maps are more than just visual representations. They are a gateway to a vast dataset encompassing:
- Earthquake Catalogs: Comprehensive databases meticulously record details of past earthquakes, including location, magnitude, depth, and time of occurrence.
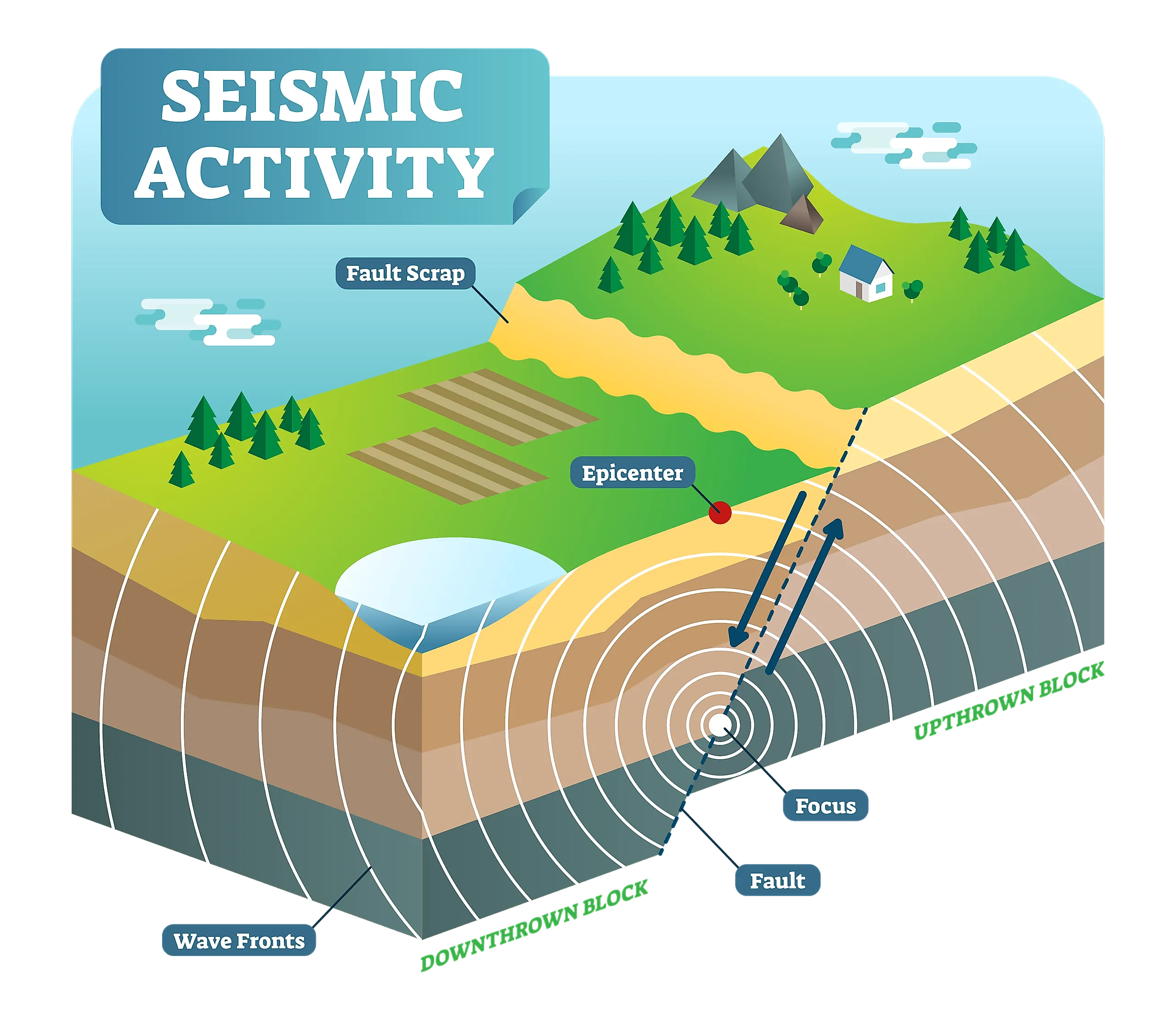
- Seismic Wave Analysis: Analyzing the patterns of seismic waves generated by earthquakes provides insights into the Earth’s internal structure and the dynamics of tectonic plates.
- Statistical Modeling: Using statistical models, scientists can predict the probability and intensity of future earthquakes, enhancing earthquake risk assessment and preparedness.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Data Collection:
World earthquake maps are dynamic entities, constantly evolving as new data becomes available. Continuous monitoring of seismic activity is crucial for maintaining the accuracy and relevance of these maps. This involves:
- Global Seismic Networks: Networks of sensitive seismometers scattered across the globe continuously monitor ground motion, providing real-time data on earthquake occurrences.
- Satellite Data Analysis: Satellite imagery and remote sensing techniques offer additional insights into earthquake-induced ground deformation and fault movement.
- Collaborative Efforts: Sharing data and research findings between scientists and institutions worldwide is essential for building a comprehensive understanding of global seismic activity.
Frequently Asked Questions About World Earthquake Maps:
Q1: What are the most earthquake-prone regions in the world?
A: The most earthquake-prone regions are located along tectonic plate boundaries, particularly the "Ring of Fire" around the Pacific Ocean, the Mediterranean-Himalayan belt, and the mid-Atlantic ridge.
Q2: How often do earthquakes occur?
A: Earthquakes occur constantly, with thousands of small tremors happening every day. However, major earthquakes with devastating consequences are less frequent, occurring on average a few times per year.
Q3: How accurate are earthquake predictions?
A: Predicting the exact time and location of a major earthquake is currently impossible. However, scientists can assess the probability of an earthquake occurring in a specific region based on historical data and seismic activity.
Q4: Can earthquakes be prevented?
A: Earthquakes are natural phenomena driven by the Earth’s internal processes and cannot be prevented. However, we can mitigate their impact through earthquake-resistant construction, early warning systems, and disaster preparedness measures.
Q5: What are the benefits of using world earthquake maps?
A: World earthquake maps provide valuable insights into global seismic activity, enabling informed decision-making for earthquake risk assessment, infrastructure design, disaster preparedness, and public education.
Tips for Using World Earthquake Maps Effectively:
- Consider the scale and scope: Different maps provide varying levels of detail and focus. Choose a map that suits your specific needs and interests.
- Interpret the data accurately: Pay attention to the color-coding, legends, and other visual cues to understand the meaning of the data presented.
- Combine with other resources: Integrate earthquake maps with other relevant data sources, such as population density, geological information, and vulnerability assessments, for a more comprehensive understanding of earthquake risk.
- Stay informed about updates: World earthquake maps are dynamic and constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest information and data releases.
Conclusion:
World earthquake maps are indispensable tools for understanding, managing, and mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes. They provide a visual representation of global seismic activity, enabling researchers, policymakers, and individuals to make informed decisions regarding earthquake preparedness, infrastructure design, and disaster response. By continuously monitoring seismic activity, collecting data, and sharing knowledge, we can leverage the power of these maps to build a safer and more resilient future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Tremors: A Comprehensive Look at World Earthquake Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!