Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Finland’s Topographical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Finland’s Topographical Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Finland’s Topographical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Finland’s Topographical Map
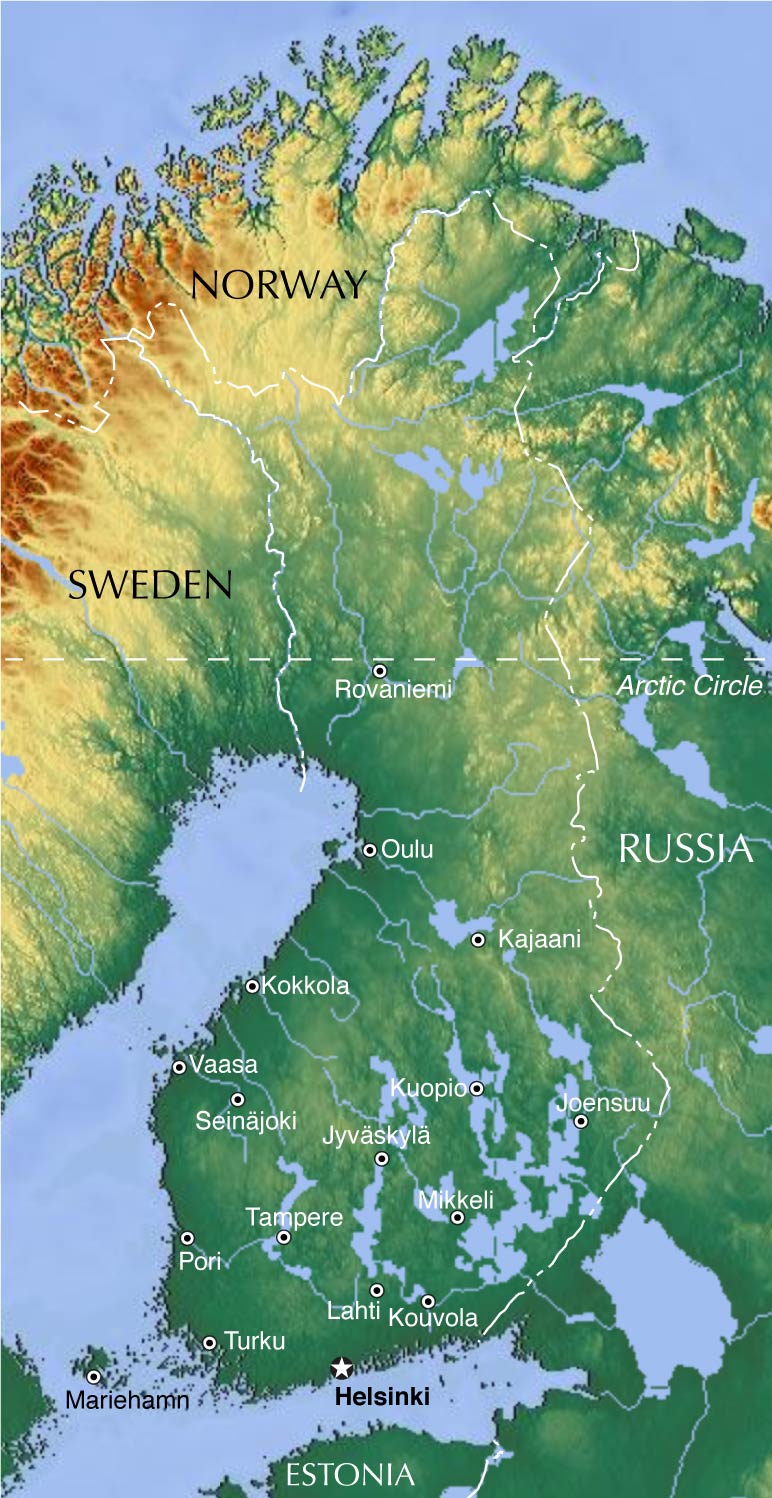
Finland, the land of a thousand lakes, boasts a unique and captivating landscape. Understanding this landscape, with its rolling hills, vast lakes, and extensive forests, is crucial for navigating, planning, and appreciating the country’s natural beauty. A topographical map serves as a powerful tool for unraveling the intricacies of this diverse terrain, providing a visual representation of elevation, landforms, and key geographical features.
The Foundation of Understanding: Deciphering the Map’s Elements
Topographical maps employ a specific set of symbols and conventions to convey information about the land’s physical characteristics. Understanding these elements is essential for interpreting the map effectively:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation Points: Numbers indicating specific elevations are often placed alongside contour lines, providing precise height measurements.
- Water Features: Lakes, rivers, and other water bodies are depicted with specific symbols, highlighting their location and extent.
- Land Cover: Symbols representing forests, meadows, urban areas, and other land cover types help users understand the landscape’s composition.
- Cultural Features: Roads, railways, towns, and other man-made elements are included on the map to provide context and aid navigation.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling Finland’s Topographical Treasures
Finland’s topographical map reveals a captivating tapestry of geological forces and natural processes that have shaped its landscape.
- The Baltic Shield: Finland rests on the ancient and stable Baltic Shield, a vast expanse of Precambrian bedrock that forms the foundation of Scandinavia. This geological formation has influenced the country’s overall topography, resulting in a generally low-lying landscape.
- Glacial Shaping: The last glacial period, which ended around 10,000 years ago, profoundly shaped Finland’s terrain. The movement of massive ice sheets carved out valleys, sculpted hills, and deposited vast amounts of sediment, leaving behind a landscape characterized by lakes, moraines, and eskers.
- The Lake District: Finland’s most iconic feature is its vast network of lakes, often referred to as the "Lake District." These lakes, formed by glacial activity, cover over 10% of the country’s surface, creating a unique and picturesque landscape.
- Forests and Wetlands: Finland is known for its extensive forests, covering over 70% of the country. These forests, primarily composed of coniferous species, are interspersed with wetlands, bogs, and marshes, adding to the diversity of the landscape.
- Coastal Areas: Finland’s coastline is characterized by a mix of rocky shores, sandy beaches, and numerous islands. The archipelago, particularly in the southwestern part of the country, is a popular destination for boating, fishing, and enjoying the coastal scenery.
Navigating the Terrain: The Practical Benefits of Topographical Maps
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, Finland’s topographical map serves as an invaluable tool for various purposes:
- Outdoor Recreation: Hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities are popular in Finland. The map provides crucial information about elevation changes, trail routes, water sources, and potential hazards, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Land Management: Forestry, agriculture, and other land-based industries rely on topographical maps to understand the terrain, manage resources, and plan infrastructure development.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists and researchers use topographical maps to study geological formations, analyze environmental changes, and monitor natural resources.
- Disaster Management: In case of natural disasters, topographical maps assist emergency responders in navigating affected areas, assessing damage, and coordinating rescue efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions About Finland’s Topographical Map
1. What is the most accurate source for Finnish topographical maps?
The Finnish Geospatial Research Institute (FGI) is the official source for topographic maps of Finland. Their website provides access to various digital and printed map resources.
2. Are there different scales available for Finnish topographical maps?
Yes, topographical maps are available in various scales, from large-scale maps covering small areas to small-scale maps depicting the entire country.
3. How can I access and use Finnish topographical maps online?
Several online platforms provide access to Finnish topographical maps, including the FGI website, Google Maps, and specialized mapping applications.
4. Are there any specific features unique to Finnish topographical maps?
Finnish topographical maps often include detailed information about forest cover, lakes, and bogs, reflecting the country’s distinctive landscape.
5. How are topographical maps used for conservation efforts in Finland?
Topographical maps are crucial for identifying sensitive ecological areas, planning protected zones, and monitoring environmental changes, contributing to conservation efforts.
Tips for Using Finnish Topographical Maps
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a map scale that matches your specific needs and the area you plan to explore.
- Understand the symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map to interpret elevation, landforms, and other features accurately.
- Consider the map’s date: Topographical maps are updated periodically. Ensure you are using the most recent version for accurate information.
- Combine with other resources: Utilize GPS devices, online maps, and other resources to enhance your understanding and navigation capabilities.
- Respect the environment: Use topographical maps responsibly, leaving no trace and minimizing your impact on the natural environment.
Conclusion
Finland’s topographical map is more than just a collection of lines and symbols. It serves as a window into the country’s rich geological history, diverse landscape, and unique natural beauty. By understanding the elements of the map and appreciating the information it conveys, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of Finland’s terrain, plan outdoor adventures, and contribute to the responsible management of its natural resources. The topographical map, therefore, stands as a valuable tool for navigating, appreciating, and ultimately, protecting the unique and captivating landscape of Finland.
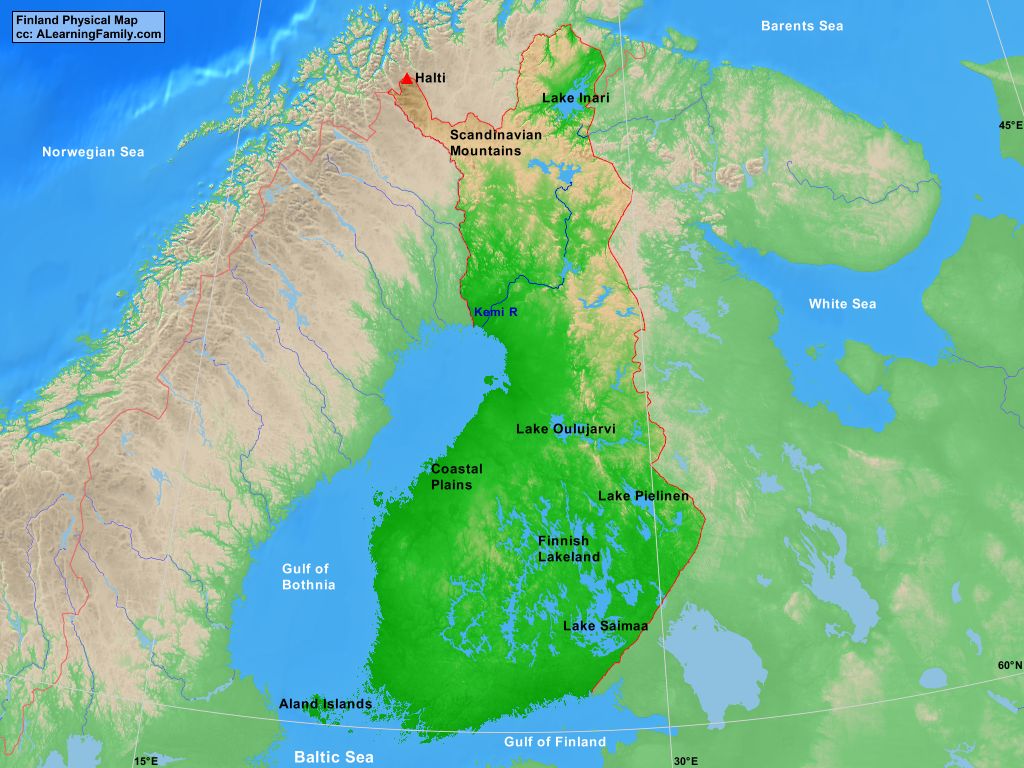
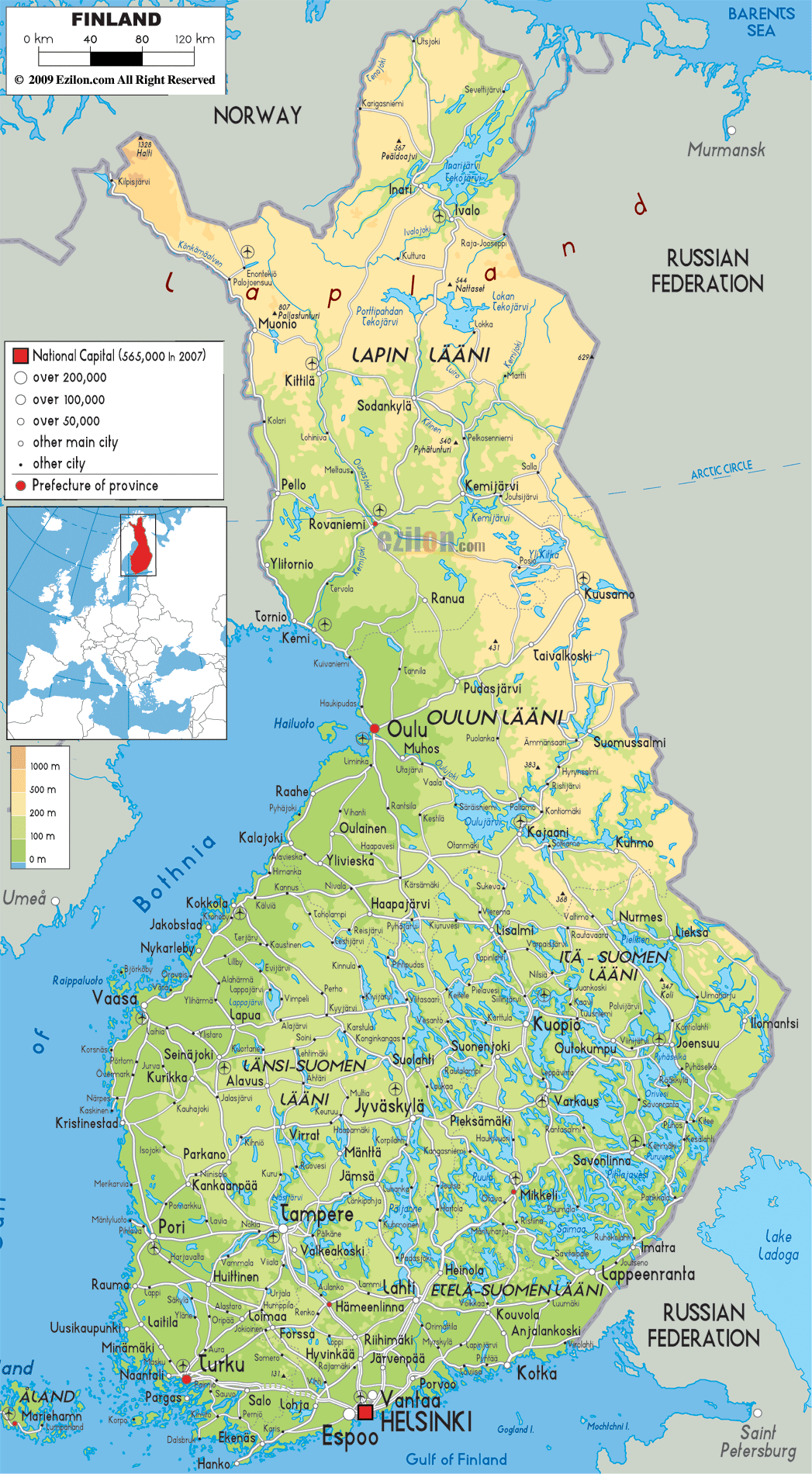

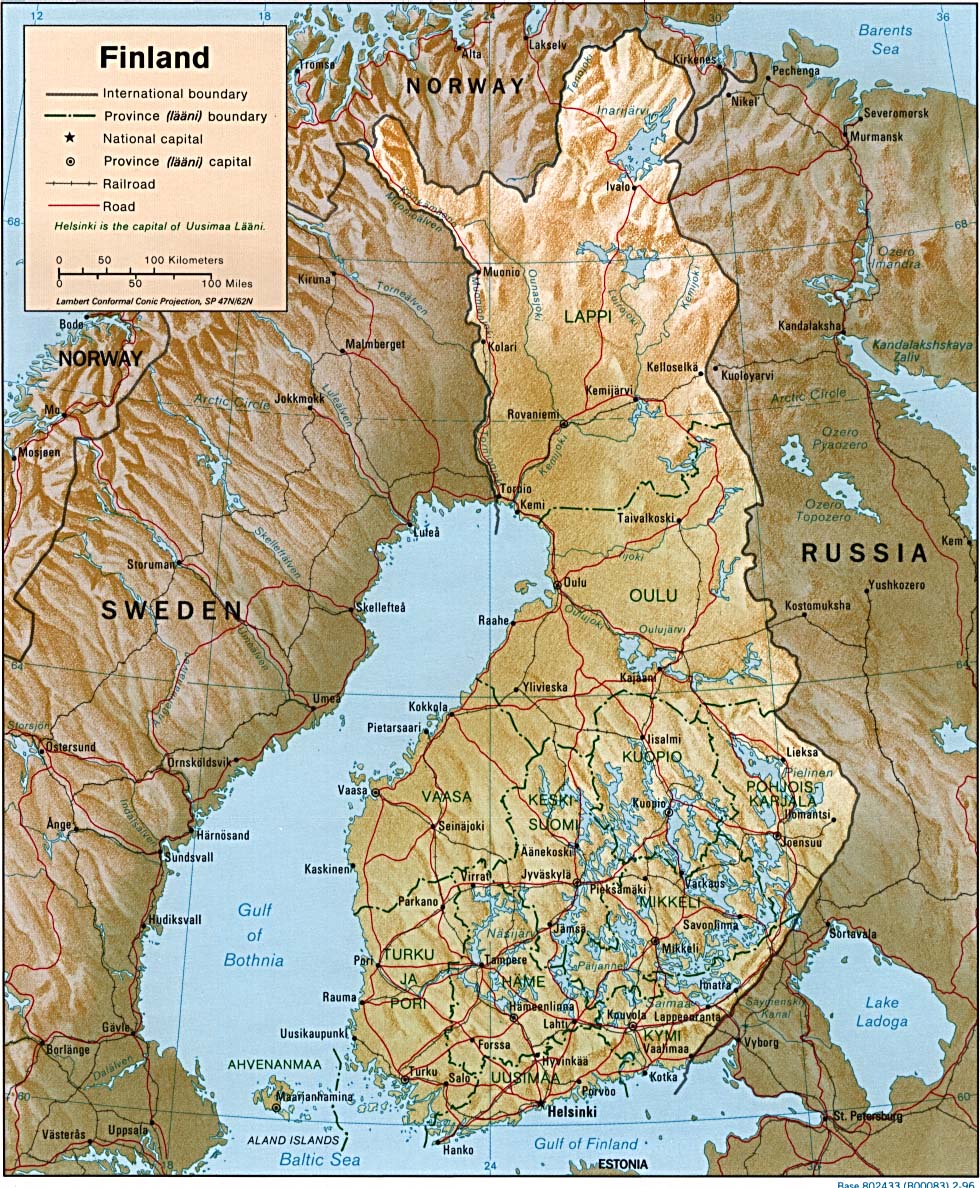




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Finland’s Topographical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!