Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Topographical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Topographical Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Topographical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Topographical Map
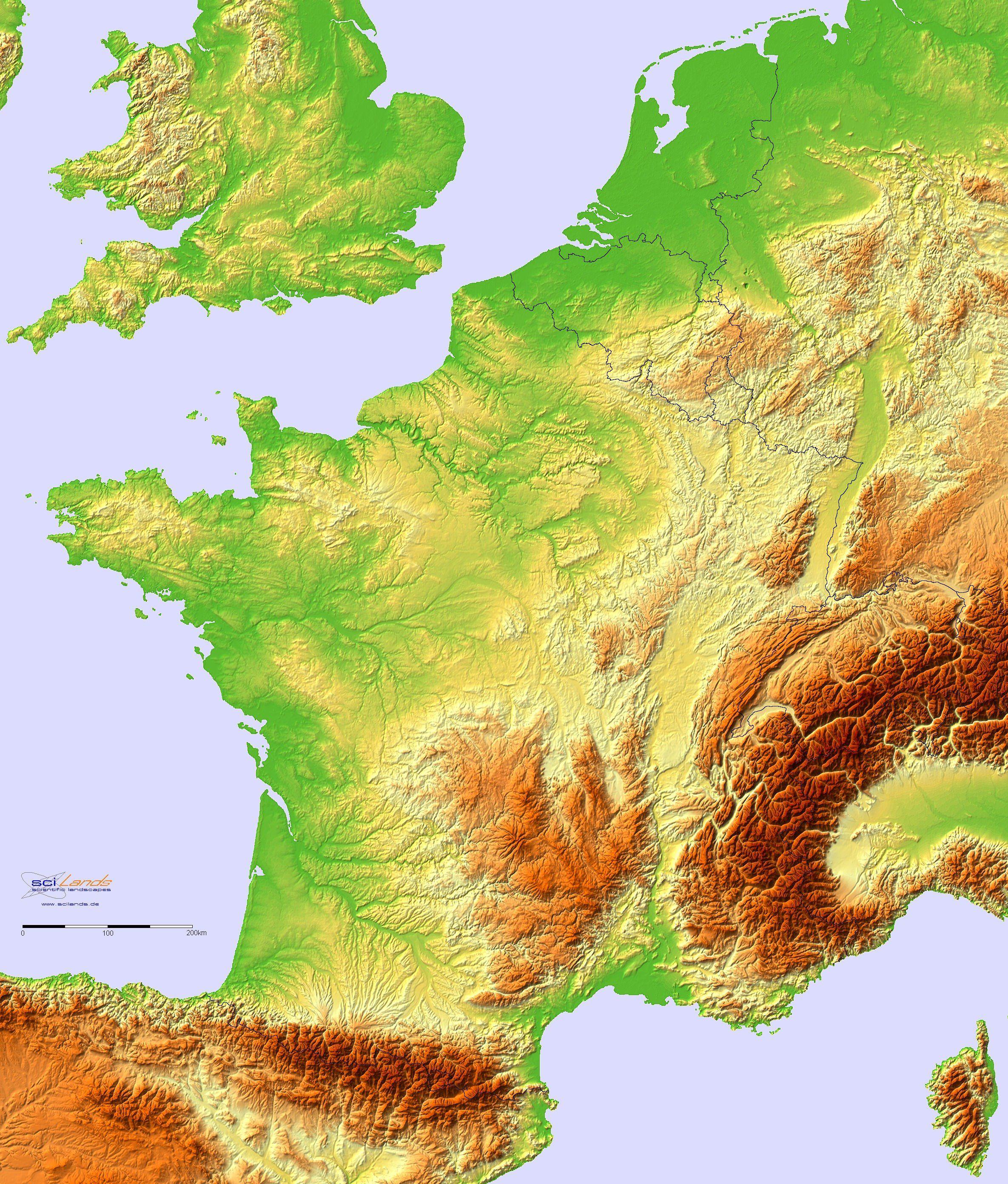
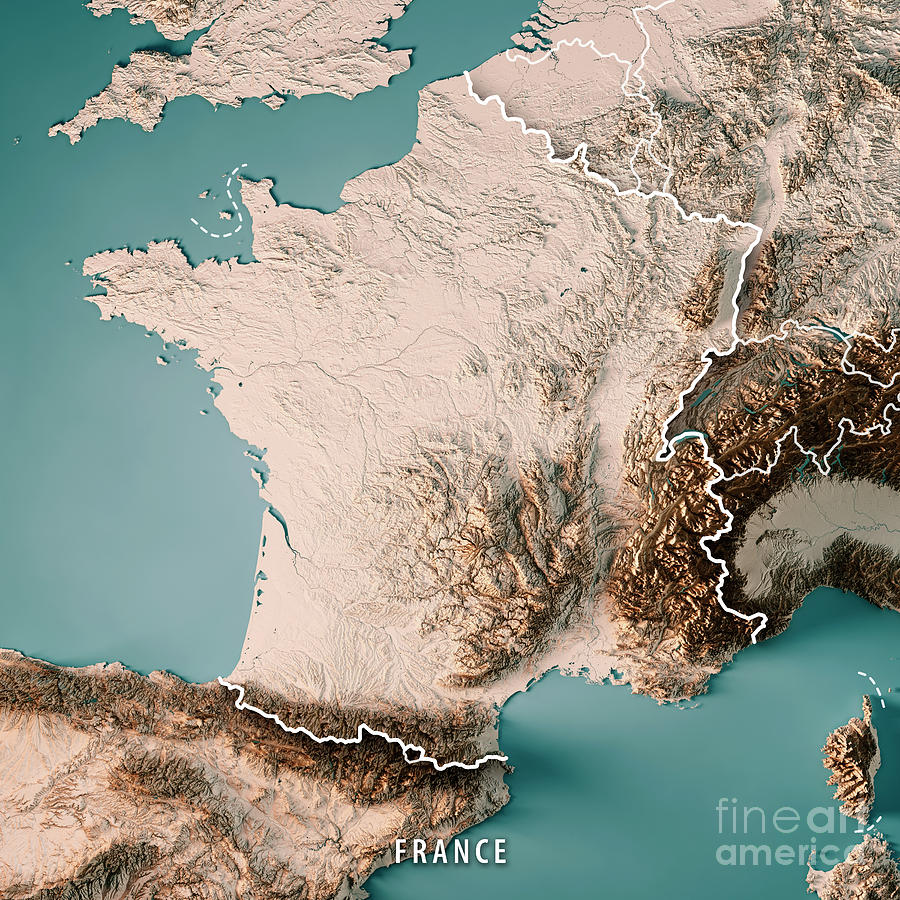
France, a nation celebrated for its cultural richness and historical significance, also boasts a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding the topography of this European powerhouse is crucial for appreciating its unique character and unraveling the intricate relationship between its physical features and human activity. This exploration delves into the intricacies of France’s topographical map, revealing the country’s geographical tapestry and its profound influence on various aspects of French life.
The Shape of France: A Diverse Landscape
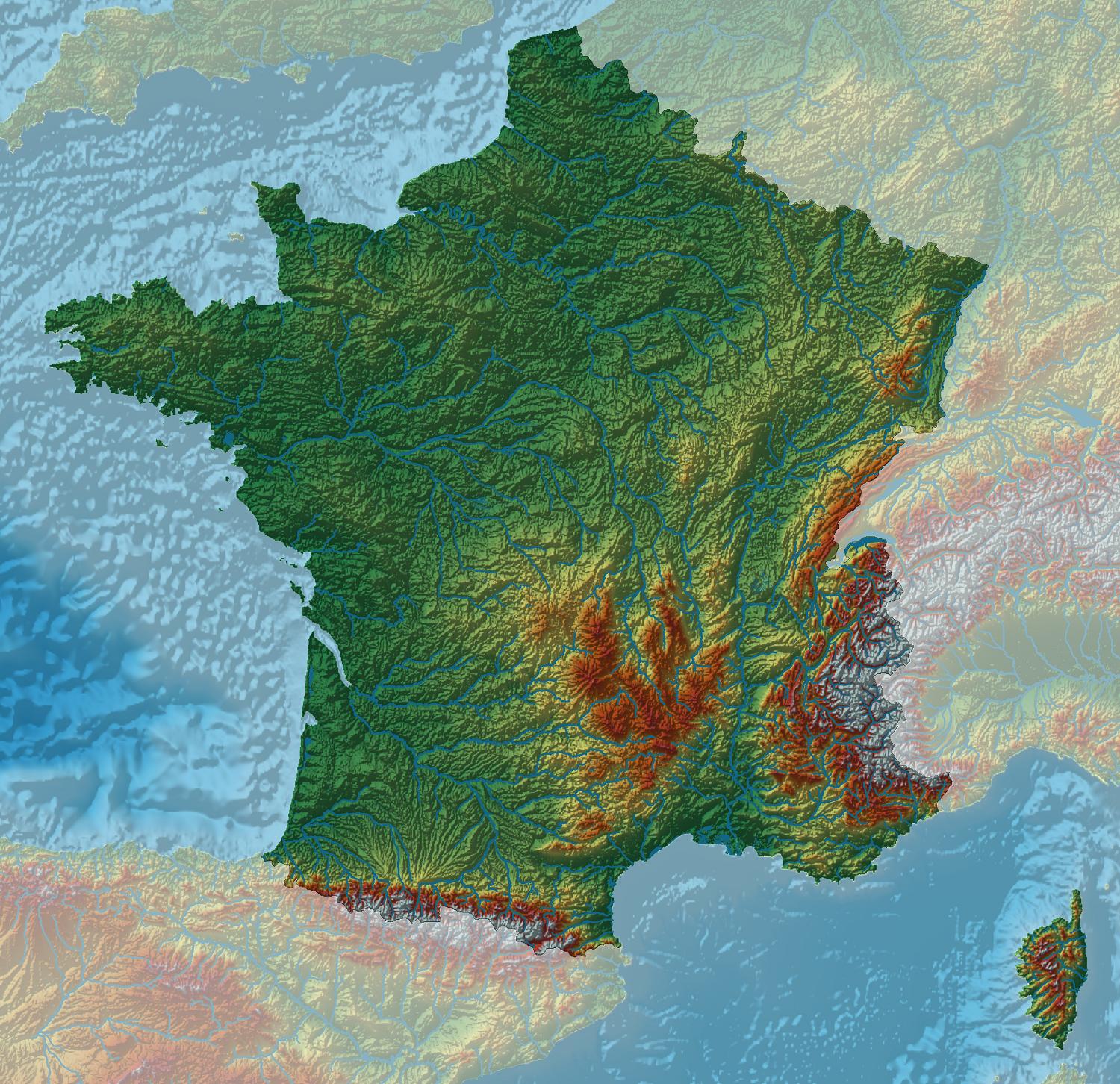
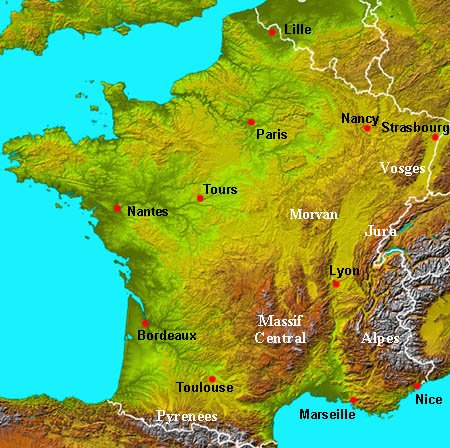
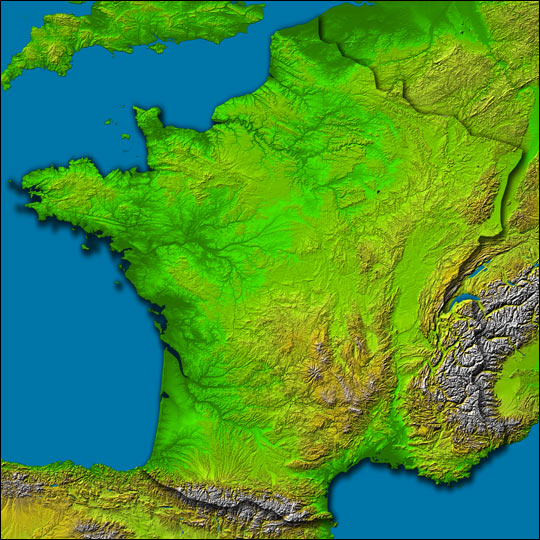
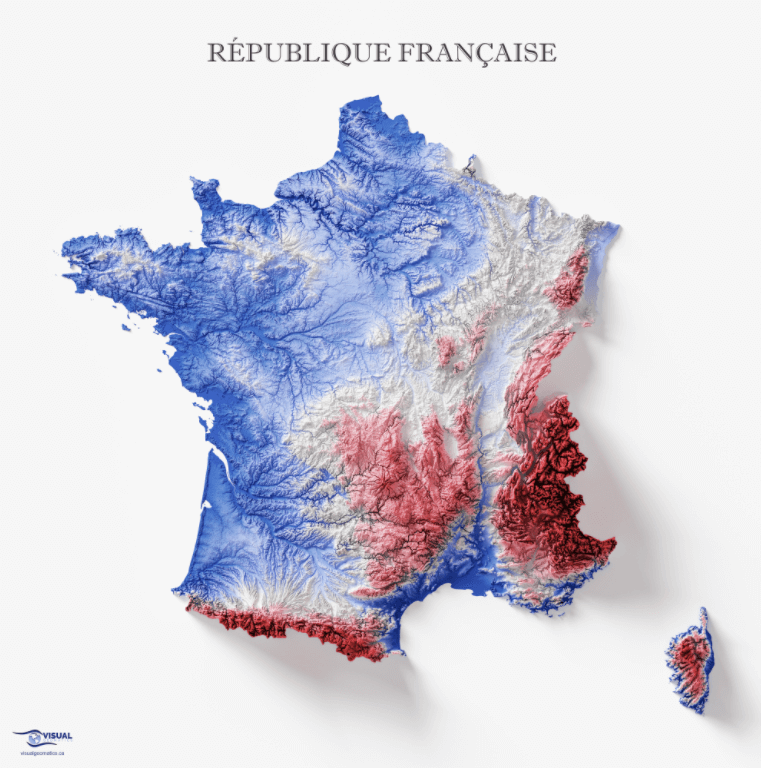
The topographical map of France reveals a country sculpted by a complex interplay of geological forces. From the towering peaks of the Alps and Pyrenees to the rolling hills of the Massif Central and the vast plains of the Paris Basin, France exhibits a remarkable range of elevations and landforms.
-
The Majestic Alps: Dominating the southeastern border, the Alps stand as a testament to the immense power of tectonic forces. This majestic mountain range, home to towering peaks like Mont Blanc, Europe’s highest, is a paradise for climbers, skiers, and nature enthusiasts. The Alps influence the climate of southeastern France, creating a distinct microclimate with heavy snowfall in winter and cool, dry summers.
-
The Pyrenees: Sharing a border with Spain, the Pyrenees are another formidable mountain range. Although less imposing than the Alps, they offer stunning vistas and challenging hiking trails. The Pyrenees act as a natural barrier, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct ecosystems on either side of the mountain range.
-
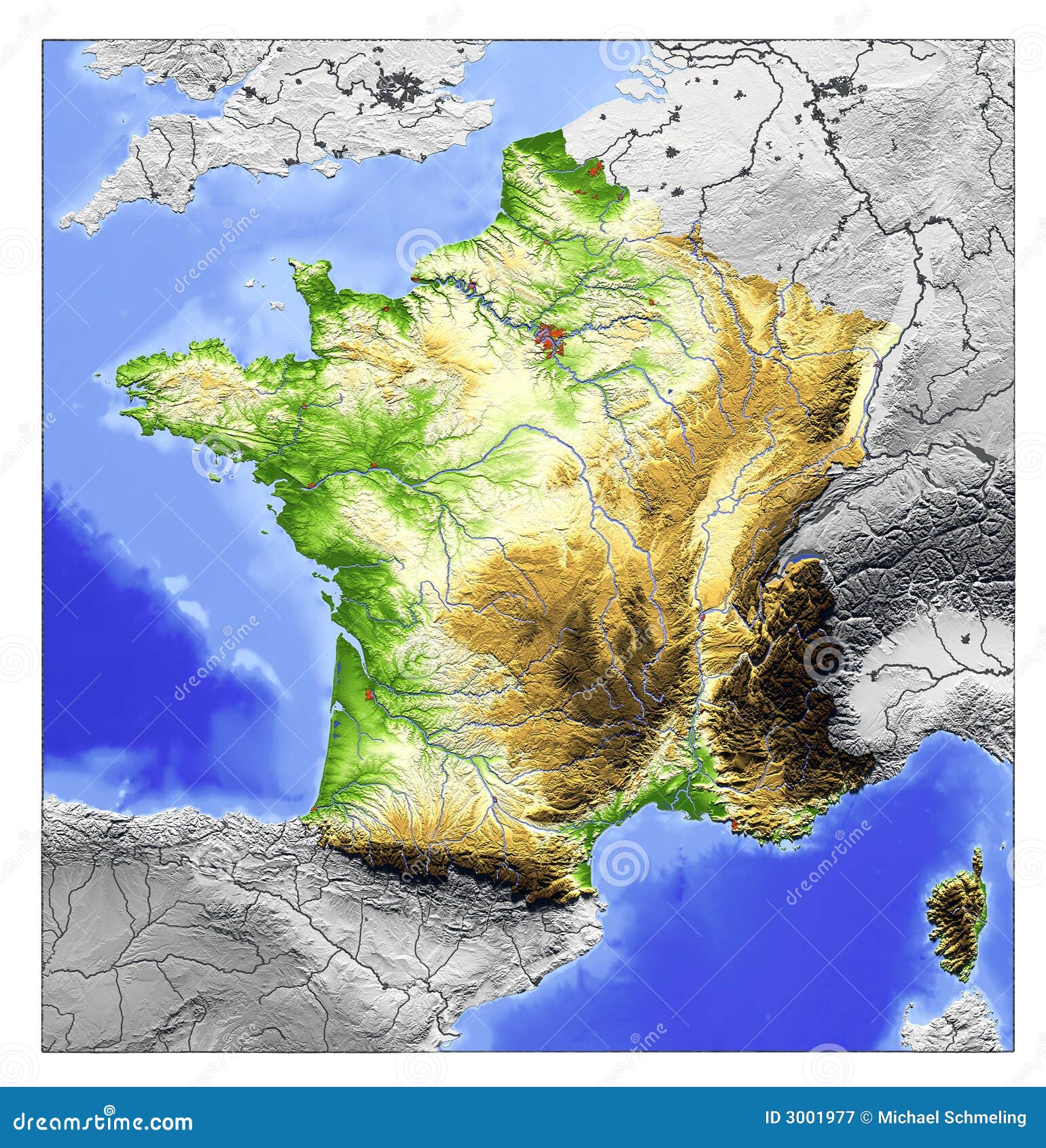
The Massif Central: Occupying the heart of France, the Massif Central is a vast plateau characterized by volcanic activity, ancient mountains, and deep gorges. This region boasts a unique geological history, with extinct volcanoes and remnants of past volcanic eruptions shaping its landscape. The Massif Central is a source of important rivers, including the Loire, which flows westward across France.
-
The Paris Basin: Occupying the northern part of France, the Paris Basin is a vast plain formed by sedimentary deposits. This region is characterized by its flat terrain, fertile soils, and abundant water resources. The Paris Basin is a major agricultural hub, producing a significant portion of France’s agricultural output.
-
The Coastal Zones: France enjoys an extensive coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the English Channel. These coastal zones are characterized by diverse landscapes, including sandy beaches, rugged cliffs, and estuaries. The coastline plays a crucial role in France’s economy, with tourism, fishing, and shipping industries thriving in these areas.
The Impact of Topography on French Life
France’s diverse topography profoundly influences various aspects of life, from agriculture and transportation to climate and culture.
-
Agriculture: The topography of France dictates the types of crops that can be grown in different regions. The fertile plains of the Paris Basin are ideal for cultivating grains, while the vineyards of the Rhône Valley and Bordeaux produce world-renowned wines. The mountainous regions are often utilized for grazing livestock and forestry.
-
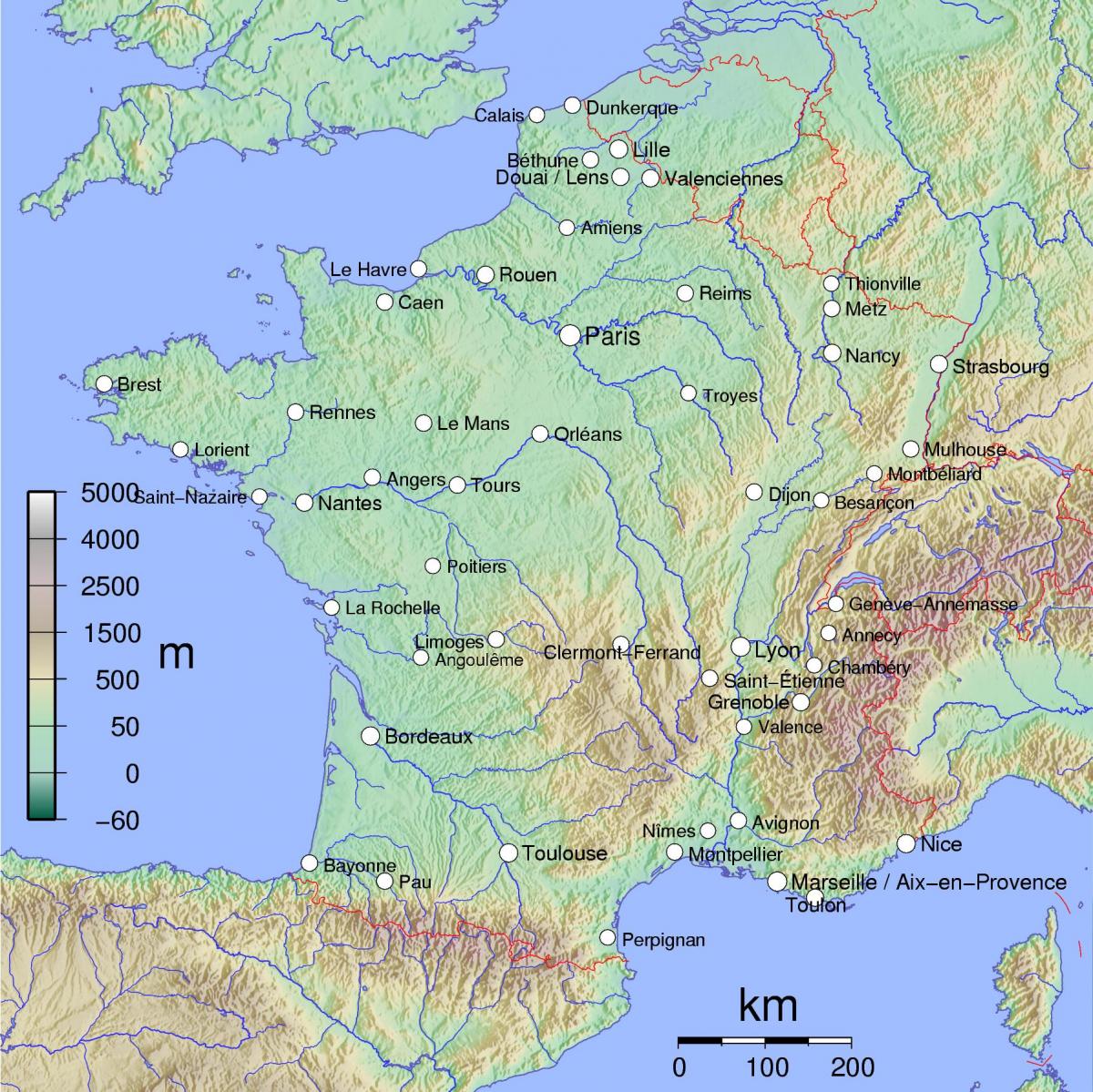
Transportation: The mountainous terrain poses challenges for transportation infrastructure. Roads and railways must navigate steep inclines and winding passes. However, the topography also provides opportunities for water transport, with major rivers like the Loire, Seine, and Rhône serving as important trade routes.
-
Climate: France’s topography plays a significant role in shaping its climate. The mountains act as natural barriers, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates. The Alps and Pyrenees experience heavy snowfall in winter, while the Mediterranean coast enjoys warm, sunny summers. The interior regions have a more continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
-
Culture: The topography of France has shaped the country’s cultural identity. The mountainous regions have fostered a sense of independence and self-sufficiency, while the coastal areas have developed a maritime culture. The diverse landscapes have inspired artists, writers, and musicians, contributing to France’s rich cultural heritage.
Understanding the Topographical Map: A Key to Exploration
The topographical map of France is an invaluable tool for understanding the country’s diverse landscape and its impact on human activity. It reveals the intricate relationship between physical features and cultural development, providing insights into the country’s history, economy, and identity.
-
Elevation Contours: The topographical map utilizes contour lines to represent elevation. These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. By studying the spacing of contour lines, one can discern the steepness of slopes and the presence of valleys, ridges, and plateaus.
-
Landform Symbols: The topographical map uses symbols to represent different landforms, such as mountains, hills, valleys, rivers, and lakes. These symbols provide a clear and concise representation of the landscape’s features.
-
Scale and Projection: The topographical map is drawn to a specific scale, indicating the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. The map also utilizes a projection system, which transforms the curved surface of the Earth onto a flat plane.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into France’s Topography
Q: What is the highest point in France?
A: The highest point in France is Mont Blanc, located in the Alps, with an elevation of 4,808.73 meters (15,777 feet).
Q: How does the topography of France influence its wine production?
A: The topography of France plays a crucial role in wine production. The slopes of the vineyards receive optimal sunlight, while the soil composition and drainage patterns influence the flavor and quality of the grapes. The different microclimates created by the mountains and valleys also contribute to the diversity of wine production across the country.
Q: What are the major rivers in France?
A: Some of the major rivers in France include the Loire, Seine, Rhône, Garonne, and Meuse. These rivers play a vital role in transportation, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
Q: How does the topography of France affect its tourism industry?
A: The diverse topography of France attracts tourists from around the world. The mountains offer opportunities for skiing, hiking, and mountain biking, while the coastal areas are popular for sunbathing, swimming, and watersports. The rolling hills and vineyards provide picturesque landscapes for cycling and wine tours.
Tips for Exploring France’s Topography
- Consult a Topographical Map: Utilize a detailed topographical map to plan your explorations, identifying mountain ranges, valleys, rivers, and other key features.
- Embrace Hiking and Trekking: Hike through the mountains and valleys to experience the diverse landscapes firsthand.
- Explore Coastal Zones: Visit the beaches, cliffs, and estuaries to witness the influence of the sea on the French coastline.
- Visit National Parks: Discover the beauty and ecological significance of France’s national parks, which showcase diverse landscapes and wildlife.
- Engage with Local Communities: Talk to locals to learn about the impact of topography on their lives and livelihoods.
Conclusion: A Legacy Shaped by the Land
The topographical map of France is more than just a collection of lines and symbols; it is a visual representation of a rich and complex landscape. This map provides a window into the country’s geological history, its diverse ecosystems, and its cultural heritage. By understanding the topography of France, we gain a deeper appreciation for its unique character and the intricate relationship between its physical features and human activity. As we continue to explore this captivating country, the topographical map serves as a guide, revealing the secrets of the land and the stories it holds.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Topographical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!